Intel® oneAPI Data Analytics Library Developer Guide and Reference
A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
Distributed Processing
This mode assumes that the data set is split into nBlocks blocks across computation nodes.
To compute DBSCAN algorithm in the distributed processing mode, use the general schema described in Algorithms with the following steps:
Step 1 - on Local Nodes
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm has the following parameters:
Parameter |
Default Valude |
Description |
|---|---|---|
algorithmFPType |
float |
The floating-point type that the algorithm uses for intermediate computations. Can be float or double. |
method |
defaultDense |
Available methods for computation of DBSCAN algorithm:
|
blockIndex |
Not applicable |
Unique identifier of block initially passed for computation on the local node. |
nBlocks |
Not applicable |
The number of blocks initially passed for computation on all nodes. |
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm accepts the input described below. Pass the Input ID as a parameter to the methods that provide input for your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Input ID |
Input |
|---|---|
step1Data |
Pointer to the
NOTE:
The input can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable.
|
Algorithm Output
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithms calculates the partial results described below. Pass the Partial Result ID as a parameter to the methods that access the partial result of your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Partial Result ID |
Result |
|---|---|
partialOrder |
Pointer to the
NOTE:
By default, this result is an object of the HomogenNumericTable class, but you can define the result as an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
Step 2 - on Local Nodes
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm has the following parameters:
Parameter |
Default Valude |
Description |
|---|---|---|
algorithmFPType |
float |
The floating-point type that the algorithm uses for intermediate computations. Can be float or double. |
method |
defaultDense |
Available methods for computation of DBSCAN algorithm:
|
blockIndex |
Not applicable |
Unique identifier of block initially passed for computation on the local node. |
nBlocks |
Not applicable |
The number of blocks initially passed for computation on all nodes. |
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm accepts the input described below. Pass the Input ID as a parameter to the methods that provide input for your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Input ID |
Input |
|---|---|
partialData |
Pointer to the collection of numeric tables with p columns and arbitrary number of rows, containing observations to be clustered.
NOTE:
The input can be an object of any class derived from DataCollection. The numeric tables in the collection can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable.
|
Algorithm Output
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithms calculates the partial results described below. Pass the Partial Result ID as a parameter to the methods that access the partial result of your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Partial Result ID |
Result |
|---|---|
boundingBox |
Pointer to the
NOTE:
By default, this result is an object of the HomogenNumericTable class, but you can define the result as an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
Step 3 - on Local Nodes
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm has the following parameters:
Parameter |
Default Valude |
Description |
|---|---|---|
algorithmFPType |
float |
The floating-point type that the algorithm uses for intermediate computations. Can be float or double. |
method |
defaultDense |
Available methods for computation of DBSCAN algorithm:
|
leftBlocks |
Not applicable |
The number of blocks that will process observations with value of selected split feature smaller than selected split value. |
rightBlocks |
Not applicable |
The number of blocks that will process observations with value of selected split feature greater than selected split value. |
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm accepts the input described below. Pass the Input ID as a parameter to the methods that provide input for your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Input ID |
Input |
|---|---|
partialData |
Pointer to the collection of numeric tables with p columns and arbitrary number of rows, containing observations to be clustered.
NOTE:
The input can be an object of any class derived from DataCollection. The numeric tables in the collection can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable.
|
step3PartialBoundingBoxes |
Pointer to the collection of the
NOTE:
The numeric tables in collection can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
Algorithm Output
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithms calculates the partial results described below. Pass the Partial Result ID as a parameter to the methods that access the partial result of your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Partial Result ID |
Result |
|---|---|
split |
Pointer to the
NOTE:
By default, this result is an object of the HomogenNumericTable class, but you can define the result as an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
Step 4 - on Local Nodes
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm has the following parameters:
Parameter |
Default Valude |
Description |
|---|---|---|
algorithmFPType |
float |
The floating-point type that the algorithm uses for intermediate computations. Can be float or double. |
method |
defaultDense |
Available methods for computation of DBSCAN algorithm:
|
leftBlocks |
Not applicable |
The number of blocks that will process observations with value of selected split feature smaller than selected split value. |
rightBlocks |
Not applicable |
The number of blocks that will process observations with value of selected split feature greater than selected split value. |
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm accepts the input described below. Pass the Input ID as a parameter to the methods that provide input for your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Input ID |
Input |
|---|---|
partialData |
Pointer to the collection of numeric tables with p columns and arbitrary number of rows, containing observations to be clustered.
