MIPI D-PHY IP User Guide: Agilex™ 3 and Agilex™ 5 FPGAs
ID
817561
Date
3/30/2025
Public
A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
1. About the MIPI D-PHY IP
2. Configuring and Generating the MIPI D-PHY IP
3. MIPI D-PHY Interface Design Guidelines
4. Simulating the MIPI D-PHY IP
5. Validating the MIPI D-PHY IP
6. Debugging the MIPI-PHY IP
7. MIPI D-PHY Architecture
8. Interface Signals and Register Maps
9. Verification Test Plan
10. Document Revision History for the MIPI D-PHY IP User Guide
6.1. Creating a Simplified Design that Demonstrates the Same Problem
6.2. Evaluating FPGA Timing Problems
6.3. Determining if the Problem Exists in Previous Quartus Prime Versions
6.4. Determining if the Problem Exists in the Current Version of Software
6.5. Verifying the MIPI D-PHY IP Using the Signal Tap Logic Analyzer
6.6. Varying the Voltage
6.7. Operating at Lower Speed
6.8. Trying a Different PCB
8.2.1.1. IP_ID
8.2.1.2. IP_CAP
8.2.1.3. D0_CAP
8.2.1.4. DN_CAP
8.2.1.5. RX_CAP
8.2.1.6. TX_CAP
8.2.1.7. TX_PREAMBLE_LEN
8.2.1.8. D-PHY_CSR
8.2.1.9. TX_CLK_LANE_PS
8.2.1.10. RX_DLANE_ERR
8.2.1.11. SKEW_CAL_LEN_B0
8.2.1.12. SKEW_CAL_LEN_B1
8.2.1.13. SKEW_CAL_LEN_B2
8.2.1.14. SKEW_CAL_LEN_B3
8.2.1.15. ALT_CAL_LEN_B0
8.2.1.16. ALT_CAL_LEN_B1
8.2.1.17. ALT_CAL_LEN_B2
8.2.1.18. ALT_CAL_LEN_B3
8.2.1.19. CLK_CSR
8.2.1.20. CLK_STATUS
8.2.1.21. DLANE_CSR_0
8.2.1.22. DLANE_STATUS_0
8.2.1.23. RX_DLANE_DESKEW_DELAY_0
8.2.1.24. RX_DLANE_ERR_0
8.2.1.25. DLANE_CSR_1
8.2.1.26. DLANE_STATUS_1
8.2.1.27. RX_DLANE_DESKEW_DELAY_1
8.2.1.28. RX_DLANE_ERR_1
8.2.1.29. DLANE_CSR_2
8.2.1.30. DLANE_STATUS_2
8.2.1.31. RX_DLANE_DESKEW_DELAY_2
8.2.1.32. RX_DLANE_ERR_2
8.2.1.33. DLANE_CSR_3
8.2.1.34. DLANE_STATUS_3
8.2.1.35. RX_DLANE_DESKEW_DELAY_3
8.2.1.36. RX_DLANE_ERR_3
8.2.1.37. DLANE_CSR_4
8.2.1.38. DLANE_STATUS_4
8.2.1.39. RX_DLANE_DESKEW_DELAY_4
8.2.1.40. RX_DLANE_ERR_4
8.2.1.41. DLANE_CSR_5
8.2.1.42. DLANE_STATUS_5
8.2.1.43. RX_DLANE_DESKEW_DELAY_5
8.2.1.44. RX_DLANE_ERR_5
8.2.1.45. DLANE_CSR_6
8.2.1.46. DLANE_STATUS_6
