1. Nios II Custom Instruction Overview
2. Custom Instruction Hardware Interface
3. Custom Instruction Software Interface
4. Design Example: Cyclic Redundancy Check
5. Introduction to Nios® II Floating Point Custom Instructions
6. Nios II Floating Point Hardware 2 Component
7. Nios® II Floating Point Hardware (FPH1) Component
8. Document Revision History for Nios II Custom Instruction User Guide
4.1.1. Setting up the Environment for the CRC Example Design
4.1.2. Opening the Component Editor
4.1.3. Specifying the Custom Instruction Component Type
4.1.4. Displaying the Custom Instruction Block Symbol
4.1.5. Adding the CRC Custom Instruction HDL Files
4.1.6. Configuring the Custom Instruction Parameter Type
4.1.7. Setting Up the CRC Custom Instruction Interfaces
4.1.8. Configuring the Custom Instruction Signal Type
4.1.9. Saving and Adding the CRC Custom Instruction
4.1.10. Generating and Compiling the CRC Example System
6.1. Overview of the Floating Point Hardware 2 Component
6.2. Floating Point Hardware 2 IEEE 754 Compliance
6.3. IEEE 754 Exception Conditions with FPH2
6.4. Floating Point Hardware 2 Operations
6.5. Building the FPH2 Example Hardware
6.6. Building the FPH2 Example Software
6.7. FPH2 Implementation of GCC Options
6.8. Nios II FPH2 and the Newlib Library
6.9. C Macros for round(), fmins(), and fmaxs()
4.1.6. Configuring the Custom Instruction Parameter Type
To configure the custom instruction parameter type, follow these steps:
- Click Next to display the Parameters tab. The parameters in the .v files are displayed.
Figure 16. Custom Instruction Parameters
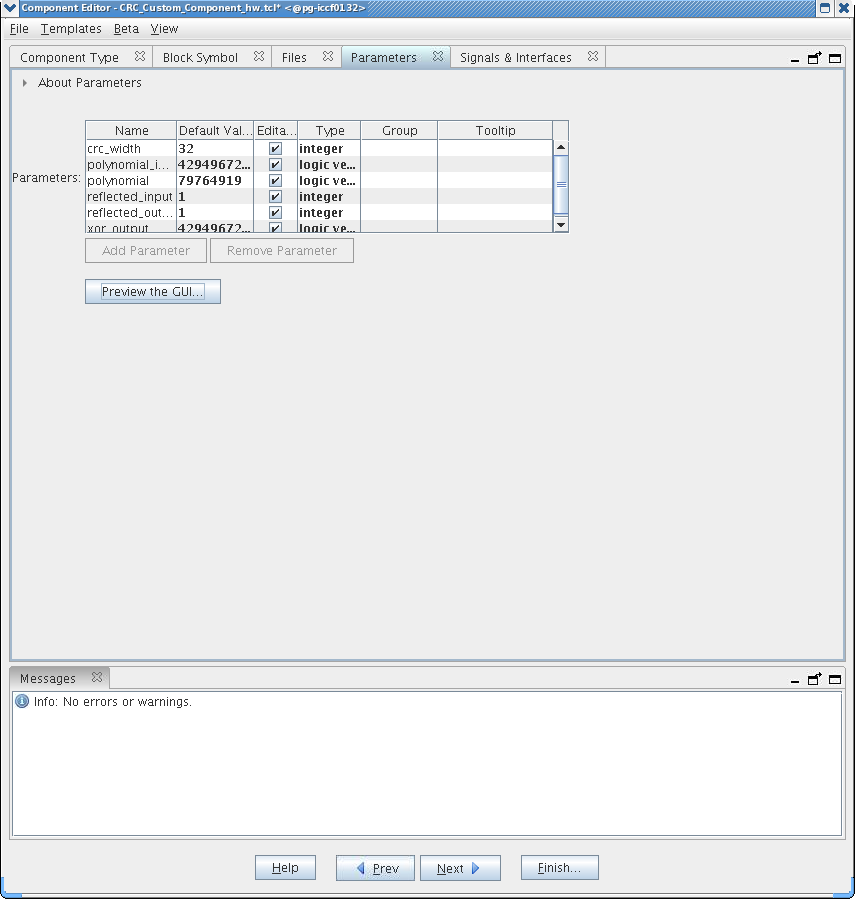
The Editable checkbox next to each parameter indicates whether the parameter will appear in the custom component's parameter editor. By default, all parameters are editable.
- To remove a parameter from the custom instruction parameter editor, you can turn off Editable next to the parameter. For the CRC example, you can leave all parameters editable.
When Editable is off, the user cannot see or control the parameter, and it is set to the value in the Default Value column. When Editable is on, the user can control the parameter value, and it defaults to the value in the Default Value column.
- To see a preview of the custom component's parameter editor, you can click Preview the GUI.