Intel® Hyperflex™ Architecture High-Performance Design Handbook
ID
683353
Date
10/04/2021
Public
A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
1. Intel® Hyperflex™ FPGA Architecture Introduction
2. Intel® Hyperflex™ Architecture RTL Design Guidelines
3. Compiling Intel® Hyperflex™ Architecture Designs
4. Design Example Walk-Through
5. Retiming Restrictions and Workarounds
6. Optimization Example
7. Intel® Hyperflex™ Architecture Porting Guidelines
8. Appendices
9. Intel® Hyperflex™ Architecture High-Performance Design Handbook Archive
10. Intel® Hyperflex™ Architecture High-Performance Design Handbook Revision History
2.4.2.1. High-Speed Clock Domains
2.4.2.2. Restructuring Loops
2.4.2.3. Control Signal Backpressure
2.4.2.4. Flow Control with FIFO Status Signals
2.4.2.5. Flow Control with Skid Buffers
2.4.2.6. Read-Modify-Write Memory
2.4.2.7. Counters and Accumulators
2.4.2.8. State Machines
2.4.2.9. Memory
2.4.2.10. DSP Blocks
2.4.2.11. General Logic
2.4.2.12. Modulus and Division
2.4.2.13. Resets
2.4.2.14. Hardware Re-use
2.4.2.15. Algorithmic Requirements
2.4.2.16. FIFOs
2.4.2.17. Ternary Adders
5.2.1. Insufficient Registers
5.2.2. Short Path/Long Path
5.2.3. Fast Forward Limit
5.2.4. Loops
5.2.5. One Critical Chain per Clock Domain
5.2.6. Critical Chains in Related Clock Groups
5.2.7. Complex Critical Chains
5.2.8. Extend to locatable node
5.2.9. Domain Boundary Entry and Domain Boundary Exit
5.2.10. Critical Chains with Dual Clock Memories
5.2.11. Critical Chain Bits and Buses
5.2.12. Delay Lines
2.2.7.3.1. Implementing Clock Gating
To implement clock gating, you access the USER_CLKGATE signal by use of the following Intel® FPGA IP available in the Intel® Quartus® Prime software:
- Reset Release Intel® FPGA IP—holds your design in reset until configuration is complete by gating clocks, resets, or write enables. This IP outputs the nINIT_DONE signal. When nINIT_DONE is low, the device is no longer in configuration mode.
- Clock Control Intel® FPGA IP—uses the inverted nINIT_DONE signal as a clock enable signal.
Follow these steps to implement clock gating:
- Open a design in the Intel® Quartus® Prime software.
- In IP Catalog, type reset release in the search field, and double-click the Reset Release Intel® FPGA IP .
- Specify appropriate parameters for your configuration in the parameter editor, and then click Generate HDL.
- Repeat steps 2 and 3 to add the Clock Control Intel® FPGA IP to your project. Prior to IP generation, specify the following options for the IP in the parameter editor:
- Under Clock Gating, turn on the Clock Enable option.
- For Clock Enable Type, select Root Level.
- For Enable Register Mode, select Negative Latch.
- Connect the Reset Release and Clock Control Intel® FPGA IP together:
- To gate the clocks, use inverted nINIT_DONE as the enable input to the Clock Control Intel® FPGA IP.
- If initial conditions are required, Intel recommends that the Clock Control Intel® FPGA IP also use root clock gating.
The following figure shows proper connections between the Reset Release and Clock Control Intel® FPGA IP to ensure accurate initial conditions after configuration:
Figure 19. Connections between the Reset Release (reset_release) and Clock Control (clock_control) Intel® FPGA IP Cores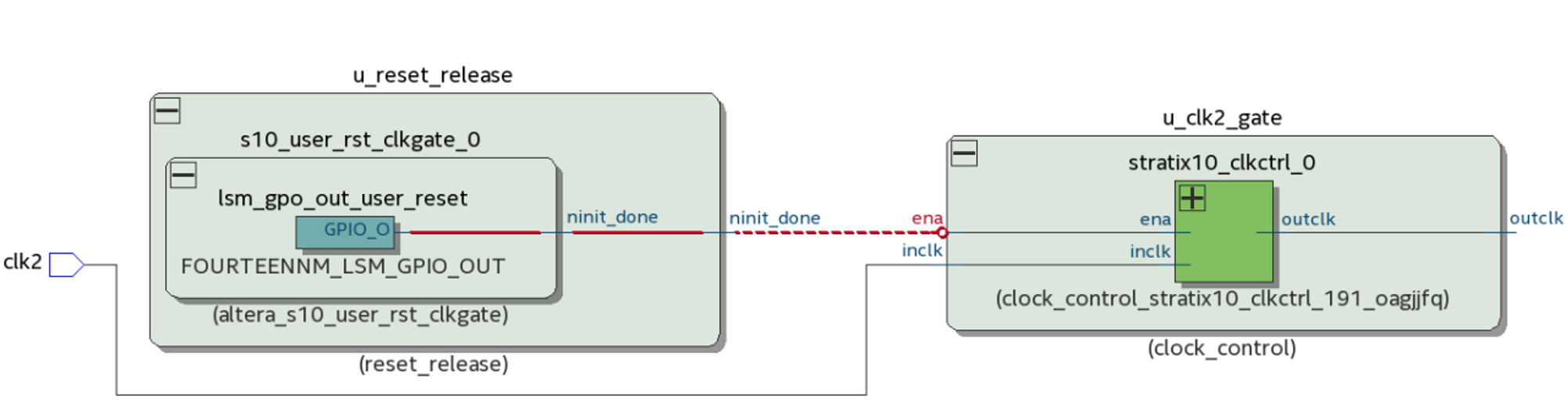
The Clock Control Intel® FPGA IP uses the ena signal to perform the clock gating function. The clock signal on the output of the Clock Control Intel® FPGA IP is then safe for use with the initialized registers (ALM and Hyper-Registers).