Developer Reference for Intel® oneAPI Math Kernel Library for Fortran
A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
?gges
Computes the generalized eigenvalues, Schur form, and the left and/or right Schur vectors for a pair of nonsymmetric matrices.
call sgges(jobvsl, jobvsr, sort, selctg, n, a, lda, b, ldb, sdim, alphar, alphai, beta, vsl, ldvsl, vsr, ldvsr, work, lwork, bwork, info)
call dgges(jobvsl, jobvsr, sort, selctg, n, a, lda, b, ldb, sdim, alphar, alphai, beta, vsl, ldvsl, vsr, ldvsr, work, lwork, bwork, info)
call cgges(jobvsl, jobvsr, sort, selctg, n, a, lda, b, ldb, sdim, alpha, beta, vsl, ldvsl, vsr, ldvsr, work, lwork, rwork, bwork, info)
call zgges(jobvsl, jobvsr, sort, selctg, n, a, lda, b, ldb, sdim, alpha, beta, vsl, ldvsl, vsr, ldvsr, work, lwork, rwork, bwork, info)
call gges(a, b, alphar, alphai, beta [,vsl] [,vsr] [,select] [,sdim] [,info])
call gges(a, b, alpha, beta [, vsl] [,vsr] [,select] [,sdim] [,info])
- mkl.fi, lapack.f90
The ?gges routine computes the generalized eigenvalues, the generalized real/complex Schur form (S,T), optionally, the left and/or right matrices of Schur vectors (vsl and vsr) for a pair of n-by-n real/complex nonsymmetric matrices (A,B). This gives the generalized Schur factorization
(A,B) = ( vsl*S *vsrH, vsl*T*vsrH )
Optionally, it also orders the eigenvalues so that a selected cluster of eigenvalues appears in the leading diagonal blocks of the upper quasi-triangular matrix S and the upper triangular matrix T. The leading columns of vsl and vsr then form an orthonormal/unitary basis for the corresponding left and right eigenspaces (deflating subspaces).
If only the generalized eigenvalues are needed, use the driver ggev instead, which is faster.
A generalized eigenvalue for a pair of matrices (A,B) is a scalar w or a ratio alpha / beta = w, such that A - w*B is singular. It is usually represented as the pair (alpha, beta), as there is a reasonable interpretation for beta=0 or for both being zero. A pair of matrices (S,T) is in the generalized real Schur form if T is upper triangular with non-negative diagonal and S is block upper triangular with 1-by-1 and 2-by-2 blocks. 1-by-1 blocks correspond to real generalized eigenvalues, while 2-by-2 blocks of S are "standardized" by making the corresponding elements of T have the form:
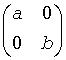
and the pair of corresponding 2-by-2 blocks in S and T will have a complex conjugate pair of generalized eigenvalues. A pair of matrices (S,T) is in generalized complex Schur form if S and T are upper triangular and, in addition, the diagonal of T are non-negative real numbers.
The ?gges routine replaces the deprecated ?gegs routine.
- jobvsl
-
CHARACTER*1. Must be 'N' or 'V'.
If jobvsl = 'N', then the left Schur vectors are not computed.
If jobvsl = 'V', then the left Schur vectors are computed.
- jobvsr
-
CHARACTER*1. Must be 'N' or 'V'.
If jobvsr = 'N', then the right Schur vectors are not computed.
If jobvsr = 'V', then the right Schur vectors are computed.
- sort
-
CHARACTER*1. Must be 'N' or 'S'. Specifies whether or not to order the eigenvalues on the diagonal of the generalized Schur form.
If sort = 'N', then eigenvalues are not ordered.
If sort = 'S', eigenvalues are ordered (see selctg).
- selctg
-
LOGICAL FUNCTION of three REAL arguments for real flavors.
LOGICAL FUNCTION of two COMPLEX arguments for complex flavors.
selctg must be declared EXTERNAL in the calling subroutine.
If sort = 'S', selctg is used to select eigenvalues to sort to the top left of the Schur form.
