AN 999: Drive-on-Chip with Functional Safety Design Example: Agilex™ 7 Devices
4.2. HPS Safety Subsystem
The HPS in this design boots a custom version of Linux based on Yocto to implement the HPS safety channel. Internally, the subsystem comprises the HPS, EMIF for external DDR4 on the development kit, and lightweight and full HPS-to-FPGA bridges. The lightweight bridge accesses blocks related to the drive-on -chip application (drives, motor models, encoders, control memory, GUI memories). The full HPS-to-FPGA bridge connects safety-related blocks (shared safety memory, FPGA safety blocks). The HPS controls the timer that controls the safety function, reads and writes safety payloads, and cleans the FPGA channel control registers if necessary.
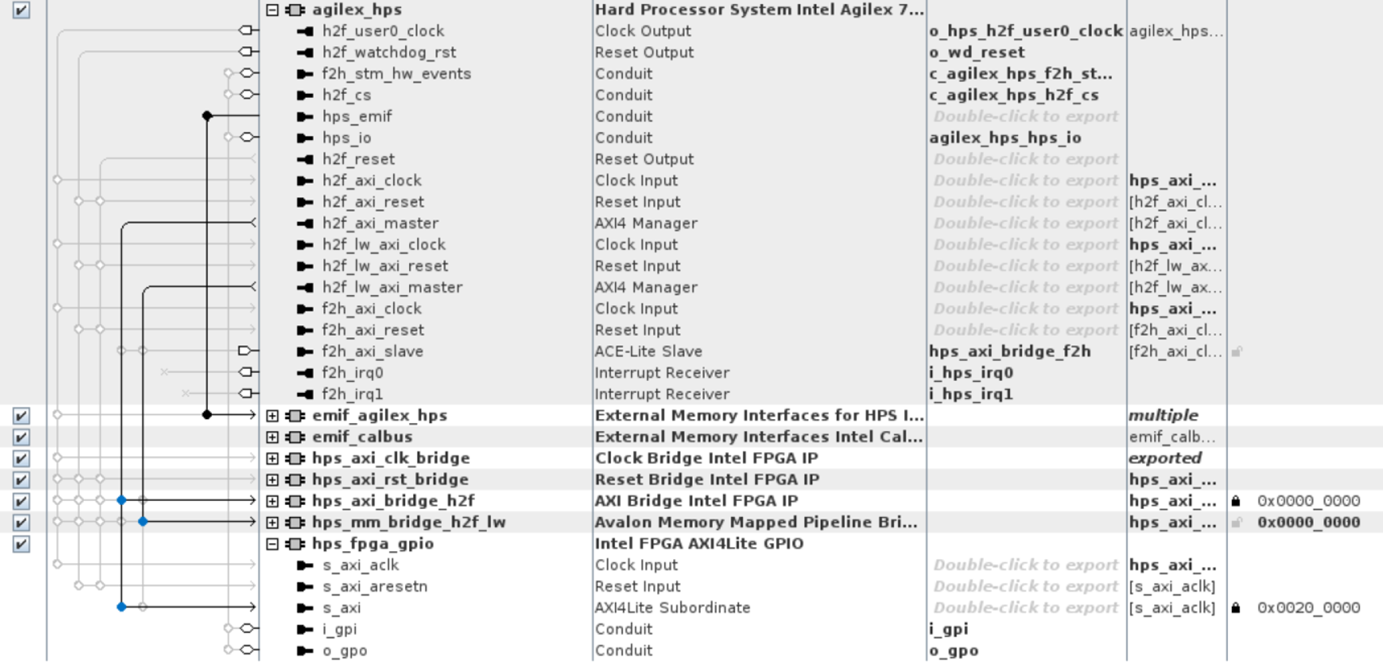
This design connects the HPS to the block hps_fpga_gpio for the inputs for the external safety logic if any of the safe state conditions in the HPS safety channel is asserted.
This design subsystem connects the HPS to the hps_fpga_gpio block. The outputs from hps_fpga_gpio are inputs the external safety logic. Asserting the signals from hps_fpga_gpio triggers the safe state condition from the HPS safety channel.