Intel® Hyperflex™ Architecture High-Performance Design Handbook
ID
683353
Date
12/08/2023
Public
A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
Answers to Top FAQs
1. Intel® Hyperflex™ FPGA Architecture Introduction
2. Intel® Hyperflex™ Architecture RTL Design Guidelines
3. Compiling Intel® Hyperflex™ Architecture Designs
4. Design Example Walk-Through
5. Retiming Restrictions and Workarounds
6. Optimization Example
7. Intel® Hyperflex™ Architecture Porting Guidelines
8. Appendices
9. Intel® Hyperflex™ Architecture High-Performance Design Handbook Archive
10. Intel® Hyperflex™ Architecture High-Performance Design Handbook Revision History
2.4.2.1. High-Speed Clock Domains
2.4.2.2. Restructuring Loops
2.4.2.3. Control Signal Backpressure
2.4.2.4. Flow Control with FIFO Status Signals
2.4.2.5. Flow Control with Skid Buffers
2.4.2.6. Read-Modify-Write Memory
2.4.2.7. Counters and Accumulators
2.4.2.8. State Machines
2.4.2.9. Memory
2.4.2.10. DSP Blocks
2.4.2.11. General Logic
2.4.2.12. Modulus and Division
2.4.2.13. Resets
2.4.2.14. Hardware Re-use
2.4.2.15. Algorithmic Requirements
2.4.2.16. FIFOs
2.4.2.17. Ternary Adders
2.4.2.9.1. Intel® Hyperflex™ Architecture True Dual-Port Memory
2.4.2.9.2. Use Simple Dual-Port Memories
2.4.2.9.3. Intel® Hyperflex™ Architecture Simple Dual-Port Memory Example
Simple Dual-Port RAM Inference
True Dual-Port RAM Behavior Emulation
2.4.2.9.4. Memory Mixed Port Width Ratio Limits
2.4.2.9.5. Unregistered RAM Outputs
5.2.1. Insufficient Registers
5.2.2. Short Path/Long Path
5.2.3. Fast Forward Limit
5.2.4. Loops
5.2.5. One Critical Chain per Clock Domain
5.2.6. Critical Chains in Related Clock Groups
5.2.7. Complex Critical Chains
5.2.8. Extend to locatable node
5.2.9. Domain Boundary Entry and Domain Boundary Exit
5.2.10. Critical Chains with Dual Clock Memories
5.2.11. Critical Chain Bits and Buses
5.2.12. Delay Lines
2.4.2.9.3. Intel® Hyperflex™ Architecture Simple Dual-Port Memory Example
Using two simple dual-port memories can double the use of M20K blocks in the device. However, this memory structure can perform at a frequency up to 1 GHz. This frequency is not possible when using true dual-port memory with independent clocks in Intel® Hyperflex™ architecture FPGAs.
Figure 74. Simple Dual-Port Memory Implementation
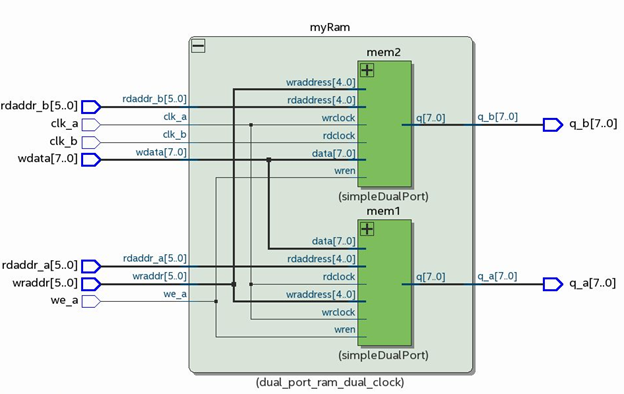

You can achieve similar frequency results by inferring simple dual-port memory in RTL, rather than by instantiation in the Intel® Quartus® Prime IP parameter editor.
Simple Dual-Port RAM Inference
module simple_dual_port_ram_with_SDPs #(parameter DATA_WIDTH=8, parameter ADDR_WIDTH=6) ( input [(DATA_WIDTH-1):0] wrdata, input [(ADDR_WIDTH-1):0] wraddr, rdaddr, input we_a, wrclock, rdclock, output reg [(DATA_WIDTH-1):0] q_a ); // Declare the RAM variable reg [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] ram[2**ADDR_WIDTH-1:0]; always @ (posedge wrclock) begin // Port A is for writing only if (we_a) begin ram[wraddr] <= wrdata; end end always @ (posedge rdclock) begin // Port B is for reading only begin q_a <= ram[rdaddr]; end end endmodule
True Dual-Port RAM Behavior Emulation
module test (wrdata, wraddr, rdaddr_a, rdaddr_b, clk_a, clk_b, we_a, q_a, q_b); input [7:0] wrdata; input clk_a, clk_b, we_a; input [5:0] wraddr, rdaddr_a, rdaddr_b; output [7:0] q_a, q_b; simple_dual_port_ram_with_SDPs myRam1 ( .wrdata(wrdata), .wraddr(wraddr), .rdaddr(rdaddr_a), .we_a(we_a), .wrclock(clk_a), .rdclock(clk_b), .q_a(q_a) ); simple_dual_port_ram_with_SDPs myRam2 ( .wrdata(wrdata), .wraddr(wraddr), .rdaddr(rdaddr_b), .we_a(we_a), .wrclock(clk_a), .rdclock(clk_a), .q_a(q_b) ); endmodule