2.1.16. COM Analysis
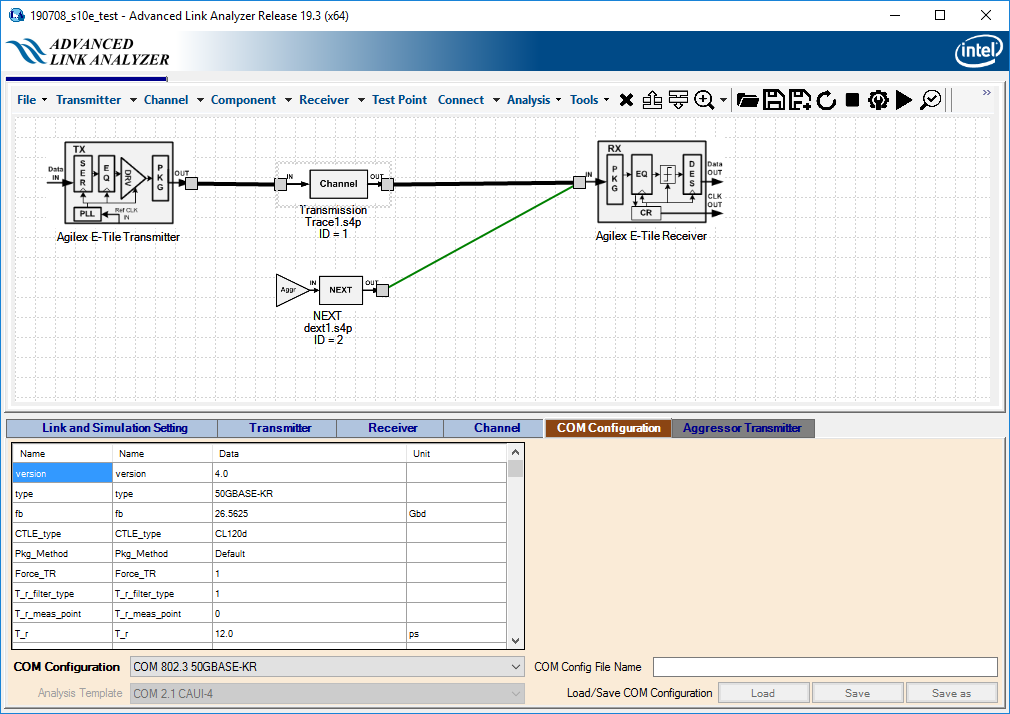
- Set up or configure a link in the Link Designer.
- Click COM Configuration.
- Select your COM configuration from the COM Configuration menu.
- Click COM Analysis, or select Analysis > COM Analysis to perform a COM computation.
As COM is a standards driven analysis, the parameters are specified and fixed for each COM configuration. To perform a custom COM analysis, follow the process below.
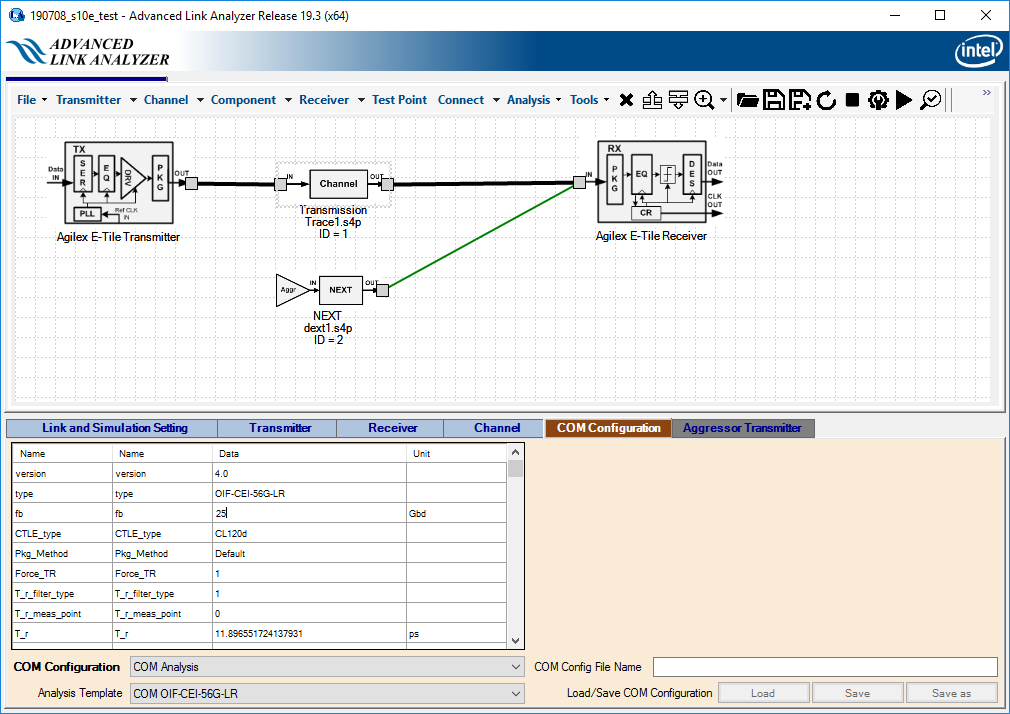
- Set up or configure a link in the Link Designer.
- Click COM Configuration.
- Select COM Analysis from the COM Configuration menu.
- Select a COM configuration using the Analysis Template menu that is closest to the your target link configuration
Example: If you want to compute COM for an OIF CEI 4.0 long reach link at 50 Gbps (PAM4), choose COM OIF-CEI-56G-LR, and then use it as a starting point for your customization.
- Edit COM parameters to suit your link configuration.
Example: Click on the fb parameter, and enter 25 for 50 Gbps OIF-CEI 4.0 long reach COM analysis. Click on the CTLE_Auto_Scale parameter, and enter 1 for automatic CTLE model scaling.
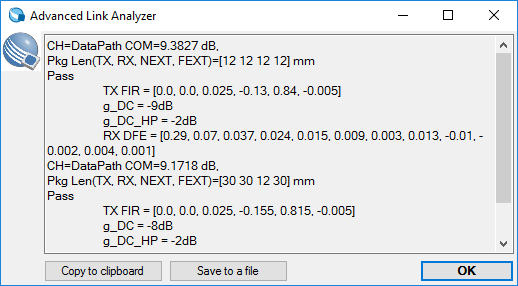
- Click the COM Analysis or select COM Analysis in the Analysis menu to perform a COM computation.
Use Save or Save as to save your customized COM configuration for future use. To load a previously saved custom COM configuration, select COM Configuration > Load from file.
The COM Analysis function shares the same COM computation engine within the Intel® Advanced Link Analyzer’s Channel View (see Intel® Advanced Link Analyzer Channel Viewer Module). The main difference is that the COM Analysis function reads channel configurations from the Link Designer and then performs channel manipulations, for example, channel model generation and channel cascading, for the COM computation. In the Channel Viewer, you have to pre-process the channels before adding them to the Channel Viewer and computing the COM.