A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
1. DisplayPort Intel® FPGA IP Quick Reference
2. About This IP
3. Getting Started
4. DisplayPort Intel® FPGA IP Hardware Design Examples
5. DisplayPort Source
6. DisplayPort Sink
7. DisplayPort Intel® FPGA IP Parameters
8. DisplayPort Intel® FPGA IP Simulation Example
9. DisplayPort API Reference
10. DisplayPort Source Register Map and DPCD Locations
11. DisplayPort Sink Register Map and DPCD Locations
12. DisplayPort Intel® FPGA IP User Guide Archives
13. Document Revision History for the DisplayPort Intel® FPGA IP User Guide
4.1. DisplayPort Intel® FPGA IP Hardware Design Examples for Intel® Arria® 10, Intel® Cyclone® 10 GX, and Intel® Stratix® 10 Devices
4.2. HDCP Over DisplayPort Design Example for Intel® Arria® 10 and Intel® Stratix® 10 Devices
4.3. DisplayPort Intel® FPGA IP Hardware Design Examples for Arria V, Cyclone V, and Stratix V Devices
6.5.1. Controller Interface
6.5.2. AUX Interface
6.5.3. Debugging Interface
6.5.4. Video Interface
6.5.5. Clocked Video Input Interface
6.5.6. RX Transceiver Interface
6.5.7. Transceiver Reconfiguration Interface
6.5.8. Secondary Stream Interface
6.5.9. Audio Interface
6.5.10. Non-GPU Mode EDID Interface
6.5.11. MSA Interface
9.1. Using the Library
9.2. btc_dprx_syslib API Reference
9.3. btc_dprx_aux_get_request
9.4. btc_dprx_aux_handler
9.5. btc_dprx_aux_post_reply
9.6. btc_dprx_baseaddr
9.7. btc_dprx_dpcd_gpu_access
9.8. btc_dprx_edid_set
9.9. btc_dprx_hpd_get
9.10. btc_dprx_hpd_pulse
9.11. btc_dprx_hpd_set
9.12. btc_dprx_lt_eyeq_init
9.13. btc_dprx_lt_force
9.14. btc_dprx_rtl_ver
9.15. btc_dprx_sw_ver
9.16. btc_dprx_syslib_add_rx
9.17. btc_dprx_syslib_info
9.18. btc_dprx_syslib_init
9.19. btc_dprx_syslib_monitor
9.20. btc_dprx_mst_link_addr_rep_set
9.21. btc_dprx_mst_conn_stat_notify_req
9.22. btc_dprx_mst_conn_stat_notify_rep
9.23. btc_dptx_syslib API Reference
9.24. btc_dptx_aux_i2c_read
9.25. btc_dptx_aux_i2c_write
9.26. btc_dptx_aux_read
9.27. btc_dptx_aux_write
9.28. btc_dptx_baseaddr
9.29. btc_dptx_edid_block_read
9.30. btc_dptx_edid_read
9.31. btc_dptx_fast_link_training
9.32. btc_dptx_hpd_change
9.33. btc_dptx_is_link_up
9.34. btc_dptx_link_bw
9.35. btc_dptx_link_training
9.36. btc_dptx_rtl_ver
9.37. btc_dptx_set_color_space
9.38. btc_dptx_sw_ver
9.39. btc_dptx_syslib_add_tx
9.40. btc_dptx_syslib_init
9.41. btc_dptx_syslib_monitor
9.42. btc_dptx_test_autom
9.43. btc_dptx_video_enable
9.44. btc_dptx_mst_allocate_payload_rep
9.45. btc_dptx_mst_allocate_payload_req
9.46. btc_dptx_mst_clear_payload_table_rep
9.47. btc_dptx_mst_clear_payload_table_req
9.48. btc_dptx_mst_conn_stat_notify_req
9.49. btc_dptx_mst_down_rep_irq
9.50. btc_dptx_mst_enable