If sort = 'N', selctg is not referenced.
For real flavors:
An eigenvalue (alphar(j) + alphai(j))/beta(j) is selected if selctg(alphar(j), alphai(j), beta(j)) is true; that is, if either one of a complex conjugate pair of eigenvalues is selected, then both complex eigenvalues are selected.
Note that in the ill-conditioned case, a selected complex eigenvalue may no longer satisfy selctg(alphar(j), alphai(j), beta(j)) = .TRUE. after ordering. In this case info is set to n+2 .
For complex flavors:
An eigenvalue alpha(j) / beta(j) is selected if selctg(alpha(j), beta(j)) is true.
Note that a selected complex eigenvalue may no longer satisfy selctg(alpha(j), beta(j)) = .TRUE. after ordering, since ordering may change the value of complex eigenvalues (especially if the eigenvalue is ill-conditioned); in this case info is set to n+2 (see info below).
- n
-
INTEGER. The order of the matrices A, B, vsl, and vsr (n≥ 0).
- a, b, work
-
REAL for sgges
DOUBLE PRECISION for dgges
COMPLEX for cgges
DOUBLE COMPLEX for zgges.
Arrays:
a(lda,*) is an array containing the n-by-n matrix A (first of the pair of matrices).
The second dimension of a must be at least max(1, n).
b(ldb,*) is an array containing the n-by-n matrix B (second of the pair of matrices).
The second dimension of b must be at least max(1, n).
work is a workspace array, its dimension max(1, lwork).
- lda
-
INTEGER. The leading dimension of the array a. Must be at least max(1, n).
- ldb
-
INTEGER. The leading dimension of the array b. Must be at least max(1, n).
- ldvsl, ldvsr
-
INTEGER. The leading dimensions of the output matrices vsl and vsr, respectively. Constraints:
ldvsl≥ 1. If jobvsl = 'V', ldvsl≥ max(1, n).
ldvsr≥ 1. If jobvsr = 'V', ldvsr≥ max(1, n).
- lwork
-
INTEGER.
The dimension of the array work.
lwork≥ max(1, 8n+16) for real flavors;
lwork≥ max(1, 2n) for complex flavors.
For good performance, lwork must generally be larger.
If lwork = -1, then a workspace query is assumed; the routine only calculates the optimal size of the work array, returns this value as the first entry of the work array, and no error message related to lwork is issued by xerbla.
- rwork
-
REAL for cgges
DOUBLE PRECISION for zgges
Workspace array, size at least max(1, 8n).
This array is used in complex flavors only.
- bwork
-
LOGICAL.
Workspace array, size at least max(1, n).
Not referenced if sort = 'N'.
- a
-
On exit, this array has been overwritten by its generalized Schur form S.
- b
-
On exit, this array has been overwritten by its generalized Schur form T.
- sdim
-
INTEGER.
If sort = 'N', sdim= 0.
If sort = 'S', sdim is equal to the number of eigenvalues (after sorting) for which selctg is true.
Note that for real flavors complex conjugate pairs for which selctg is true for either eigenvalue count as 2.
- alphar, alphai
-
REAL for sgges;
DOUBLE PRECISION for dgges.
Arrays, size at least max(1, n) each. Contain values that form generalized eigenvalues in real flavors.
See beta.
- alpha
-
COMPLEX for cgges;
DOUBLE COMPLEX for zgges.
Array, size at least max(1, n). Contain values that form generalized eigenvalues in complex flavors. See beta.
- beta
-
REAL for sgges
DOUBLE PRECISION for dgges
COMPLEX for cgges
DOUBLE COMPLEX for zgges.
Array, size at least max(1, n).
For real flavors:
On exit, (alphar(j) + alphai(j)*i)/beta(j), j=1,..., n, will be the generalized eigenvalues.
alphar(j) + alphai(j)*i and beta(j), j=1,..., n are the diagonals of the complex Schur form (S,T) that would result if the 2-by-2 diagonal blocks of the real generalized Schur form of (A,B) were further reduced to triangular form using complex unitary transformations. If alphai(j) is zero, then the j-th eigenvalue is real; if positive, then the j-th and (j+1)-st eigenvalues are a complex conjugate pair, with alphai(j+1) negative.
