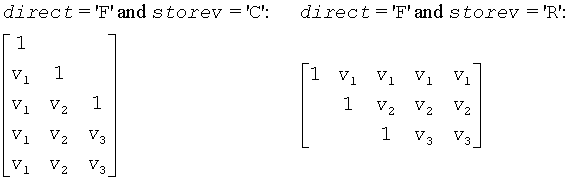Developer Reference for Intel® oneAPI Math Kernel Library for C
A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
?larfb
Applies a block reflector or its transpose/conjugate-transpose to a general rectangular matrix.
lapack_int LAPACKE_slarfb (int matrix_layout , char side , char trans , char direct , char storev , lapack_int m , lapack_int n , lapack_int k , const float * v , lapack_int ldv , const float * t , lapack_int ldt , float * c , lapack_int ldc );
lapack_int LAPACKE_dlarfb (int matrix_layout , char side , char trans , char direct , char storev , lapack_int m , lapack_int n , lapack_int k , const double * v , lapack_int ldv , const double * t , lapack_int ldt , double * c , lapack_int ldc );lapack_int LAPACKE_clarfb (int matrix_layout , char side , char trans , char direct , char storev , lapack_int m , lapack_int n , lapack_int k , const lapack_complex_float * v , lapack_int ldv , const lapack_complex_float * t , lapack_int ldt , lapack_complex_float * c , lapack_int ldc );
lapack_int LAPACKE_zlarfb (int matrix_layout , char side , char trans , char direct , char storev , lapack_int m , lapack_int n , lapack_int k , const lapack_complex_double * v , lapack_int ldv , const lapack_complex_double * t , lapack_int ldt , lapack_complex_double * c , lapack_int ldc );
- mkl.h
The real flavors of the routine ?larfb apply a real block reflector H or its transpose HT to a real m-by-n matrix C from either left or right.
The complex flavors of the routine ?larfb apply a complex block reflector H or its conjugate transpose HH to a complex m-by-n matrix C from either left or right.
A <datatype> placeholder, if present, is used for the C interface data types in the C interface section above. See C Interface Conventions for the C interface principal conventions and type definitions.
- side
-
If side = 'L': apply H or HT for real flavors and H or HH for complex flavors from the left.
If side = 'R': apply H or HT for real flavors and H or HH for complex flavors from the right.
- trans
-
If trans = 'N': apply H (No transpose).
If trans = 'C': apply HH (Conjugate transpose).
If trans = 'T': apply HT (Transpose).
- direct
-
Indicates how H is formed from a product of elementary reflectors
If direct = 'F': H = H(1)*H(2)*. . . *H(k) (forward)
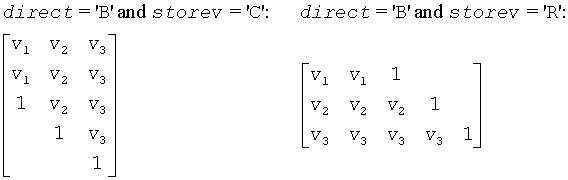
If direct = 'B': H = H(k)* . . . H(2)*H(1) (backward)
- storev
-
Indicates how the vectors which define the elementary reflectors are stored:
If storev = 'C': Column-wise
If storev = 'R': Row-wise
- m
-
The number of rows of the matrix C.
- n
-
The number of columns of the matrix C.
- k
-
The order of the matrix T (equal to the number of elementary reflectors whose product defines the block reflector).
- v
-
The size limitations depend on values of parameters storev and side as described in the following table:
storev = C
storev = R
side = L
side = R
side = L
side = R
Column major
max(1,ldv*k)
max(1,ldv*k)
max(1,ldv*m)
max(1,ldv*n)
Row major
max(1,ldv*m)
max(1,ldv*n)
max(1,ldv*k)
max(1,ldv*k)
The matrix v. See Application Notes below.
- ldv
-
The leading dimension of the array v.It should satisfy the following conditions:
storev = C
storev = R
side = L
side = R
side = L
side = R
Column major
max(1,m)
max(1,n)
max(1,k)
max(1,k)
Row major
max(1,k)
max(1,k)
max(1,m)
max(1,n)
- t
-
Array, size at least max(1,ldt * k).
Contains the triangular k-by-k matrix T in the representation of the block reflector.
- ldt
-
The leading dimension of the array t.
ldt≥k.
- c
-
Array, size at least max(1, ldc * n) for column major layout and max(1, ldc * m) for row major layout.
On entry, the m-by-n matrix C.
- ldc
-
The leading dimension of the array c.
ldc≥ max(1,m) for column major layout and ldc≥ max(1,n) for row major layout.
- c
-
On exit, c is overwritten by the product of the following:
H*C, or HT*C, or C*H, or C*HT for real flavors
H*C, or HH*C, or C*H, or C*HH for complex flavors
This function returns a value info.
If info = 0, the execution is successful.
If info = -i, the i-th parameter had an illegal value.
If info = -1011, memory allocation error occurred.
The shape of the matrix V and the storage of the vectors which define the H(i) is best illustrated by the following example with n = 5 and k = 3. The elements equal to 1 are not stored; the corresponding array elements are modified but restored on exit. The rest of the array is not used.