Developer Reference for Intel® oneAPI Math Kernel Library for C
A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
?ggsvd3
Computes generalized SVD.
lapack_int LAPACKE_sggsvd3 (int matrix_layout, char jobu, char jobv, char jobq, lapack_int m, lapack_int n, lapack_int p, lapack_int * k, lapack_int * l, float * a, lapack_int lda, float * b, lapack_int ldb, float * alpha, float * beta, float * u, lapack_int ldu, float * v, lapack_int ldv, float * q, lapack_int ldq, lapack_int * iwork);
lapack_int LAPACKE_dggsvd3 (int matrix_layout, char jobu, char jobv, char jobq, lapack_int m, lapack_int n, lapack_int p, lapack_int * k, lapack_int * l, double * a, lapack_int lda, double * b, lapack_int ldb, double * alpha, double * beta, double * u, lapack_int ldu, double * v, lapack_int ldv, double * q, lapack_int ldq, lapack_int * iwork);
lapack_int LAPACKE_cggsvd3 (int matrix_layout, char jobu, char jobv, char jobq, lapack_int m, lapack_int n, lapack_int p, lapack_int * k, lapack_int * l, lapack_complex_float * a, lapack_int lda, lapack_complex_float * b, lapack_int ldb, float * alpha, float * beta, lapack_complex_float * u, lapack_int ldu, lapack_complex_float * v, lapack_int ldv, lapack_complex_float * q, lapack_int ldq, lapack_int * iwork);
lapack_int LAPACKE_zggsvd3 (int matrix_layout, char jobu, char jobv, char jobq, lapack_int m, lapack_int n, lapack_int p, lapack_int * k, lapack_int * l, lapack_complex_double * a, lapack_int lda, lapack_complex_double * b, lapack_int ldb, double * alpha, double * beta, lapack_complex_double * u, lapack_int ldu, lapack_complex_double * v, lapack_int ldv, lapack_complex_double * q, lapack_int ldq, lapack_int * iwork);
- mkl.h
?ggsvd3 computes the generalized singular value decomposition (GSVD) of an m-by-n real or complex matrix A and p-by-n real or complex matrix B:
UT*A*Q = D1*( 0 R ), VT*B*Q = D2*( 0 R ) for real flavors
or
UH*A*Q = D1*( 0 R ), VH*B*Q = D2*( 0 R ) for complex flavors
where U, V and Q are orthogonal/unitary matrices.
Let k+l = the effective numerical rank of the matrix (ATBT)T for real flavors or the matrix (AH,BH)H for complex flavors, then R is a (k + l)-by-(k + l) nonsingular upper triangular matrix, D1 and D2 are m-by-(k + l) and p-by-(k + l) "diagonal" matrices and of the following structures, respectively:
If m-k-l≥ 0,
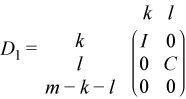
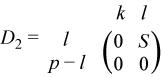
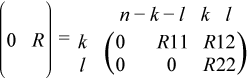
where
C = diag( alpha(k+1), ... , alpha(k+l) ),
S = diag( beta(k+1), ... , beta(k+l) ),
C2 + S2 = I.
If m - k - l < 0,
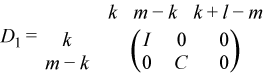
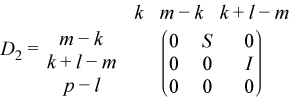

where
C = diag(alpha(k + 1), ... , alpha(m)),
S = diag(beta(k + 1), ... , beta(m)),
C2 + S2 = I.
The routine computes C, S, R, and optionally the orthogonal/unitary transformation matrices U, V and Q.
In particular, if B is an n-by-n nonsingular matrix, then the GSVD of A and B implicitly gives the SVD of A*inv(B):
A*inv(B) = U*(D1*inv(D2))*VT for real flavors
or
A*inv(B) = U*(D1*inv(D2))*VH for complex flavors.