For complex flavors:
On exit, alpha(j)/beta(j), j=1,..., n, will be the generalized eigenvalues. alphaalpha(j) and beta(j), j=1,..., n are the diagonals of the complex Schur form (S,T) output by cgges/zgges. The beta(j) will be non-negative real.
See also Application Notes below. - vsl, vsr
-
REAL for sgges
DOUBLE PRECISION for dgges
COMPLEX for cgges
DOUBLE COMPLEX for zgges.
Arrays:
vsl(ldvsl,*), the second dimension of vsl must be at least max(1, n).
If jobvsl = 'V', this array will contain the left Schur vectors.
If jobvsl = 'N', vsl is not referenced.
vsr(ldvsr,*), the second dimension of vsr must be at least max(1, n).
If jobvsr = 'V', this array will contain the right Schur vectors.
If jobvsr = 'N', vsr is not referenced.
- work(1)
-
On exit, if info = 0, then work(1) returns the required minimal size of lwork.
- info
-
INTEGER.
If info = 0, the execution is successful.
If info = -i, the ith parameter had an illegal value.
If info = i, and
i≤n:
the QZ iteration failed. (A, B) is not in Schur form, but alphar(j), alphai(j) (for real flavors), or alpha(j) (for complex flavors), and beta(j), j=info+1,..., n should be correct.
i > n: errors that usually indicate LAPACK problems:
i = n+1: other than QZ iteration failed in hgeqz;
i = n+2: after reordering, roundoff changed values of some complex eigenvalues so that leading eigenvalues in the generalized Schur form no longer satisfy selctg = .TRUE.. This could also be caused due to scaling;
i = n+3: reordering failed in tgsen.
Routines in Fortran 95 interface have fewer arguments in the calling sequence than their FORTRAN 77 counterparts. For general conventions applied to skip redundant or restorable arguments, see LAPACK 95 Interface Conventions.
Specific details for the routine gges interface are the following:
- a
-
Holds the matrix A of size (n, n).
- b
-
Holds the matrix B of size (n, n).
- alphar
-
Holds the vector of length n. Used in real flavors only.
- alphai
-
Holds the vector of length n. Used in real flavors only.
- alpha
-
Holds the vector of length n. Used in complex flavors only.
- beta
-
Holds the vector of length n.
- vsl
-
Holds the matrix VSL of size (n, n).
- vsr
-
Holds the matrix VSR of size (n, n).
- jobvsl
-
Restored based on the presence of the argument vsl as follows:
jobvsl = 'V', if vsl is present,
jobvsl = 'N', if vsl is omitted.
- jobvsr
-
Restored based on the presence of the argument vsr as follows:
jobvsr = 'V', if vsr is present,
jobvsr = 'N', if vsr is omitted.
- sort
-
Restored based on the presence of the argument select as follows:
sort = 'S', if select is present,
sort = 'N', if select is omitted.
If you are in doubt how much workspace to supply, use a generous value of lwork for the first run or set lwork = -1.
If you choose the first option and set any of admissible lwork sizes, which is no less than the minimal value described, the routine completes the task, though probably not so fast as with a recommended workspace, and provides the recommended workspace in the first element of the corresponding array work on exit. Use this value (work(1)) for subsequent runs.
If you set lwork = -1, the routine returns immediately and provides the recommended workspace in the first element of the corresponding array (work). This operation is called a workspace query.
Note that if you set lwork to less than the minimal required value and not -1, the routine returns immediately with an error exit and does not provide any information on the recommended workspace.
The quotients alphar(j)/beta(j) and alphai(j)/beta(j) may easily over- or underflow, and beta(j) may even be zero. Thus, you should avoid simply computing the ratio. However, alphar and alphai will be always less than and usually comparable with norm(A) in magnitude, and beta always less than and usually comparable with norm(B).