NOTE:
The input can be an object of any class derived from DataCollection. The numeric tables in the collection can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable.
|
step4PartialOrders |
Pointer to the collection of numeric table with 2 columns and arbitrary number of rows containing information about observations: identifier of initial block and index in initial block.
NOTE:
The input can be an object of any class derived from DataCollection. The numeric tables in the collection can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
step4PartialSplits |
Pointer to the collection of the
NOTE:
The input can be an object of any class derived from DataCollection. The numeric tables in the collection can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
Algorithm Output
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithms calculates the partial results described below. Pass the Partial Result ID as a parameter to the methods that access the partial result of your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Partial Result ID |
Result |
|---|---|
partitionedData |
Pointer to the collection of (leftBlocks + rightBlocks) numeric tables with p columns and arbitrary number of rows containing observations for processing on nodes participating in current iteration of geometric repartitioning.
NOTE:
By default, this result is an object of the HomogenNumericTable class, but you can define the result as an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
Step 5 - on Local Nodes
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm has the following parameters:
Parameter |
Default Valude |
Description |
|---|---|---|
algorithmFPType |
float |
The floating-point type that the algorithm uses for intermediate computations. Can be float or double. |
method |
defaultDense |
Available methods for computation of DBSCAN algorithm:
|
blockIndex |
Not applicable |
Unique identifier of block initially passed for computation on the local node. |
nBlocks |
Not applicable |
The number of blocks initially passed for computation on all nodes. |
epsilon |
Not applicable |
The maximum distance between observations lying in the same neighborhood. |
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm accepts the input described below. Pass the Input ID as a parameter to the methods that provide input for your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Input ID |
Input |
|---|---|
partialData |
Pointer to the collection of numeric tables with p columns and arbitrary number of rows, containing observations to be clustered.
NOTE:
The input can be an object of any class derived from DataCollection. The numeric tables in the collection can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable.
|
step5PartialBoundingBoxes |
Pointer to the collection of
NOTE:
The input can be an object of any class derived from DataCollection. The numeric tables in the collection can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
Algorithm Output
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithms calculates the partial results described below. Pass the Partial Result ID as a parameter to the methods that access the partial result of your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Partial Result ID |
Result |
|---|---|
partitionedHaloData |
Pointer to the collection of nBlocks numeric tables with p columns and arbitrary number of rows containing observations from current node that should be used as halo observations on each node. Numeric tables in the collection are ordered by the identifiers of initial block of nodes. |
partitionedHaloDataIndices |
Pointer to the collection of nBlocks numeric tables with 1 column and arbitrary number of rows containing indices of observations from current node that should be used as halo observations on each node. Numeric tables in the collection are ordered by the identifiers of initial block of nodes. |
Step 6 - on Local Nodes
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm has the following parameters:
Parameter |
Default Valude |
Description |
|---|---|---|
algorithmFPType |
float |
The floating-point type that the algorithm uses for intermediate computations. Can be float or double. |
method |
defaultDense |
Available methods for computation of DBSCAN algorithm:
|
blockIndex |
Not applicable |
Unique identifier of block initially passed for computation on the local node. |
nBlocks |
Not applicable |
The number of blocks initially passed for computation on all nodes. |
epsilon |
Not applicable |
The maximum distance between observations lying in the same neighborhood. |
minObservations |
Not applicable |
The number of observations in a neighborhood for an observation to be considered as a core. |
memorySavingMode |
false |
If flag is set to false, all neighborhoods will be computed and stored prior to clustering. It will require up to |
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm accepts the input described below. Pass the Input ID as a parameter to the methods that provide input for your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Input ID |
Input |
|---|---|
partialData |
Pointer to the collection of numeric tables with p columns and arbitrary number of rows, containing observations to be clustered.
NOTE:
The input can be an object of any class derived from DataCollection. The numeric tables in the collection can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable.
|
haloData |
Pointer to the collection of numeric tables with p columns and arbitrary number of rows, containing halo observations for current node computed on step 5.
NOTE:
The input can be an object of any class derived from DataCollection. The numeric tables in the collection can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable.
|
haloDataIndices |
Pointer to the collection of numeric tables with 1 column and arbitrary number of rows, containing indices for halo observations for current node computed on step 5. Size of this collection should be equal to the size of collection for haloData’s Input ID.
