High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface FPGA IP User Guide
ID
683189
Date
3/29/2024
Public
1. About the High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel® FPGA IP
2. Introduction to High Bandwidth Memory
3. Stratix® 10 HBM2 Architecture
4. Creating and Parameterizing the High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel® FPGA IP
5. Simulating the High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel® FPGA IP
6. High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel® FPGA IP Interface
7. High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel® FPGA IP Controller Performance
8. High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel® FPGA IP User Guide Archives
9. Document Revision History for High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface FPGA IP User Guide
4.2.1. General Parameters for High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel® FPGA IP
4.2.2. FPGA I/O Parameters for High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel® FPGA IP
4.2.3. Controller Parameters for High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel® FPGA IP
4.2.4. Diagnostic Parameters for High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel® FPGA IP
4.2.5. Example Designs Parameters for High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel® FPGA IP
4.2.6. Register Map IP-XACT Support for HBM2 IP
5.1. High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel® FPGA IP Example Design
5.2. Simulating High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel® FPGA IP with ModelSim* and Questa*
5.3. Simulating High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel® FPGA IP with Synopsys VCS*
5.4. Simulating High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel® FPGA IP with Riviera-PRO*
5.5. Simulating High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel® FPGA IP with Cadence Xcelium* Parallel Simulator
5.6. Simulating High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel® FPGA IP for High Efficiency
5.7. Simulating High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface IP Instantiated in Your Project
6.1. High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel® FPGA IP High Level Block Diagram
6.2. High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel® FPGA IP Controller Interface Signals
6.3. User AXI Interface Timing
6.4. User APB Interface Timing
6.5. User-controlled Accesses to the HBM2 Controller
6.6. Soft AXI Switch
7.1. High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) DRAM Bandwidth
7.2. High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel® FPGA IP HBM2 IP Efficiency
7.3. High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel® FPGA IP Latency
7.4. High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel® FPGA IP Timing
7.5. High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel® FPGA IP DRAM Temperature Readout
4.2.4. Diagnostic Parameters for High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel® FPGA IP
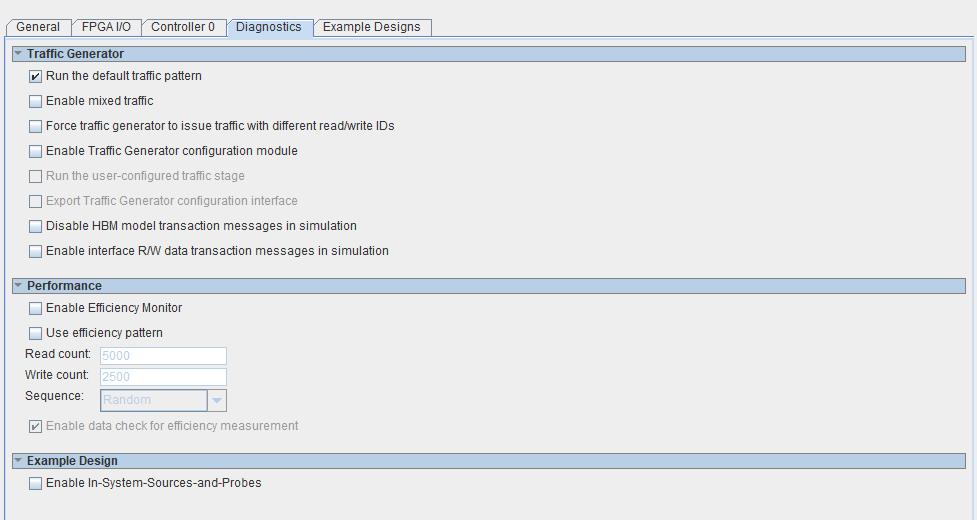
The Diagnostics tab allows you to select traffic options and to enable the efficiency monitor that measures HBM2 controller efficiency during functional simulation.