8.2.1.47. RX_DLANE_DESKEW_DELAY_6
8.2.1.48. RX_DLANE_ERR_6
8.2.1.49. DLANE_CSR_7
8.2.1.50. DLANE_STATUS_7
8.2.1.51. RX_DLANE_DESKEW_DELAY_7
8.2.1.52. RX_DLANE_ERR_7
8.2.1.53. TX_LPX
8.2.1.54. TX_HS_EXIT
8.2.1.55. TX_LP_EXIT
8.2.1.56. TX_CLK_PREPARE
8.2.1.57. TX_CLK_ZERO
8.2.1.58. TX_CLK_POST
8.2.1.59. TX_CLK_PRE
8.2.1.60. TX_HS_PREPARE
8.2.1.61. TX_HS_ZERO
8.2.1.62. TX_HS_TRAIL
8.2.1.63. TX_INIT
8.2.1.64. TX_WAKE
8.2.1.65. RX_CLK_LOSS_DETECT
8.2.1.66. RX_CLK_SETTLE
8.2.1.67. RX_HS_SETTLE
8.2.1.68. RX_INIT
8.2.1.69. RX_CLK_POST
8.2.1.70. RX_CAL_REG_CTRL
8.2.1.71. RX_CAL_STATUS_D-PHY
8.2.1.72. RX_CAL_SKEW_W_START_MUX
8.2.1.73. RX_CAL_SKEW_W_END_MUX
8.2.1.74. RX_CAL_ALT_W_START_MUX
8.2.1.75. RX__CAL_ALT_W_END_MUX
8.2.1.76. RX_DESKEW_DELAY_MUX
8.2.1.77. RX_CAL_STATUS_LANE_MUX
8.2.1.78. PRBS_INIT_0
8.2.1.79. PRBS_INIT_1
8.2.1.80. PRBS_INIT_2
8.2.1.81. PRBS_INIT_3
8.2.1.82. PRBS_INIT_4
8.2.1.83. PRBS_INIT_5
8.2.1.84. PRBS_INIT_6
8.2.1.85. TX_TM_CONTROL
8.2.1.86. TX_MNL_IO_0
8.2.1.87. TX_MNL_D_LP_EN
8.2.1.88. RX_TM_CONTROL
8.2.2.1. TG_TOP_CTRL_0
8.2.2.2. TG_TOP_CTRL_1
8.2.2.3. TG_TOP_DONE
8.2.2.4. TG_TOP_FAIL
8.2.2.5. TG_TOP_TEST_EN
8.2.2.6. TG_TOP_TEST_LINK
8.2.2.7. TARGET_TEST_CNT
8.2.2.8. TCHK_CONTROL
8.2.2.9. TCHK_LINK_STATUS
8.2.2.10. HS_DONE_LANES
8.2.2.11. TCHK_LINK_ERR_STATUS
8.2.2.12. LANE_ERROR_SOT_LANES
8.2.2.13. CAL_ERROR_LANES
8.2.2.14. HS_ERR_LANES
8.2.2.15. HS_TEST_CNT
8.2.2.16. LPDT_TEST_CNT
8.2.2.17. TRIGGER_TEST_CNT
8.2.2.18. ULPS_TEST_CNT
8.2.2.19. TG_RX_OVRD_DATA_PAT
8.2.2.20. TG_RX_BIT_ERROR_CNT
8.2.2.21. TG_RX_HS_TXFER_CNT
8.2.2.22. TG_LINK_CONTROL
8.2.2.23. TG_INIT_CNT
8.2.2.24. TG_HS_LEN
8.2.2.25. TG_LP_LEN
8.2.2.26. TG_SKEW_CAL
8.2.2.27. TG_ALT_CAL
8.2.2.28. TG_PER_SKEW_CAL_LEN
8.2.2.29. TG_TEST_CNT
8.2.2.30. TG_OVRD_DATA_PAT
8.2.2.31. TG_TX_HS_TXFER_CNT
2.1. Creating a MIPI D-PHY Project
You must create a Quartus® Prime project before generating the MIPI D-PHY IP and design example.
- Launch the Quartus® Prime software and select File > New Project Wizard and click Next.
