Intel® Quartus® Prime Pro Edition User Guide: Power Analysis and Optimization
ID
683174
Date
6/22/2022
Public
A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
1.3.2.1. Using Simulation Signal Activity Data in Power Analysis
1.3.2.2. Signal Activities from RTL (Functional) Simulation, Supplemented by Vectorless Estimation
1.3.2.3. Signal Activities from Vectorless Estimation and User-Supplied Input Pin Activities
1.3.2.4. Signal Activities from User Defaults Only
1.5.1. Complete Design Simulation Power Analysis Flow
1.5.2. Modular Design Simulation Power Analysis Flow
1.5.3. Multiple Simulation Power Analysis Flow
1.5.4. Overlapping Simulation Power Analysis Flow
1.5.5. Partial Design Simulation Power Analysis Flow
1.5.6. Vectorless Estimation Power Analysis Flow
2.4.1. Clock Power Management
2.4.2. Pipelining and Retiming
2.4.3. Architectural Optimization
2.4.4. I/O Power Guidelines
2.4.5. Dynamically Controlled On-Chip Terminations (OCT)
2.4.6. Memory Optimization (M20K/MLAB)
2.4.7. DDR Memory Controller Settings
2.4.8. DSP Implementation
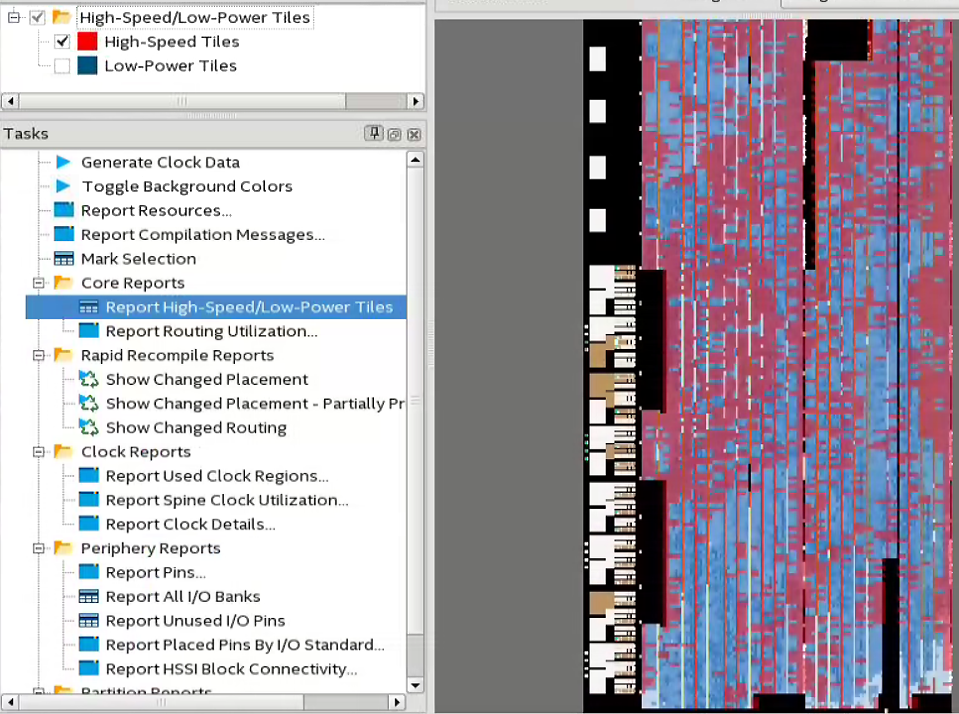
2.4.9. Reducing High-Speed Tile (HST) Usage
2.4.10. Unused Transceiver Channels
2.4.11. Periphery Power reduction XCVR Settings
2.4.9. Reducing High-Speed Tile (HST) Usage
High-Speed tiles are available in the Intel® Arria® 10 design family.
- In the Advanced Fitter Settings pane, The Programmable Power Technology Optimization logic option controls how the fitter configures tiles to operate in high-speed mode or low-power mode. Select Minimize Power Only.
Figure 37. Programmable Power Technology Optimization
- Identify entity modules that use HST by plotting entity modules and HST heatmap on the Chip Planner and modify the floorplan to reduce usage.
Figure 38. Entity Modules and HST Heatmap on the Chip Planner