AN 999: Drive-on-Chip with Functional Safety Design Example: Agilex™ 7 Devices
ID
823627
Date
7/04/2024
Public
1. About the Drive-on-Chip with Functional Safety Design Example for Agilex™ 7 Devices
2. Getting Started
3. Rebuilding the Drive-on-Chip Design
4. Functional Description of the Drive-On-Chip with Functional Safety Design Example for Agilex 7 Devices
5. HPS Channel Safety Software
6. Drive-on-Chip Design Recommendations and Disclaimers
7. Document Revision History for AN 999: Drive-on-Chip with Functional Safety Design Example for Agilex 7 Devices
2.1. Software Requirements for the Drive-On-Chip with Functional Safety Design Example for Agilex 7 Devices
2.2. Hardware Requirements for the Safe Drive-On-Chip with Functional Safety Design Example for Agilex 7 Devices
2.3. Downloading and Installing the Design
2.4. Installing Python
2.5. Creating an SD Card Image
2.6. Setting Up your Development Board for the Drive-On-Chip with Functional Safety Design Example for Agilex 7 Devices
2.7. Debugging and Monitoring the Drive-On-Chip with Functional Safety Design Example for Agilex 7 Devices with Python GUI
2.8. Looking into the Drive-On-Chip Output
3.1. Generating the Platform Designer System
3.2. Generating and Building the NiosV/g BSP for the Drive-On-Chip Design Example
3.3. Compiling the Hardware in the Intel Quartus Prime Software
3.4. Modifying the Motor Control Software Application
3.5. Generating .jic and .rbf files After Hardware Modifications
3.6. Recreate an SD Card Image
3.7. Modifying the HPS Safety Function Application
5.2.6. Core Isolation and Core Affinity
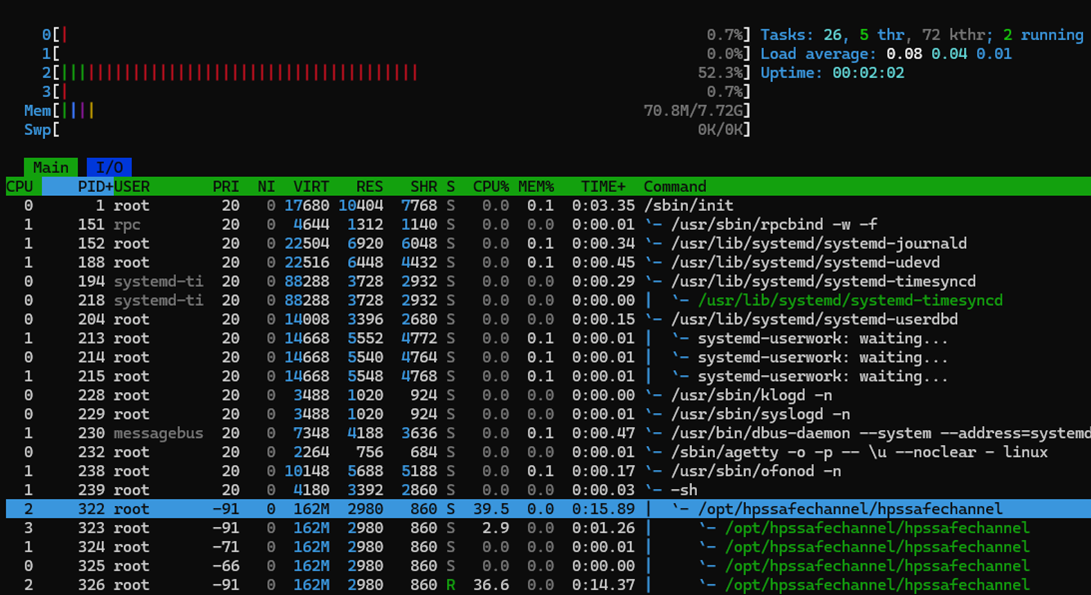
This system isolates design cores 2 and 3 for timing critical functions.. Core 2 runs the HPS safety function and serves the interrupt generated by the Interval timer. Core 3 is for the thread that does speed estimation. The Linux Kernel scheduler allocates other threads to core 1 and 0. Core isolation and core affinity ensures the timing critical parts of the application meet their deadlines (1 ms, safety response time). You can check the core allocation using the tool htop.
.
Figure 28. HTOP View The figure shows the intended core allocation for HPS safe application threads. The figure shows no other kernel or user-space application runs in core 2 or 3, only core 0 and 1 are available for the remainder of the applications and services.