Video and Vision Processing Suite Intel® FPGA IP User Guide
A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
52.3.1. Block Cache Tool
The block cache tool also detects if the configured transform exceeds maximum supported downscale ratio of 256:1, if mipmaps are on or 2:1 otherwise, in any part of the image.These values are the maximum supported compression values of the Warp IP. The block cache tool supports both single bounce and double bounce warp IP configurations.
The block cache tool provides a command line interface that allows you to specify the desired warp by using several available options such as rotation, mirroring, keystone, or by using a warp mesh file generated by the Warp SoC Design Example. The tool then estimates block cache usage for all supported block cache sizes. For each size option the tool prints the result in the following form:
| Result | Description |
|---|---|
| Pass | Requested warp is possible using this block cache size per processing engine |
| Pass, Block cache usage too high | Requested warp might be possible. However the IP does not guarantee the output quality because of high block cache usage. The configuration requires further evaluation on the target system |
| Fail | Requested warp is not possible using this block cache size. The estimation also fails if the warp exceeds a maximum supported local compression of 256:1 or 2:1 depending on the mipmap setting, in which case it fails for all block cache sizes |
The block cache tool can visualize configured transform by warping a reference image and saving it as a bitmap (bmp) file on the disk.
The block cache tool is a command line application and included with the Quartus Prime Software.
Block Cache Tool Options
The block cache tool options:
vidip_bct.exe [option]…
| Option | Description | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| -h | Help | Print the tool usage information.
|
| -iw -ih -ow -oh | Input width (pixels) Input height (pixels) Output width (pixels) Output height (pixels) |
Set input and output dimensions of the transformed image in pixels. Default image dimensions are 7680x4320 pixels. |
| -r | Rotation angle |
Set rotation angle in degrees. Image is rotated around the center. |
| -mh | Mirror horizontally |
Mirror image along horizontal axis. |
| -mv | Mirror vertically |
Mirror image along vertical axis. |
| -ho | Horizontal offset (pixels) |
Set horizontal offset in pixels. |
| -vo | Vertical offset (pixels) |
Set vertical offset in pixels. |
| -hk | Horizontal keystone angle |
Set horizontal keystone compensation angle in degrees. |
| -vk | Vertical keystone angle | Set vertical keystone compensation angle in degrees. |
| -z | Zoom | Set image zoom value: less than 1 to zoom out, greater than 1 to zoom in. |
| -pb | Radial distortion |
Set radial distortion compensation value in the range: [-0.45..0.45]. |
| -f | Mesh file name |
Path to the warp mesh file generated by the Warp SoC Example application |
| -e | Number of warp engines. |
Number of the warp processing engines. Supported values: 1 or 2 (default); |
| -db | Double bounce |
Assume double bounce Warp IP configuration. By default, the tool assumes Single bounce configuration. Use this option to override default behavior. |
| -mm | Use mipmaps |
Use mipmaps to allow warps with downscale ratios to a limit of 256:1 |
| -s | Run warp simulator |
Warp a reference image using provided settings and save result on disk. The output file name is warp_output.bmp. |
Examples
This command:
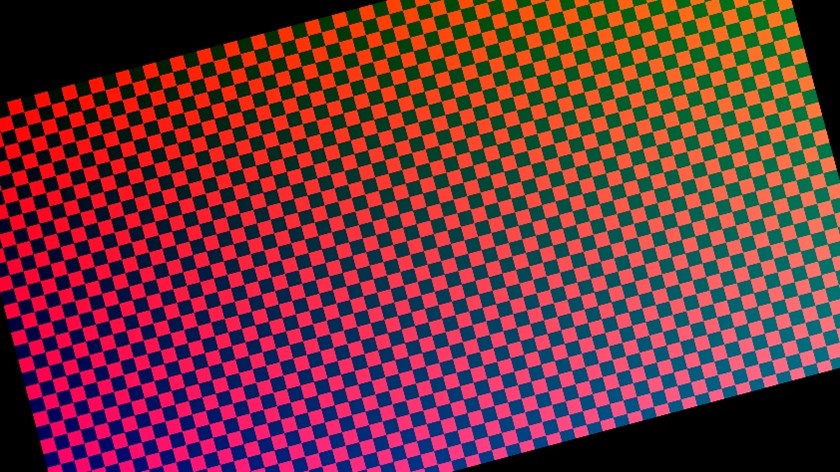
vidip_bct.exe -iw 1920 -ih 1080 -ow 3840 -oh 2160 -r 15.0 -s
- Sets the input resolution to full HD, output resolution to 4K
- Performs a 15 degree rotation anticlockwise
- Stores warped reference image on the disk.
