Intel® FPGA SDK for OpenCL™ Standard Edition: Best Practices Guide
ID
683176
Date
9/24/2018
Public
1. Introduction to Standard Edition Best Practices Guide
2. Reviewing Your Kernel's report.html File
3. OpenCL Kernel Design Best Practices
4. Profiling Your Kernel to Identify Performance Bottlenecks
5. Strategies for Improving Single Work-Item Kernel Performance
6. Strategies for Improving NDRange Kernel Data Processing Efficiency
7. Strategies for Improving Memory Access Efficiency
8. Strategies for Optimizing FPGA Area Usage
A. Additional Information
2.1. High Level Design Report Layout
2.2. Reviewing the Report Summary
2.3. Reviewing Loop Information
2.4. Reviewing Area Information
2.5. Verifying Information on Memory Replication and Stalls
2.6. Optimizing an OpenCL Design Example Based on Information in the HTML Report
2.7. HTML Report: Area Report Messages
2.8. HTML Report: Kernel Design Concepts
3.1. Transferring Data Via Channels or OpenCL Pipes
3.2. Unrolling Loops
3.3. Optimizing Floating-Point Operations
3.4. Allocating Aligned Memory
3.5. Aligning a Struct with or without Padding
3.6. Maintaining Similar Structures for Vector Type Elements
3.7. Avoiding Pointer Aliasing
3.8. Avoid Expensive Functions
3.9. Avoiding Work-Item ID-Dependent Backward Branching
4.3.4.1. High Stall Percentage
4.3.4.2. Low Occupancy Percentage
4.3.4.3. Low Bandwidth Efficiency
4.3.4.4. High Stall and High Occupancy Percentages
4.3.4.5. No Stalls, Low Occupancy Percentage, and Low Bandwidth Efficiency
4.3.4.6. No Stalls, High Occupancy Percentage, and Low Bandwidth Efficiency
4.3.4.7. Stalling Channels
4.3.4.8. High Stall and Low Occupancy Percentages
7.1. General Guidelines on Optimizing Memory Accesses
7.2. Optimize Global Memory Accesses
7.3. Performing Kernel Computations Using Constant, Local or Private Memory
7.4. Improving Kernel Performance by Banking the Local Memory
7.5. Optimizing Accesses to Local Memory by Controlling the Memory Replication Factor
7.6. Minimizing the Memory Dependencies for Loop Pipelining
2.2. Reviewing the Report Summary
The report summary gives you a quick overview of the results of compiling your design including a summary of each kernel in your design and a summary of the estimated resources that each kernel in your design uses.
The report summary is divided into four sections: Info, Kernel Summary , Estimated Resource Usage, and Compile Warnings.
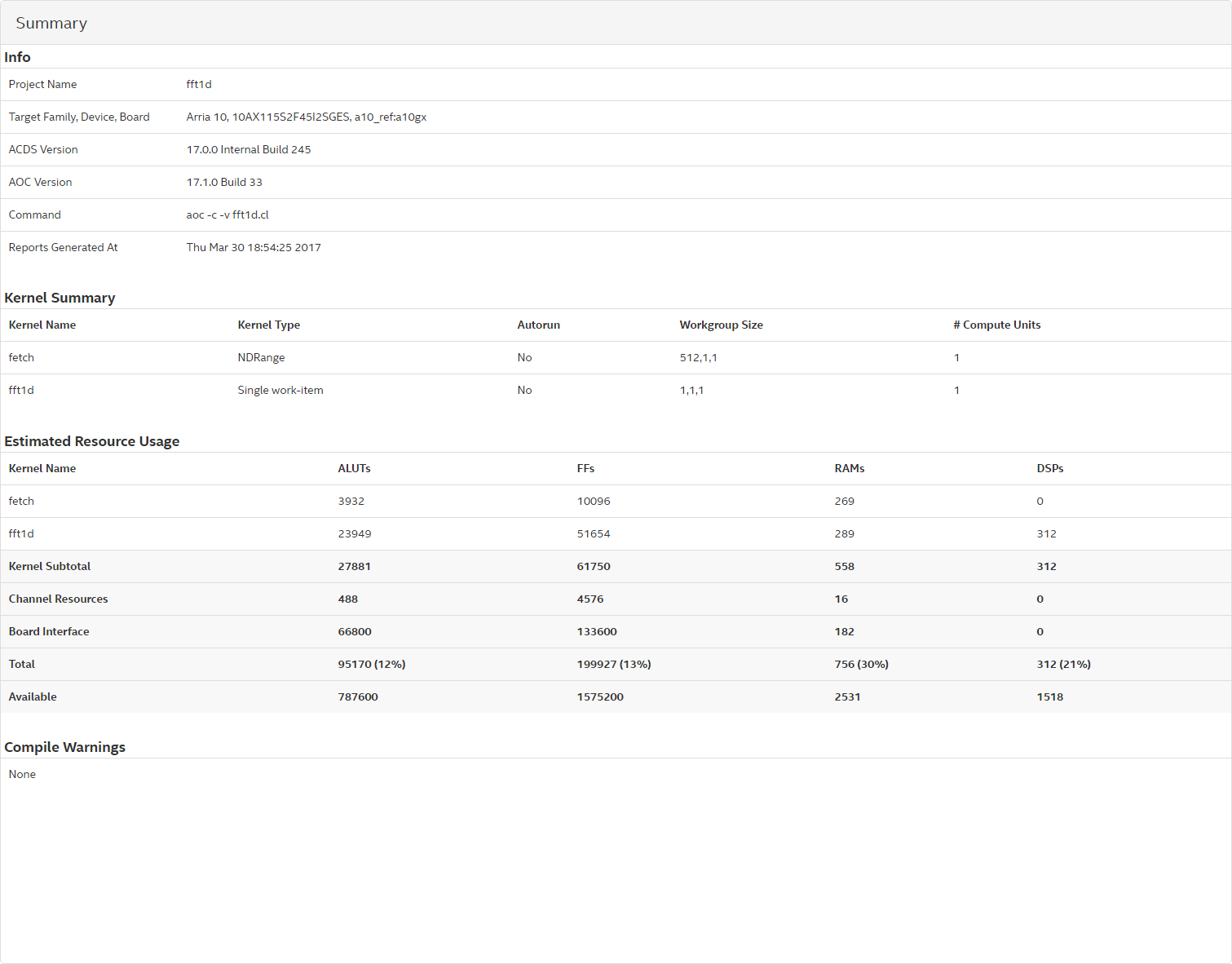
Info
The Info section shows general information about the compile including the following items:
- Name of the project
- Target FPGA family, device, and board
- Intel® Quartus® Prime Standard Edition software version
- version
- The command that was used to compile the design
- The date and time at which the reports were generated
Kernel Summary
The Kernel Summary lists each kernel in your design, and some information about each of the kernels, including the following items:
- Whether the kernel is an NDRange or a Single Work-Item kernel
- Whether the autorun attribute is used
- The required workgroup size for the kernel
- The number of compute units
- The vectorization of the kernel
- The maximum global work dimension
- The maximum workgroup size
Estimated Resource Usage
The Estimated Resource Usage section shows a summary of the estimated resources used by each kernel in your design, as well as the estimated resources used for all channels, estimated resources for the global interconnect, constant cache, and board interface.
Compile Warnings
The Compile Warnings section shows some of the compiler warnings generated during the compilation.