9.51. btc_dptx_mst_enum_path_rep
9.52. btc_dptx_mst_enum_path_req
9.53. btc_dptx_mst_get_msg_transact_ver_rep
9.54. btc_dptx_mst_get_msg_transact_ver_req
9.55. btc_dptx_mst_link_address_rep
9.56. btc_dptx_mst_link_address_req
9.57. btc_dptx_mst_remote_dpcd_wr_rep
9.58. btc_dptx_mst_remote_dpcd_wr_req
9.59. btc_dptx_mst_remote_i2c_rd_rep
9.60. btc_dptx_mst_remote_i2c_rd_req
9.61. btc_dptx_mst_set_color_space
9.62. btc_dptx_mst_tavgts_set
9.63. btc_dptx_mst_up_req_irq
9.64. btc_dptx_mst_vcpid_set
9.65. btc_dptx_mst_vcptab_addvc
9.66. btc_dptx_mst_vcptab_clear
9.67. btc_dptx_mst_vcptab_delvc
9.68. btc_dptx_mst_vcptab_update
9.69. btc_dptxll_syslib API Reference
9.70. btc_dptxll_hpd_change
9.71. btc_dptxll_hpd_irq
9.72. btc_dptxll_mst_cmp_ports
9.73. btc_dptxll_mst_edid_read_rep
9.74. btc_dptxll_mst_edid_read_req
9.75. btc_dptxll_mst_get_device_ports
9.76. btc_dptxll_mst_set_csn_callback
9.77. btc_dptxll_mst_topology_discover
9.78. btc_dptxll_stream_allocate_rep
9.79. btc_dptxll_stream_allocate_req
9.80. btc_dptxll_stream_calc_VCP_size
9.81. btc_dptxll_stream_delete_rep
9.82. btc_dptxll_stream_delete_req
9.83. btc_dptxll_stream_get
9.84. btc_dptxll_stream_set_color_space
9.85. btc_dptxll_stream_set_pixel_rate
9.86. btc_dptxll_sw_ver
9.87. btc_dptxll_syslib_add_tx
9.88. btc_dptxll_syslib_init
9.89. btc_dptxll_syslib_monitor
9.90. btc_dpxx_syslib Additional Types
9.91. btc_dprx_syslib Supported DPCD Locations
10.2.1. DPTX0_MSA_MVID
10.2.2. DPTX0_MSA_NVID
10.2.3. DPTX0_MSA_HTOTAL
10.2.4. DPTX0_MSA_VTOTAL
10.2.5. DPTX0_MSA_HSP
10.2.6. DPTX0_MSA_HSW
10.2.7. DPTX0_MSA_HSTART
10.2.8. DPTX0_MSA_VSTART
10.2.9. DPTX0_MSA_VSP
10.2.10. DPTX0_MSA_VSW
10.2.11. DPTX0_MSA_HWIDTH
10.2.12. DPTX0_MSA_VHEIGHT
10.2.13. DPTX0_MSA_MISC0
10.2.14. DPTX0_MSA_MISC1
10.2.15. DPTX0_MSA_COLOR
10.2.16. DPTX0_VBID
10.8.1. DPTX_AUX_CONTROL
10.8.2. DPTX_AUX_COMMAND
10.8.3. DPTX_AUX_BYTE0
10.8.4. DPTX_AUX_BYTE1
10.8.5. DPTX_AUX_BYTE2
10.8.6. DPTX_AUX_BYTE3
10.8.7. DPTX_AUX_BYTE4
10.8.8. DPTX_AUX_BYTE5
10.8.9. DPTX_AUX_BYTE6
10.8.10. DPTX_AUX_BYTE7
10.8.11. DPTX_AUX_BYTE8
10.8.12. DPTX_AUX_BYTE9
10.8.13. DPTX_AUX_BYTE10
10.8.14. DPTX_AUX_BYTE11
10.8.15. DPTX_AUX_BYTE12
10.8.16. DPTX_AUX_BYTE13
10.8.17. DPTX_AUX_BYTE14
10.8.18. DPTX_AUX_BYTE15
10.8.19. DPTX_AUX_BYTE16
10.8.20. DPTX_AUX_BYTE17
10.8.21. DPTX_AUX_BYTE18
10.8.22. DPTX_AUX_RESET
11.4.1. DPRX0_MSA_MVID
11.4.2. DPRX0_MSA_NVID
11.4.3. DPRX0_MSA_HTOTAL
11.4.4. DPRX0_MSA_VTOTAL
11.4.5. DPRX0_MSA_HSP
11.4.6. DPRX0_MSA_HSW
11.4.7. DPRX0_MSA_HSTART
11.4.8. DPRX0_MSA_VSTART
11.4.9. DPRX0_MSA_VSP
11.4.10. DPRX0_MSA_VSW
11.4.11. DPRX0_MSA_HWIDTH
11.4.12. DPRX0_MSA_VHEIGHT
11.4.13. DPRX0_MSA_MISC0
11.4.14. DPRX0_MSA_MISC1
