GTS AXI Multichannel DMA IP for PCI Express* User Guide
5.1.1. AXI-S Device-side Packet Loopback Design Example
In this device-side packet loopback design example, the host initially sets up specific memory locations within its memory. Data from the host memory is then transferred to the device-side memory by the GTS AXI Multichannel DMA IP through Host-to-Device (H2D) DMA operations. Subsequently, the IP loops this data back to the host memory using Device-to-Host (D2H) DMA operations.
Additionally, the design example enables the AXI-Lite PIO master, which bypasses the DMA path. This allows the application running in the host to perform single, non-bursting register read/write operations with the on-chip memory block.
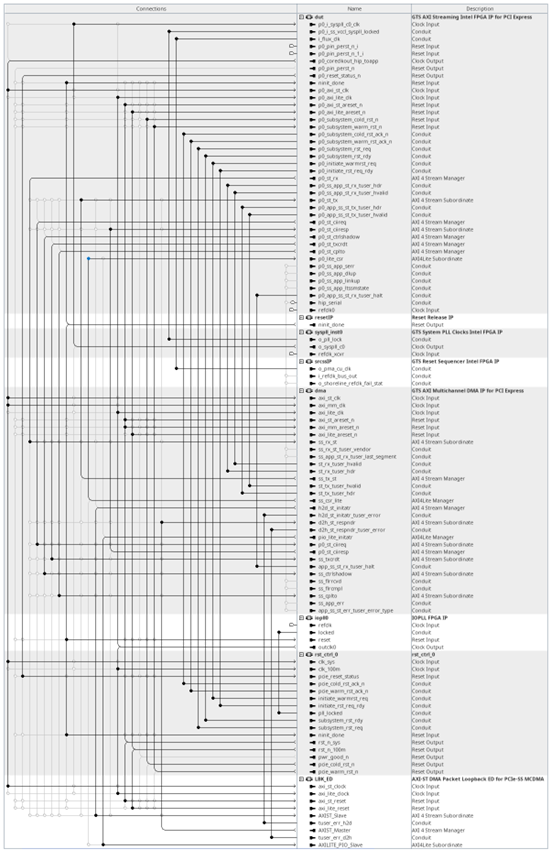
| Design Components | Description |
|---|---|
| GTS AXI Streaming FPGA IP for PCI Express | Incorporates PCI Express (PCIe) into your design utilizing an advanced PCIe hardened protocol stack, which encompasses the transaction, data link, and physical layers. It also includes optional components like Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) for virtualization applications that demand high-bandwidth data transfer to and from the host memory. This component converts the PCIe serial link transfer to the AXI Stream interface and directs the TLP data received to the GTS AXI Multichannel DMA IP. |
| GTS AXI Multichannel DMA IP for PCI Express | Facilitates efficient data transfer between the local FPGA and the host through multiple DMA channels over the PCIe link. Each DMA channel comprises a host-to-device (H2D) and a device-to-host (D2H) queue pair, operating on descriptor-based queues established by driver software for data transfer. It is engineered to support standalone Endpoint or Rootport functionality, offering AXI-S and AXI-MM interfaces to the user logic. |
| GTS System PLL Clocks IP | This IP is required for PCIe interface implementation on Agilex™ 5 devices to configure the reference clock for the System PLL and provides the clock signal for the p<n>_i_syspll_c0_clk of the GTS AXI Streaming IP.
Note: For more information, refer to the Implementing the GTS System PLL Clocks IP section in the GTS Transceiver PHY User Guide.
|
| GTS Reset Sequencer IP | This IP must be instantiated for each Agilex™ 5 FPGA side that uses transceivers for simulation and proper device operation. It provides the PMA Control Unit clock to the i_flux_clk clock of the GTS AXI Streaming IP.
Note: For more information, refer to the Implementing the GTS Reset Sequencer IP section in the GTS Transceiver PHY User Guide.
|
| Reset Release IP | This IP holds a control circuit in reset until the device has fully entered user mode. The FPGA asserts the INIT_DONE output to signal that the device is in user mode. It is required when using the GTS AXI Streaming IP.
Note: For more information on the Reset Release IP, refer to the Device Configuration User Guide: Agilex™ 5 FPGAs and SoCs.
|
| AXI-S DMA Packet Loopback ED for PCIe-SS MCDMA | This design example module implements the device-side memory and allows data from the host memory to transfer to it by the AXI Multichannel DMA IP through Host-to-Device (H2D) DMA operations. Subsequently, the IP loops this data back to the host memory using Device-to-Host (D2H) DMA operations. In addition, it provides an AXI-Lite PIO interface that allows the application to perform single, non-bursting register read/write operations with the on-chip memory block. |
| rst_ctrl_0 | This module handles the reset and handshake signals of the GTS AXI Streaming IP for graceful entry and exit for each of the resets (cold, warm, etc.) especially when initiated by the host system. |
| IOPLL FPGA IP | This IP is required to configure the settings of the Agilex™ 5 I/O PLL to provide a 100 MHz clock signal for the AXI-Lite interface in the design. |
The AXI-S device-side packet loopback design example includes the following components: