Intel® High Level Synthesis Compiler Standard Edition: Reference Manual
6. Loops in Components
Loop Pipelining
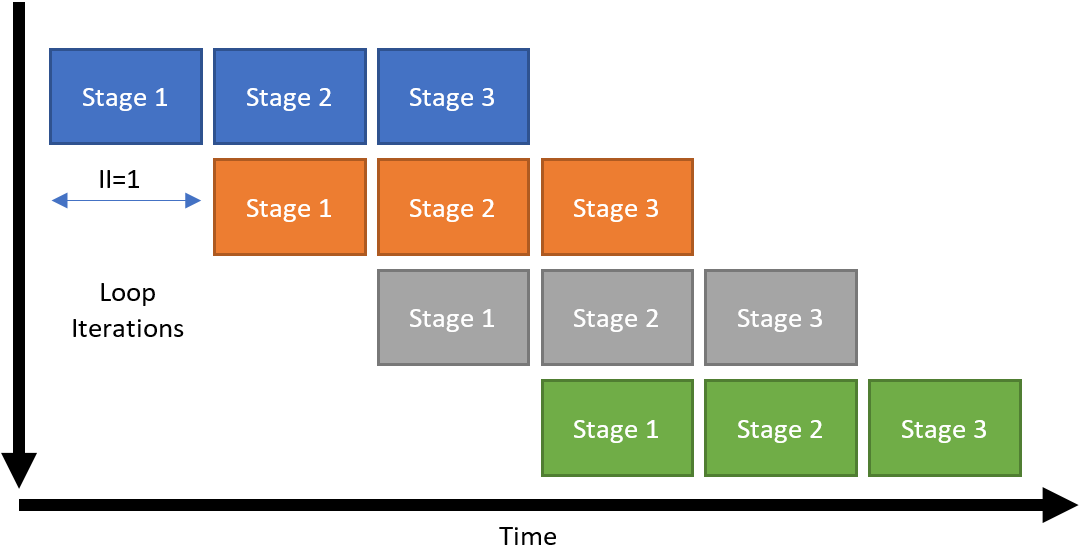
There are some cases where pipelining is not possible at all. In other cases, a new iteration of the loop cannot start until N cycles after the previous iteration.
The number of cycles for which a loop iteration must wait before it can start is called the initiation interval (II) of the loop. This loop pipelining status is captured in the high level design report (report.html). In general, an II of 1 is desirable.
A common case where II > 1 is when a part of the loop depends in some way on the results of the previous iteration of the same loop. The circuit must wait for these loop-carried dependencies to be resolved before starting a new iteration of the loop. These loop-carried dependencies are indicated in the optimization report.
In the case of nested loops, II > 1 for an outer loop is not considered a significant performance limiter if a critical inner loop carries out the majority of the work. One common performance limiter is if the HLS compiler cannot statically compute the trip count of an inner loop (for example, a variable inner loop trip count). Without a known trip count, the compiler cannot pipeline the outer loop.
For more information about loop pipelining, see Pipeline Loops in Intel® High Level Synthesis Compiler Best Practices Guide.
Compiler Pragmas Controlling Loop Pipelining
The Intel® HLS Compiler has several pragmas that you can specify in your code to control how the compiler pipelines your loops.
| Incorrect (produces a compile-time error) | Correct |
|---|---|
|
|
| Pragma | Description |
|---|---|
| ii | Forces a loop to have a loop initiation interval (II) of a specified value. |
| ivdep | Ignores memory dependencies between iterations of this loop. |
| loop_coalesce | Tries to fuse all loops nested within this loop into a single loop. |
| max_concurrency | Limits the number of iterations of a loop that can simultaneously execute at any time. |
| unroll | Unrolls the loop completely or by a number of times. |