11.4.15. DPRX0_MSA_COLOR
11.4.16. DPRX0_VBID
11.7.1. DPRX_AUX_CONTROL
11.7.2. DPRX_AUX_STATUS
11.7.3. DPRX_AUX_COMMAND
11.7.4. DPRX_AUX_BYTE0
11.7.5. DPRX_AUX_BYTE1
11.7.6. DPRX_AUX_BYTE2
11.7.7. DPRX_AUX_BYTE3
11.7.8. DPRX_AUX_BYTE4
11.7.9. DPRX_AUX_BYTE5
11.7.10. DPRX_AUX_BYTE6
11.7.11. DPRX_AUX_BYTE7
11.7.12. DPRX_AUX_BYTE8
11.7.13. DPRX_AUX_BYTE9
11.7.14. DPRX_AUX_BYTE10
11.7.15. DPRX_AUX_BYTE11
11.7.16. DPRX_AUX_BYTE12
11.7.17. DPRX_AUX_BYTE13
11.7.18. DPRX_AUX_BYTE14
11.7.19. DPRX_AUX_BYTE15
11.7.20. DPRX_AUX_BYTE16
11.7.21. DPRX_AUX_BYTE17
11.7.22. DPRX_AUX_BYTE18
11.7.23. DPRX_AUX_I2C0
11.7.24. DPRX_AUX_I2C1
11.7.25. DPRX_AUX_RESET
11.7.26. DPRX_AUX_HPD
4.3.4.5. View the Results
In this step you view the results of the hardware demonstration in the Nios II command shell and on the DisplayPort monitor.
- Power-up the connected DisplayPort monitor.
- Connect the free end of the Display Port cable that you connected to your PC to the DisplayPort RX on the Bitec daughter card. The PC now has the DisplayPort monitor available as a second monitor. The hardware demonstration loops through and displays the graphic card output as received by the sink core.
Note: Some PC drivers and graphic card adapters do not enable the DisplayPort hardware automatically upon hot plug detection. You may need to start the adapter’s control utility (e.g. Catalist Control Center, NVIDIA Control Panel) and manually enable the DisplayPort display.Figure 9. Loop-through Hardware Demonstration
- You can use your graphic card control panel to adjust the resolution of the DisplayPort monitor, which typically results in link training, related AUX channel traffic, and a corresponding new image size on the monitor.
Note: If you do not see visible output on the monitor, press push button (CPU_RESETN) to generate a reset, causing the DisplayPort TX core to re-train the link.
Press push button 0 (USER_PB[0]) to retrieve MSA statistics from the source and sink connections. The Nios II Command Shell displays the AUX channel traffic during link training with the monitor.
Figure 10. MSA Output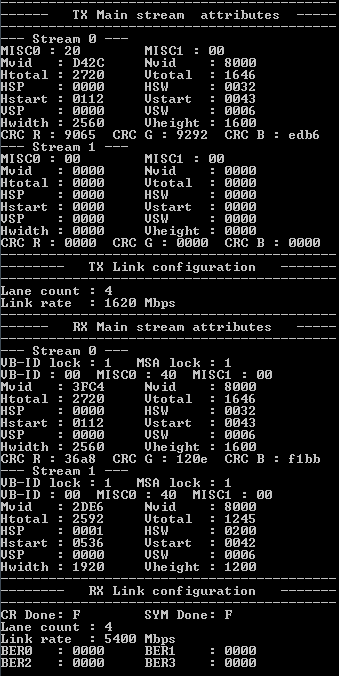
The Nios II AUX printout shows each message packet on a separate line.
- The first field is the incremental timestamp in microseconds.
- The second field indicates whether the message packet is from or to the DisplayPort sink (SNK) or source (SRC).
- The next two fields show the request and response headers and payloads. The DPCD address field on request messages are decoded into the respective DPCD location names.
When connected and enabled, USER_PB[0] on the development board illuminates to indicate that the DisplayPort receiver has locked correctly.