NOTE:
The input can be an object of any class derived from DataCollection. The numeric tables in the collection can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
haloDataBlocks |
Pointer to the collection of Size of this collection should be equal to the size of collection for haloData’s Input ID.
NOTE:
The input can be an object of any class derived from DataCollection. The numeric tables in the collection can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
Algorithm Output
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithms calculates the partial results described below. Pass the Partial Result ID as a parameter to the methods that access the partial result of your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Partial Result ID |
Result |
|---|---|
step6ClusterStructure |
Pointer to the numeric table with 4 columns and arbitrary number of rows containing information about current clustering state of observations processed on the local node.
NOTE:
By default, this result is an object of the HomogenNumericTable class, but you can define the result as an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
step6FinishedFlag |
Pointer to
NOTE:
By default, this result is an object of the HomogenNumericTable class, but you can define the result as an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
step6NClusters |
Pointer to
NOTE:
By default, this result is an object of the HomogenNumericTable class, but you can define the result as an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
step6Queries |
Pointer to the collection of nBlocks numeric tables with 3 columns and arbitrary number of rows containing clustering queries that should be processed on each node. Numeric tables in collection ordered by the identifiers of initial block of nodes.
NOTE:
By default, this result is an object of the DataCollection class. The numeric tables in the collection can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable` except for ``PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
Step 7 - on Master Node
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm has the following parameters:
Parameter |
Default Valude |
Description |
|---|---|---|
algorithmFPType |
float |
The floating-point type that the algorithm uses for intermediate computations. Can be float or double. |
method |
defaultDense |
Available methods for computation of DBSCAN algorithm:
|
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm accepts the input described below. Pass the Input ID as a parameter to the methods that provide input for your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Input ID |
Input |
|---|---|
partialFinishedFlags |
Pointer to the collection of
NOTE:
The input can be an object of any class derived from DataCollection. The numeric tables in the collection can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
Algorithm Output
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithms calculates the results and partial results described below. Pass the Result ID as a parameter to the methods that access the result and partial result of your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Partial Result ID |
Result |
|---|---|
finishedFlag |
Pointer to
NOTE:
By default, this result is an object of the HomogenNumericTable class, but you can define the result as an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
Step 8 - on Local Nodes
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm has the following parameters:
Parameter |
Default Valude |
Description |
|---|---|---|
algorithmFPType |
float |
The floating-point type that the algorithm uses for intermediate computations. Can be float or double. |
method |
defaultDense |
Available methods for computation of DBSCAN algorithm:
|
blockIndex |
Not applicable |
Unique identifier of block initially passed for computation on the local node. |
nBlocks |
Not applicable |
The number of blocks initially passed for computation on all nodes. |
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm accepts the input described below. Pass the Input ID as a parameter to the methods that provide input for your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Input ID |
Input |
|---|---|
step8InputClusterStructure |
Pointer to the numeric table with 4 columns and arbitrary number of rows containing information about current clustering state of observations processed on the local node.
NOTE:
The input can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
step8InputNClusters |
Pointer to
NOTE:
The input can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
step8PartialQueries |
Pointer to the collection of numeric tables with 3 columns and arbitrary number of rows containing clustering queries that should be processed on the local node collected from all nodes.
NOTE:
The input can be an object of any class derived from DataCollection. The numeric tables in the collection can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
Algorithm Output
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithms calculates the partial results described below. Pass the Partial Result ID as a parameter to the methods that access the partial result of your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Partial Result ID |
Result |
|---|---|
step8ClusterStructure |
Pointer to the numeric table with 4 columns and arbitrary number of rows containing information about current clustering state of observations processed on the local node.
NOTE:
By default, this result is an object of the HomogenNumericTable class, but you can define the result as an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
step8FinishedFlag |
Pointer to
NOTE:
By default, this result is an object of the HomogenNumericTable class, but you can define the result as an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
step8NClusters |
Pointer to
NOTE:
By default, this result is an object of the HomogenNumericTable class, but you can define the result as an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
step8Queries |
Pointer to the collection of nBlocks numeric tables with 3 columns and arbitrary number of rows containing clustering queries that should be processed on each node. Numeric tables in collection ordered by the identifiers of initial block of nodes.
