19.1. About the Clocked Video Input IP
The IP provides a wide variety of video statistic collection, e.g. frame counter, frame per second, active and blanking video frame information. All this information is accessible directly from a processor register interface.
The figure provides an example of the video statistics information that the IP can provide for a 1080p60 video resolution.
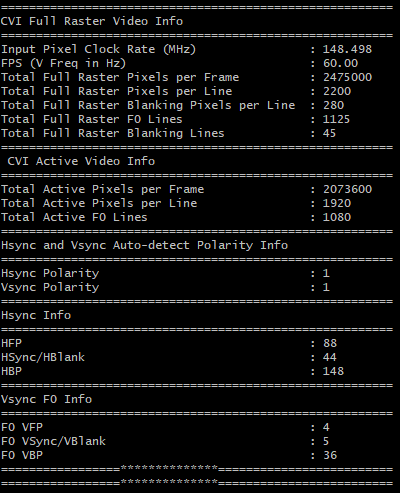
By default, the IP only provides full-raster and video active high and width information as part of the video statistic collection. However, if you select the video telemetrics information in the GUI, the IP provides a more comprehensive set of video timing parameters. An optional frame per second counter provides you with an accurate frame rate estimation and its corresponding full-raster video clock.
The IP provides autopolarity detection for the horizontal and vertical timing markers, Vsynch and Hsynch, and allows automatic detection of interlaced video formats. You can configure automatic detection using the processor control interface.
The IP also provides an asynchronous FIFO buffer to handle the clock domain jump from input to output video domain. An optional frame cleaner is available at the back end of the IP. The frame cleaner allows you to automatically pad an incomplete frame (for example, because of an unplugged cable) by inserting a user configurable color pattern. You can turn on or off the frame cleaner at run time using the processor control interface.
The IP only supports lite variants. For more information about full and lite variants, refer to the Intel FPGA Streaming Video Protocol Specification