The console output is:
intel_vvp_warp block cache tool v2.0 Input resolution: 1920x1080 Output resolution: 3840x2160 Warp engines: 4 Bounce: Single Mipmaps: No Generating warp data... Cache size Result Warnings 256 PASS 512 PASS 1024 PASS
The console output indicates the IP can perform the configured warp with all available block cache size options.
This command:
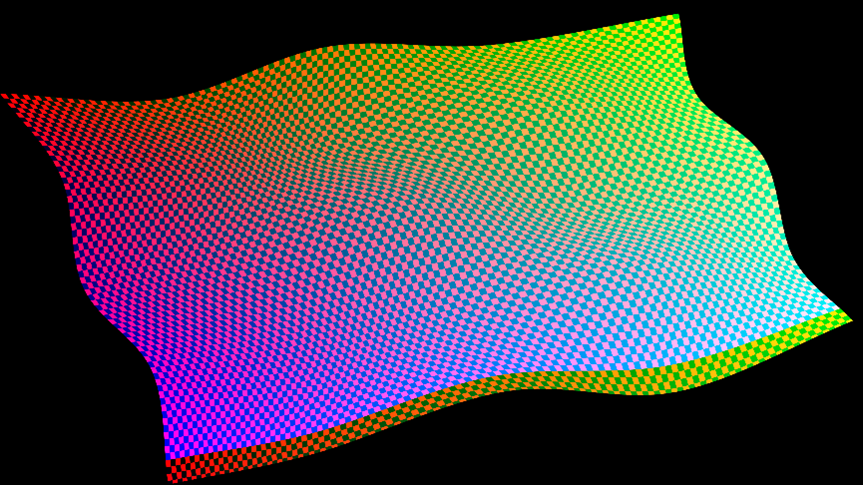
vidip_bct.exe-iw 3840 -ih 2160 -ow 3840 -oh 2160 -e 2 -f flying_flag.owf -mm -s
- Uses the warp mesh file generated by the Warp SoC Example Design, named flying_flag.owf
- Sets input and output resolutions to 4K
- Sets number of warp engines to 2
- Enables mipmap usage
- Stores warped reference image on the disk.
The console output is:
intel_vvp_warp block cache tool v2.0 Input resolution: 3840x2160 Output resolution: 3840x2160 Warp engines: 2 Bounce: Single Generating warp data... Cache size Result Warnings 256 PASS Block cache usage too high 512 PASS 1024 PASS
The console output indicates the IP can perform the warp using block cache sizes of 512 and 1024. With the block cache size of 256, the tool detects a high block cache usage. The IP cannot guarantee the output image quality and requires further evaluation on the actual hardware.
This command:
vidip_bct.exe -z 0.45
- Uses default input and output resolution of 8K
- Scaled the image down by 0.45
The console output is
intel_vvp_warp block cache tool v2.0 Input resolution: 7680x4320 Output resolution: 7680x4320 Warp engines: 4 Bounce: Single Mipmaps: No Generating warp data... Cache size Result Warnings 256 PASS Compression too high
The console output indicates the transform exceeds the maximum compression of 2:1 and therefore the output image quality is not guaranteed.