NOTE:
By default, this result is an object of the DataCollection class. The numeric tables in the collection can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable` except for ``PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
Step 9 - on Master Node
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm has the following parameters:
Parameter |
Default Valude |
Description |
|---|---|---|
algorithmFPType |
float |
The floating-point type that the algorithm uses for intermediate computations. Can be float or double. |
method |
defaultDense |
Available methods for computation of DBSCAN algorithm:
|
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm accepts the input described below. Pass the Input ID as a parameter to the methods that provide input for your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Input ID |
Input |
|---|---|
partialNClusters |
Pointer to the collection of
NOTE:
The input can be an object of any class derived from DataCollection. The numeric tables in the collection can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
Algorithm Output
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithms calculates the results and partial results described below. Pass the Result ID as a parameter to the methods that access the result and partial result of your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Result ID |
Result |
|---|---|
step9NClusters |
Pointer to
NOTE:
By default, this result is an object of the HomogenNumericTable class, but you can define the result as an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
Partial Result ID |
Result |
|---|---|
clusterOffsets |
Pointer to the collection of
NOTE:
By default, this result is an object of the DataCollection class. The numeric tables in the collection can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable` except for ``PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
Step 10 - on Local Nodes
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm has the following parameters:
Parameter |
Default Valude |
Description |
|---|---|---|
algorithmFPType |
float |
The floating-point type that the algorithm uses for intermediate computations. Can be float or double. |
method |
defaultDense |
Available methods for computation of DBSCAN algorithm:
|
blockIndex |
Not applicable |
Unique identifier of block initially passed for computation on the local node. |
nBlocks |
Not applicable |
The number of blocks initially passed for computation on all nodes. |
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm accepts the input described below. Pass the Input ID as a parameter to the methods that provide input for your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Input ID |
Input |
|---|---|
step10InputClusterStructure |
Pointer to the numeric table with 4 columns and arbitrary number of rows containing information about current clustering state of observations processed on the local node.
NOTE:
The input can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
step10ClusterOffset |
Pointer to
NOTE:
The input can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
Algorithm Output
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithms calculates the partial results described below. Pass the Partial Result ID as a parameter to the methods that access the partial result of your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Partial Result ID |
Result |
|---|---|
step10ClusterStructure |
Pointer to the numeric table with 4 columns and arbitrary number of rows containing information about current clustering state of observations processed on the local node.
NOTE:
By default, this result is an object of the HomogenNumericTable class, but you can define the result as an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
step10FinishedFlag |
Pointer to
NOTE:
By default, this result is an object of the HomogenNumericTable class, but you can define the result as an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
step10Queries |
Pointer to the collection of nBlocks numeric tables with 4 columns and arbitrary number of rows containing clusters numeration queries that should be processed on each node. Numeric tables in collection ordered by the identifiers of initial block of nodes.
NOTE:
By default, this result is an object of the DataCollection class. The numeric tables in the collection can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable` except for ``PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
Step 11 - on Local Nodes
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm has the following parameters:
Parameter |
Default Valude |
Description |
|---|---|---|
algorithmFPType |
float |
The floating-point type that the algorithm uses for intermediate computations. Can be float or double. |
method |
defaultDense |
Available methods for computation of DBSCAN algorithm:
|
blockIndex |
Not applicable |
Unique identifier of block initially passed for computation on the local node. |
nBlocks |
Not applicable |
The number of blocks initially passed for computation on all nodes. |
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm accepts the input described below. Pass the Input ID as a parameter to the methods that provide input for your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Input ID |
Input |
|---|---|
step11InputClusterStructure |
Pointer to the numeric table with 4 columns and arbitrary number of rows containing information about current clustering state of observations processed on the local node.
NOTE:
The input can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
step11PartialQueries |
Pointer to the collection of numeric tables with 4 columns and arbitrary number of rows containing clusters numeration queries that should be processed on the local node collected from all nodes.
NOTE:
The input can be an object of any class derived from DataCollection. The numeric tables in the collection can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
Algorithm Output
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithms calculates the partial results described below. Pass the Partial Result ID as a parameter to the methods that access the partial result of your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Partial Result ID |
Result |
|---|---|
step11ClusterStructure |
Pointer to the numeric table with 4 columns and arbitrary number of rows containing information about current clustering state of observations processed on the local node.
