Arria® 10 or Cyclone® 10 GX Avalon® Memory-Mapped (Avalon-MM) DMA Interface for PCI Express* Solutions User Guide
ID
683425
Date
9/10/2024
Public
1. Datasheet
2. Getting Started with the Avalon-MM DMA
3. Parameter Settings
4. Physical Layout
5. IP Core Interfaces
6. Registers
7. Reset and Clocks
8. Error Handling
9. PCI Express Protocol Stack
10. Arria® 10 or Cyclone® 10 GX Avalon-MM DMA for PCI Express
11. Design Implementation
A. Transaction Layer Packet (TLP) Header Formats
B. Arria® 10 or Cyclone® 10 GX Avalon-MM DMA Interface for PCIe Solutions User Guide Archive
C. Document Revision History
1.1. Arria® 10 or Cyclone® 10 GX Avalon-MM DMA Interface for PCIe* Datasheet
1.2. Features
1.3. Comparison of Avalon-ST, Avalon-MM and Avalon-MM with DMA Interfaces
1.4. Release Information
1.5. Device Family Support
1.6. Design Examples
1.7. IP Core Verification
1.8. Resource Utilization
1.9. Recommended Speed Grades
1.10. Creating a Design for PCI Express
5.1. Arria® 10 or Cyclone® 10 GX DMA Avalon-MM DMA Interface to the Application Layer
5.2. Clock Signals
5.3. Reset, Status, and Link Training Signals
5.4. MSI Interrupts for Endpoints
5.5. Hard IP Reconfiguration Interface
5.6. Physical Layer Interface Signals
5.7. Test Signals
5.8. Arria® 10 Development Kit Conduit Interface
5.1.1. Avalon-MM DMA Interfaces when Descriptor Controller Is Internally Instantiated
5.1.2. Read Data Mover
5.1.3. Write DMA Avalon-MM Master Port
5.1.4. RX Master Module
5.1.5. Non-Bursing Slave Module
5.1.6. 32-Bit Control Register Access (CRA) Slave Signals
5.1.7. Avalon-ST Descriptor Control Interface when Instantiated Separately
5.1.8. Descriptor Controller Interfaces when Instantiated Internally
6.1. Correspondence between Configuration Space Registers and the PCIe Specification
6.2. Type 0 Configuration Space Registers
6.3. Type 1 Configuration Space Registers
6.4. PCI Express Capability Structures
6.5. Intel-Defined VSEC Registers
6.6. Advanced Error Reporting Capability
6.7. DMA Descriptor Controller Registers
6.8. Control Register Access (CRA) Avalon-MM Slave Port
10.1. Understanding the Internal DMA Descriptor Controller
When you select Instantiate internal descriptor controller in the parameter editor, the Avalon-MM with DMA includes an internal DMA Descriptor Controller to manage read and write DMA operations. The DMA Descriptor Controller includes read and write data movers to perform local memory reads and writes. It supports up to 128 descriptors for read and write DMAs. Host software programs the DMA Descriptor Controller internal registers with the location and size of the descriptor table residing in the PCI Express main memory. The descriptor control logic directs the DMA read logic to copy the entire table to its local FIFOs.
Figure 50. Platform Designer Design Example with the Internal DMA Descriptor ControllerThis Platform Designer design example, ep_g3x8_avmm256_integrated.qsys, is available in the <install_dir>/ ip/altera/altera_pcie/altera_pcie_a10_ed/example_design/a10 directory. Refer to Getting Started with the Arria® 10 or Cyclone® 10 GX Avalon-MM DMA for instructions on simulating and compiling this example design. This screen capture filters out some interface types for clarity.
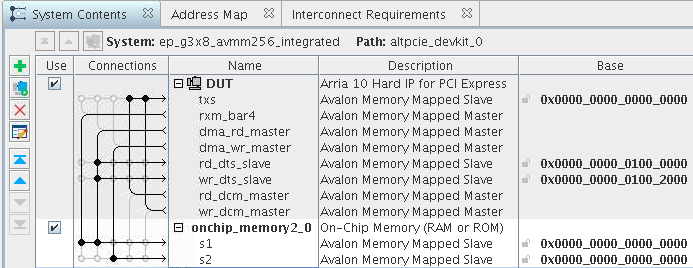

Figure 51. Avalon-MM DMA Block Diagram with the Internal DMA Descriptor ControllerThis block diagram corresponds to the Platform Designer system shown in the previous figure.
This design uses BAR0 and BAR1 to create a 64-bit address to access the DMA Descriptor Controller. These BARs cannot connect to any other interface. If BAR0 must access a different interface, you must use an external DMA descriptor controller. Intel recommends that you select the internal DMA Descriptor Controller if you do not plan to modify this component.
The high-performance BAR2 or BAR2 and BAR3 for 64-bit addresses is available to receive data for other high performance functions.
Related Information