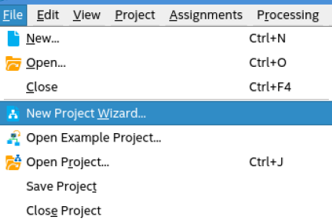
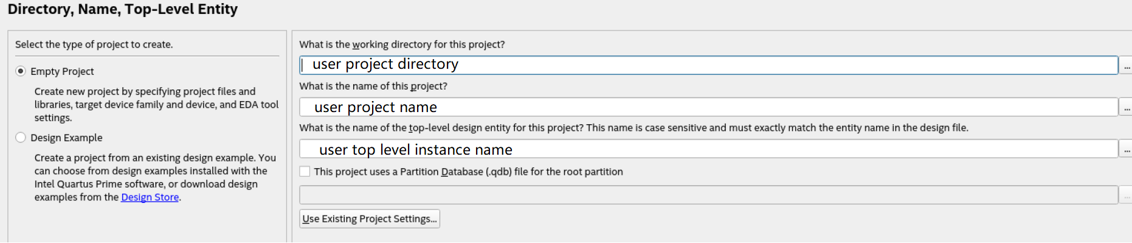
- Specify a directory (<user project directory>), a name for the Quartus® Prime project (<user project name>), and a top-level design entity name (<user top-level instance name>) that you want to create.
- Verify that Empty Project is selected.
- Under Family, select Agilex™ 3 or Agilex™ 5.
- Under Name filter, type the device part number.
- Under Available devices, select the appropriate device.
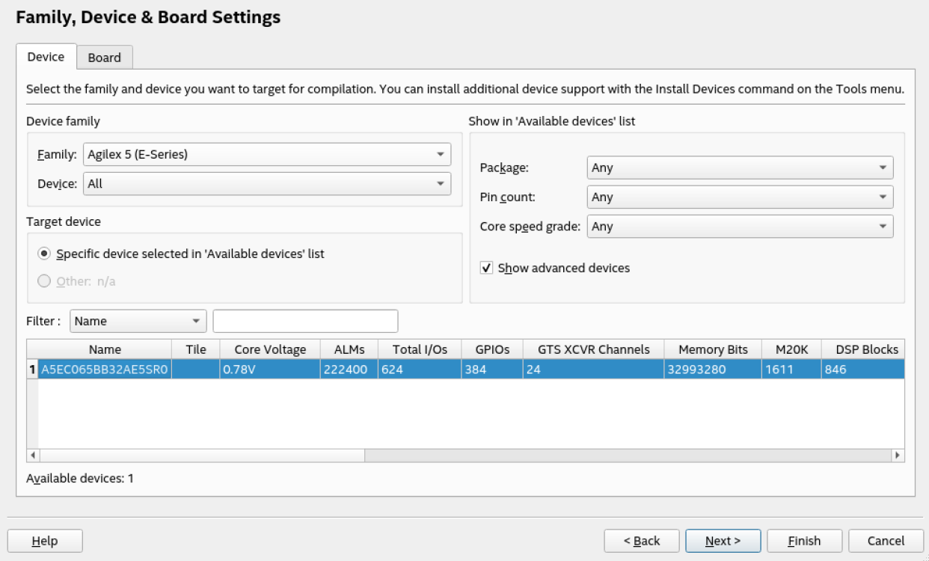
- Click Finish.
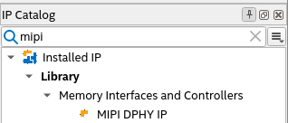
- In the IP Catalog window, select MIPI DPHY IP. (If the IP Catalog window is not visible, select View > Utility Windows > IP Catalog and double-click or click +Add for the IP parameter editor to appear.)
- In the IP Parameter Editor provide an entity name for the MIPI DPHY IP (the name that you provide here becomes the file name for the IP) and specify a directory. Click Create.
- The parameter editor has multiple tabs where you must configure parameters to reflect your MIPI D-PHY implementation.
The MIPI D-PHY IP Parameter Editor
The MIPI D-PHY IP parameter editor consists of a D-PHY IP tab and several Link n tabs.
The D-PHY IP tab is where you configure general settings for the MIPI D-PHY IP instance. You specify the number of PLLs to use, the reference OCT calibration pin location, the skew calibration length, PLL settings, and design example generation settings.
The seven Link n tabs (numbered 0 through 6) correspond to the seven D-PHY interfaces, and are where you configure the channel link for each interface. Here, you can configure the byte location as D-PHY TX or D-PHY RX.