A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
Intel® VTune™ Profiler Graphical User Interface
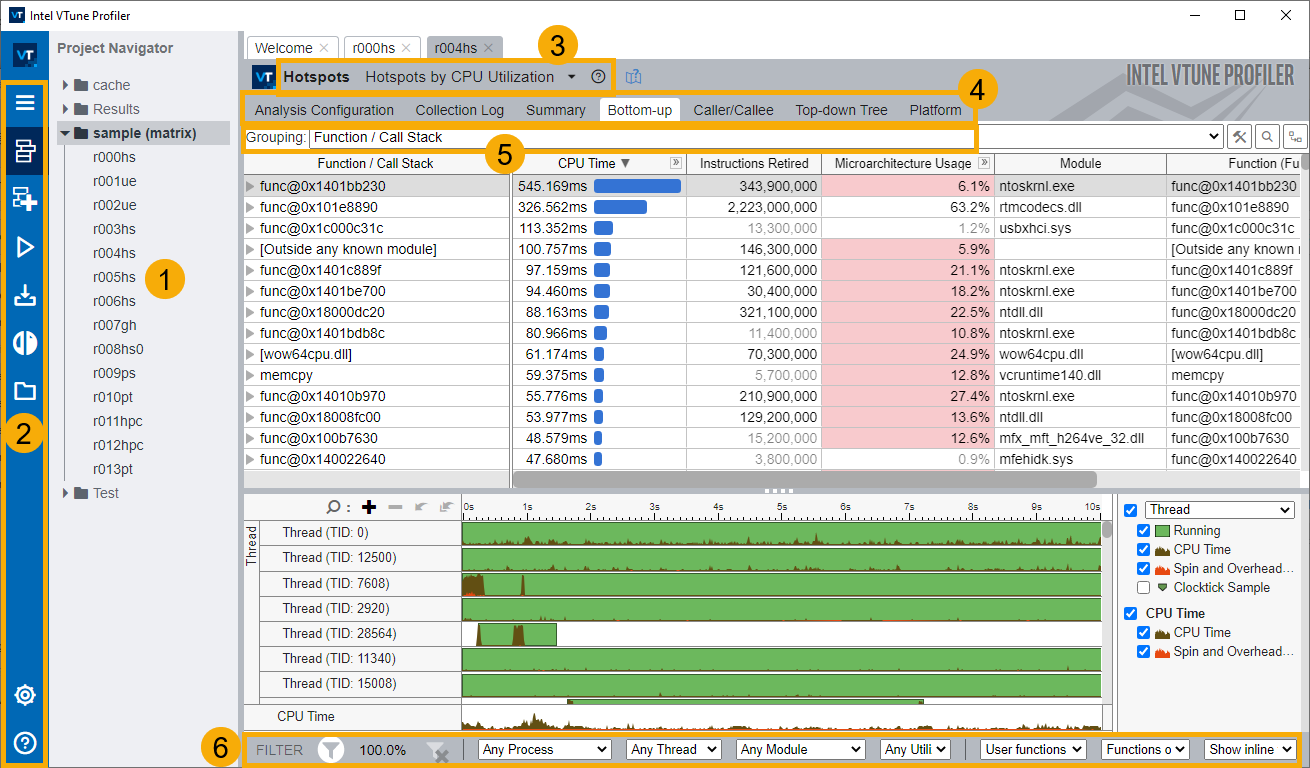
When you create a project in Intel® VTune™ Profiler, these features help you analyze data:
|
Project Navigator. Use the navigator to manage your project and collected analysis results. |
|
Menu and Toolbar. Use the VTune Profiler menu and toolbar to configure and control performance analysis, define and view project properties. Click the |
|
Analysis type and viewpoint. View the correlation of the analysis result and a viewpoint associated with it. A Viewpoint is a pre-set configuration of windows/panes for an analysis result. For most of analysis types, you can click the down arrow to switch between viewpoints and focus on particular performance metrics. |
|
Analysis Windows. Switch between window tabs to explore the analysis type configuration options and collected data provided by the selected viewpoint. |
|
Grouping. Use the Grouping drop-down menu to choose a granularity level for grouping data in the grid. Available groupings are based on the hierarchy of the program units and let you analyze the collected data from different perspectives; for example, if you are developing specific modules in an application and interested only in their performance, you may select the Module/Function/Call Stack grouping and view aggregated data per module functions. |
|
Filtering.VTune Profiler provides two basic options for filtering the collected data: per object and per time regions. Use the filter toolbar to filter out the result data according to the selected object categories: Module, Process, Thread, and so on. To filter the data by a time region, select this region on the timeline, right-click and choose Filter In by Selection content menu option. This could be useful, for example, to get region specific data in the context summary for the HPC Performance Characterization or GPU Compute/Media Hotspots analyses. |


 button to open/close the Project Navigator. Use the
button to open/close the Project Navigator. Use the  Configure Analysis toolbar button to access an analysis configuration.
Configure Analysis toolbar button to access an analysis configuration. 


