GTS AXI Multichannel DMA IP for PCI Express* User Guide
ID
847470
Date
8/25/2025
Public
1. Overview
2. Quick Start Guide
3. Configuring and Generating the GTS AXI Multichannel DMA IP for PCI Express
4. Integrating the IP With Your Application
5. Simulating the IP
6. Validating the IP
7. Known Issues
A. Functional Description
B. Software Programming Model
C. Registers
D. Document Revision History for the GTS AXI Multichannel DMA IP for PCI Express*
2.1.1. Downloading and Installing Quartus® Prime Software
2.1.2. Configuring and Generating the GTS AXI Multichannel DMA IP for PCI Express
2.1.3. Configuring and Generating the GTS AXI Streaming IP for PCI Express
2.1.4. Configuring and Generating the GTS System PLL Clocks IP
2.1.5. Configuring and Generating the GTS Reset Sequencer IP
2.1.6. Configuring and Generating the Reset Release IP
2.1.7. Instantiating and Connecting the IP Interfaces
2.1.8. Simulate, Compile and Validate the Design on Hardware
4.4.1. PCIe AXI-Stream TX Interface (ss_tx_st)
4.4.2. PCIe AXI-Stream RX Interface (ss_rx_st)
4.4.3. Control and Status Register Interface (ss_csr_lite)
4.4.4. Transmit Flow Control Credit Interface (ss_txcrdt)
4.4.5. Configuration Intercept Interface (CII)
4.4.6. Completion Timeout Interface (ss_cplto)
4.4.7. Function Level Reset (FLR) Interface
4.4.8. Control Shadow Interface (ss_ctrlshadow)
4.4.9. Error Interface
4.5.1. H2D AXI-Stream Manager (h2d_st_initatr)
4.5.2. D2H AXI-Stream Subordinate (d2h_st_respndr)
4.5.3. H2D/D2H AXI-MM Manager (dma_mm_initatr)
4.5.4. BAM AXI-MM Manager (bam_mm_initatr)
4.5.5. BAS AXI-MM Subordinate (bas_mm_respndr)
4.5.6. PIO AXI-Lite Manager (pio_lite_initiatr)
4.5.7. HIP Reconfiguration AXI-Lite Subordinate (user_csr_lite)
4.5.8. User Event MSI-X (user_msix)
4.5.9. User Event MSI (user_msi)
4.5.10. User Function Level Reset (user_flr)
4.5.11. User Configuration Intercept Interface
4.5.12. Configuration Slave (cs_lite_respndr)
A.1.1.1. H2D Data Mover
A.1.1.2. D2H Data Mover
A.1.1.3. Descriptors
A.1.1.4. AXI4-Lite PIO Manager
A.1.1.5. AXI-MM Write (H2D) and Read (D2H) Manager
A.1.1.6. AXI-Stream Manager (H2D) and Subordinate (D2H)
A.1.1.7. User MSI-X
A.1.1.8. User Function Level Reset (FLR)
A.1.1.9. Control and Status Registers
B.1.6.1. ifc_api_start
B.1.6.2. ifc_mcdma_port_by_name
B.1.6.3. ifc_qdma_device_get
B.1.6.4. ifc_num_channels_get
B.1.6.5. ifc_qdma_channel_get
B.1.6.6. ifc_qdma_acquire_channels
B.1.6.7. ifc_qdma_release_all_channels
B.1.6.8. ifc_qdma_device_put
B.1.6.9. ifc_qdma_channel_put
B.1.6.10. ifc_qdma_completion_poll
B.1.6.11. ifc_qdma_request_start
B.1.6.12. ifc_qdma_request_prepare
B.1.6.13. ifc_qdma_descq_queue_batch_load
B.1.6.14. ifc_qdma_request_submit
B.1.6.15. ifc_qdma_pio_read32
B.1.6.16. ifc_qdma_pio_write32
B.1.6.17. ifc_qdma_pio_read64
B.1.6.18. ifc_qdma_pio_write64
B.1.6.19. ifc_qdma_pio_read128
B.1.6.20. ifc_qdma_pio_write128
B.1.6.21. ifc_qdma_pio_read256
B.1.6.22. ifc_qdma_pio_write256
B.1.6.23. ifc_request_malloc
B.1.6.24. ifc_request_free
B.1.6.25. ifc_app_stop
B.1.6.26. ifc_qdma_poll_init
B.1.6.27. ifc_qdma_poll_add
B.1.6.28. ifc_qdma_poll_wait
B.1.6.29. ifc_mcdma_port_by_name
6.3.5.6. BAS Test
Note: For the Traffic Generator/Checker design example, you must disable the MSI-X parameter, IFC_QDMA_MSIX_ENABLE, in the Custom Driver's p0_software/kernel/common/include/mcdma_ip_params.h file if MSI-X is not enabled in the IP Parameter Editor. By default, the Custom Driver software parameter is enabled and MSI-X is disabled in the IP. This mismatch prevents the ifc_uio kernel module from being loaded.
For BAS x4:
BAS x4 supports a burst length of 32 by default. In the file perfq_app.h (p0_software/user/cli/perfq_app/perfq_app.h):
#define IFC_MCDMA_BAS_X4_BURST_LENGTH 32
To enable BAS, set the following software flag in p0_software/user/common/mk/common.mk):
__cflags += -DIFC_MCDMA_BAS_EN
Note: Refer to Design Example Variants and BAR Mappings for BAR mappings information.
Note: A BAS test failure may be observed when the request size exceeds 2 kB. A fix is planned in a future release.
Commands:
To verify the write operation:
$ sudo ./cli/perfq_app/perfq_app -b 0000:08:00.0 -s 512 -e -t --bar=<bar number>
Figure 38. Write Operation Results
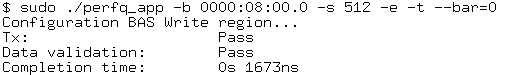

To verify the read operation:
$ sudo ./cli/perfq_app/perfq_app -b 0000:01:00.0 -s 512 -e -r --bar=<bar number>
Figure 39. Read Operation Results
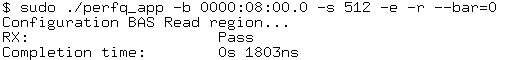

To verify the write and read operations:
$ sudo ./cli/perfq_app/perfq_app -b 0000:01:00.0 -s 512 -e -z --bar=<bar number>
Figure 40. Write and Read Operation Results
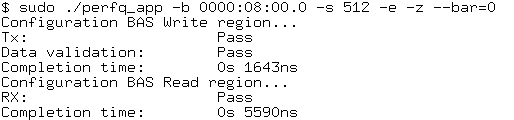

Performance test:
$ sudo ./cli/perfq_app/perfq_app -b 0000:08:00.0 -s 16384 --bas_perf -z --bar=<bar number>
Figure 41. Performance Test Results
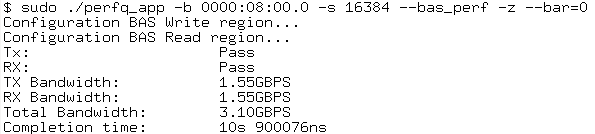

Note: You may not be able to proceed with the -z option. Add the flag #define IFC_QDMA_INTF_ST in user/common/include/mcdma_ip_params.h as a workaround to make it work.
Note: In the case of VFIO, to run BAM+BAS+MCDMA, you need to create at least three VFs and run on each VF respectively. If you try to use one VF to run BAM+BAS+MCDMA simultaneously in the case of VFIO, it gives a "resource busy" prompt.