2.1. Starting the Flash Programmer GUI
2.2. Specifying your Flash Programmer Settings
2.3. Working with Flash Programmer Settings Files
2.4. Setting the Hardware Connection
2.5. Checking System ID and System Timestamp
2.6. Generating Flash Files and Programming Flash Memory
2.7. Document Revision History for Using the Flash Programmer GUI
B.1. Overview
B.2. Start Button Grayed Out in the Flash Programmer GUI
B.3. 'No Nios® II Processors Available' Error
B.4. 'No CFI Table Found' Error
B.5. 'No EPCS Registers Found' Error
B.6. 'System Does Not Have Any Flash Memory' Error
B.7. 'Reading System ID at Address 0x<address>: FAIL' Error
B.8. 'Base Address Not Aligned on Size of Device' Error
B.9. Document Revision History for Troubleshooting
1.3. How the Flash Programmer Works
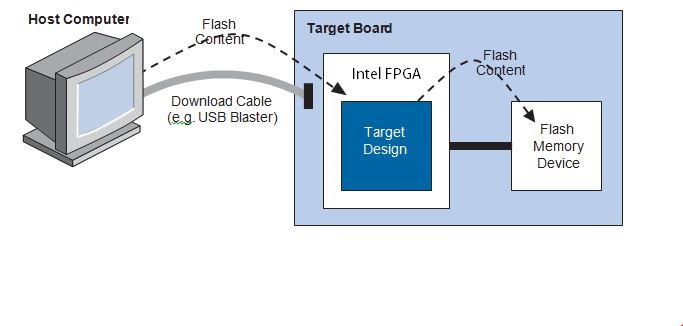
The Nios® II Flash Programmer has two parts, the host and the target, as shown in the following figure. The host portion runs on your computer. It sends flash programming files and programming instructions over a download cable to the target. The target portion is a hardware design, running in the FPGA. The target portion accepts the programming data—flash content and required information about the target flash memory device—sent by the host, and follows the instructions to write data to the flash memory device.
Figure 1. How the Nios® II Flash Programmer Works