NOTE:
By default, this result is an object of the HomogenNumericTable class, but you can define the result as an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
step11FinishedFlag |
Pointer to
NOTE:
By default, this result is an object of the HomogenNumericTable class, but you can define the result as an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
step11Queries |
Pointer to the collection of nBlocks numeric tables with 4 columns and arbitrary number of rows containing clusters numeration queries that should be processed on each node. Numeric tables in the collection are ordered by the identifiers of initial block of nodes.
NOTE:
By default, this result is an object of the DataCollection class. The numeric tables in the collection can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable` except for ``PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
Step 12 - on Local Nodes
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm has the following parameters:
Parameter |
Default Valude |
Description |
|---|---|---|
algorithmFPType |
float |
The floating-point type that the algorithm uses for intermediate computations. Can be float or double. |
method |
defaultDense |
Available methods for computation of DBSCAN algorithm:
|
blockIndex |
Not applicable |
Unique identifier of block initially passed for computation on the local node. |
nBlocks |
Not applicable |
The number of blocks initially passed for computation on all nodes. |
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm accepts the input described below. Pass the Input ID as a parameter to the methods that provide input for your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Input ID |
Input |
|---|---|
step12InputClusterStructure |
Pointer to the numeric table with 4 columns and arbitrary number of rows containing information about current clustering state of observations processed on the local node.
NOTE:
The input can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
step12PartialOrders |
Pointer to the collection of
NOTE:
The input can be an object of any class derived from DataCollection. The numeric tables in the collection can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
Algorithm Output
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithms calculates the partial results described below. Pass the Partial Result ID as a parameter to the methods that access the partial result of your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Partial Result ID |
Result |
|---|---|
assignmentQueries |
Pointer to the collection of nBlocks numeric tables with 2 columns and arbitrary number of rows containing clusters assigning queries that should be processed on each node. Numeric tables in the collection are ordered by the identifiers of initial block of nodes. |
Step 13 - on Local Nodes
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm has the following parameters:
Parameter |
Default Valude |
Description |
|---|---|---|
algorithmFPType |
float |
The floating-point type that the algorithm uses for intermediate computations. Can be float or double. |
method |
defaultDense |
Available methods for computation of DBSCAN algorithm:
|
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithm accepts the input described below. Pass the Input ID as a parameter to the methods that provide input for your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Input ID |
Input |
|---|---|
partialAssignmentQueries |
Pointer to the collection of numeric tables with 2 columns and arbitrary number of rows containing clusters assigning queries that should be processed on the local node collected from all nodes.
NOTE:
The input can be an object of any class derived from DataCollection. The numeric tables in the collection can be an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
Algorithm Output
In this step, the DBSCAN algorithms calculates the results and partial results described below. Pass the Result ID as a parameter to the methods that access the result and partial result of your algorithm. For more details, Algorithms.
Result ID |
Result |
|---|---|
step13Assignments |
Pointer to the
NOTE:
By default, this result is an object of the HomogenNumericTable class, but you can define the result as an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
Partial Result ID |
Result |
|---|---|
step13AssignmentsQueries |
Pointer to the numeric table with 2 columns and arbitrary number of rows containing clusters assigning queries that should be processed on the local node.
NOTE:
By default, this result is an object of the HomogenNumericTable class, but you can define the result as an object of any class derived from NumericTable except for PackedTriangularMatrix, PackedSymmetricMatrix, and CSRNumericTable.
|
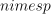 numeric table with the observations to be clustered.
numeric table with the observations to be clustered.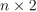 numeric table containing information about observations: identifier of initial block and index in initial block. This information will be required to reconstruct initial blocks after transferring observations among nodes.
numeric table containing information about observations: identifier of initial block and index in initial block. This information will be required to reconstruct initial blocks after transferring observations among nodes.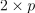 numeric table containing bounding box of input observations: first row contains minimum value of each feature, second row contains maximum value of each feature.
numeric table containing bounding box of input observations: first row contains minimum value of each feature, second row contains maximum value of each feature.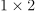 numeric table containing information about split for current iteration of geometric repartitioning.
numeric table containing information about split for current iteration of geometric repartitioning.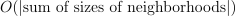 of additional memory, which in worst case can be
of additional memory, which in worst case can be 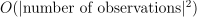 . However, in general, performance may be better.
. However, in general, performance may be better. numeric tables containing identifiers of initial block for halo observations for current node computed on
numeric tables containing identifiers of initial block for halo observations for current node computed on  numeric table with assignments of cluster indices to observations processed on
numeric table with assignments of cluster indices to observations processed on