If (AT,BT)T for real flavors or (AH,BH)H for complex flavors has orthonormal columns, then the GSVD of A and B is also equal to the CS decomposition of A and B. Furthermore, the GSVD can be used to derive the solution of the eigenvalue problem:
AT*AX = λ* BT*BX for real flavors
or
AH*AX = λ* BH*BX for complex flavors
In some literature, the GSVD of A and B is presented in the form
UT*A*X = ( 0 D1 ), VT*B*X = ( 0 D2 ) for real (A, B)
or
UH*A*X = ( 0 D1 ), VH*B*X = ( 0 D2 ) for complex (A, B)
where U and V are orthogonal and X is nonsingular, D1 and D2 are "diagonal''. The former GSVD form can be converted to the latter form by taking the nonsingular matrix X as
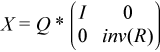
- matrix_layout
-
Specifies whether matrix storage layout is row major (LAPACK_ROW_MAJOR) or column major (LAPACK_COL_MAJOR).
- jobu
-
= 'U': Orthogonal/unitary matrix U is computed;
= 'N': U is not computed.
- jobv
-
= 'V': Orthogonal/unitary matrix V is computed;
= 'N': V is not computed.
- jobq
-
= 'Q': Orthogonal/unitary matrix Q is computed;
= 'N': Q is not computed.
- m
-
The number of rows of the matrix A.
m≥ 0.
- n
-
The number of columns of the matrices A and B.
n≥ 0.
- p
-
The number of rows of the matrix B.
p≥ 0.
- a
-
Array, size (lda*n).
On entry, the m-by-n matrix A.
- lda
-
The leading dimension of the array a.
lda≥ max(1,m).
- b
-
Array, size (ldb*n).
On entry, the p-by-n matrix B.
- ldb
-
The leading dimension of the array b.
ldb≥ max(1,p).
- ldu
-
The leading dimension of the array u.
ldu≥ max(1,m) if jobu = 'U'; ldu≥ 1 otherwise.
- ldv
-
The leading dimension of the array v.
ldv≥ max(1,p) if jobv = 'V'; ldv≥ 1 otherwise.
- ldq
-
The leading dimension of the array q.
ldq≥ max(1,n) if jobq = 'Q'; ldq≥ 1 otherwise.
- iwork
-
Array, size (n).
k, l |
On exit, k and l specify the dimension of the subblocks described in the Description section. k + l = effective numerical rank of (AT,BT)T for real flavors or (AH,BH)H for complex flavors. |
a |
On exit, a contains the triangular matrix R, or part of R. If m-k-l≥ 0, R is stored in the elements of array a corresponding to A1: k + l,n - k - l + 1:n. If m - k - l < 0, |
b |
On exit, b contains part of the triangular matrix R if m - k - l < 0. See Description for details. |
alpha |
Array, size (n) |
beta |
Array, size (n) On exit, alpha and beta contain the generalized singular value pairs of a and b; alpha[0: k - 1] = 1, beta[0: k - 1] = 0, and if m - k - l≥ 0, alpha[k:k + l - 1] = C, beta[k:k + l - 1] = S, or if m - k - l < 0, alpha[k:m - 1] = C, alpha[m: k + l - 1] = 0 beta[k: m - 1] =S, beta[m: k + l - 1] = 1 and alpha[k + l: n - 1] = 0 beta[k + l : n - 1] = 0 |
u |
Array, size (ldu*m). If jobu = 'U', u contains the m-by-m orthogonal/unitary matrix U. If jobu = 'N', u is not referenced. |
v |
Array, size (ldv*p). If jobv = 'V', v contains the p-by-p orthogonal/unitary matrix V. If jobv = 'N', v is not referenced. |
q |
Array, size (ldq*n). If jobq = 'Q', q contains the n-by-n orthogonal/unitary matrix Q. If jobq = 'N', q is not referenced. |
iwork |
On exit, iwork stores the sorting information. More precisely, the following loop uses iwork to sort alpha: for (i = k; i<min(m,k + l); i++) {
swap (alpha[i], alpha[iwork[i] - 1]);
}such that alpha[0] ≥alpha[1] ≥ ... ≥alpha[n - 1]. |
This function returns a value info.
= 0: successful exit.
< 0: if info = -i, the i-th argument had an illegal value.
> 0: if info = 1, the Jacobi-type procedure failed to converge.
For further details, see subroutine ?tgsja.
?ggsvd3 replaces the deprecated subroutine ?ggsvd.
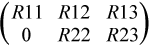 is stored in the elements of array
is stored in the elements of array