Figure 10. Diagnostics Tab

| Display Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Run the default traffic pattern | Runs the default traffic pattern after reset. The default traffic pattern consists of multiple stages testing single/block reads and writes using sequential and random addressing. This parameter applies to the AXI user interface only; the Avalon® memory-mapped interface uses the default traffic pattern. |
| Enable mixed traffic | Configures the traffic generator to send out a variety of traffic patterns, including single and block reads/writes, using a mix of sequential and random addressing. If you do not enable this parameter, the traffic generator sends block reads/writes with sequential addressing. This parameter can help you understand the HBM2 interface performance over different traffic patterns. This parameter applies to the AXI user interface only; the Avalon® memory-mapped interface uses the default traffic pattern. |
| Force traffic generator to issue traffic with different read/write IDs | Forces the traffic generator to issue traffic with different read/write IDs regardless of whether the reorder buffer is on. Using different read/write IDs allows the controller to reorder transactions for higher efficiency, but results in data mismatches if you have disabled the reorder buffer and the user logic does not handle read data returning out-of-order. When you do enable the reorder buffer, the traffic generator automatically generates transactions with different IDs.If you do not enable this parameter, the traffic generator does not issue AXI transactions with different read/write IDs, unless you have enabled the reorder buffer. This parameter applies to the AXI user interface only; the Avalon® memory-mapped interface uses the default traffic pattern. |
| Enable Traffic Generator Configuration Module | Enables instantiation of the traffic generator configuration module, which is necessary only if you are creating custom traffic patterns. This parameter applies to the AXI user interface only; the Avalon® memory-mapped interface uses the default traffic pattern. |
| Run the user-configured traffic stage | Runs the user-configured traffic pattern after reset. (You can still reconfigure the traffic generator later.) The traffic generator does not assert a pass or fail status until the Avalon configuration interface configures it and signals it to start. You can perform configuration by connecting to the traffic generator via the EMIF Debug Toolkit or by using custom logic connected to the Avalon-MM configuration slave port on the traffic generator. You can also simulate configuration with the example testbench provided in the altera_hbm_tg_axi_tb.sv file. This parameter applies to the AXI user interface only; the Avalon® memory-mapped interface uses the default traffic pattern. |
| Export Traffic Generator Configuration Interface | Exports an Avalon-MM slave port for configuring the traffic generator. This is necessary only if you are configuring the traffic generator with user-configured traffic. This parameter applies to the AXI user interface only; the Avalon® memory-mapped interface uses the default traffic pattern. |
| Disable HBM model transaction messages in simulation | If enabled, HBM model transaction messages are not displayed in simulation. |
| Enable AXI R/W data transaction messages in simulation | Displays AXI data transaction messages in simulation. |
| Display Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable Efficiency Monitor | Adds an Efficiency Monitor component to the AXI interface of the memory controller. The Efficiency Monitor gathers and reports statistics on the efficiency of the interface during simulation. The Efficiency Monitor is available only in the AXI user interface flow. |
| Use efficiency pattern | The traffic generator generates a high-efficiency concurrent traffic pattern with features integrated in the design example. This parameter applies to the AXI user interface only. |
| Read count | Defines the read count for the traffic generator. The read and write count should be equal, for the validity check to pass. This parameter applies to the AXI user interface only. |
| Write count | Defines the write count for the traffic generator. The read and write count should be equal, for the validity check to pass. This parameter applies to the AXI user interface only. |
| Sequence | Defines the write and read sequence for the traffic generator, with the selection of Random or Sequential. (For best HBM2 efficiency, select Sequential for this parameter.) This parameter applies to the AXI user interface only. |
| Enable data check for efficiency measurement | Enables a data check for soft traffic generator efficiency measurement. This parameter applies to the AXI user interface only. |
| Display Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable in-System-Source-and-Probes | Enables In-System-Sources-and-Probes in the design example for common debug signals such as calibration status or example traffic generator per-bit status. You must enable this parameter if you want to do driver margining. |