A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
CPU Roofline Report Overview
Review the controls available in the main report of the CPU / Memory Roofline Insights perspective of the Intel® Advisor.
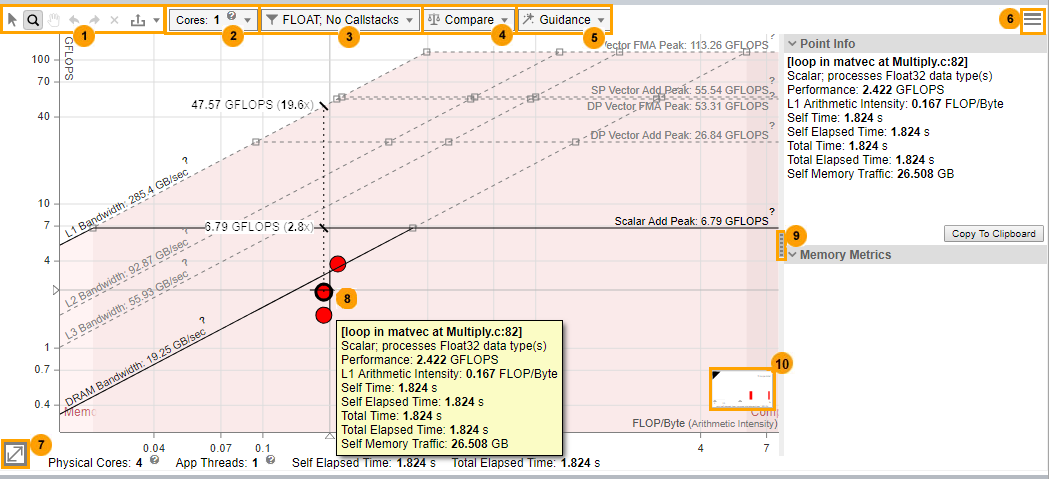
Basic Roofline Chart (Low Accuracy)
There are several controls to help you focus on the Roofline chart data most important to you, including the following.
1 |
|
2 |
Use the Cores drop-down toolbar to:
Choose the appropriate number of CPU cores to scale roof values up or down:
By default, the number of cores is set to the number of threads used by the application (even values only). You’ll see the following options if your code is running on a multisocket PC:
|
3 |
|
4 |
Display Roofline chart data from other Intel Advisor results or non-archived snapshots for comparison purposes. Use the drop-down toolbar to:
Click a loop/function dot in the current result to show the relationship (arrowed lines) between it and the corresponding loop/function dots in loaded results/snapshots.
|
5 |
Add visual indicators to the Roofline chart to make the interpretation of data easier, including performance limits and whether loops/functions are memory bound, compute bound, or both. Use the drop-down toolbar to:
The preview picture is updated as you select guidance options, allowing you to see how changes will affect the Roofline chart’s appearance. Click Apply to apply your changes, or Default to return the Roofline chart to its original appearance. Once you have a loop/function's dots highlighted, you can zoom and fit the Roofline chart to the dots for the selected loop/function by once again double-clicking the loop/function or pressing SPACE or ENTER with the loop/function selected. Repeat this action to return to the original Roofline chart view. To hide the labeled dots, select another loop/function, or double-click an empty space in the Roofline chart. |
6 |
You can save your Roofs Settings or Point Weight Representation configuration to a JSON file or load a custom configuration. |
7 |
Zoom in and out using numerical values. |
8 |
Click a loop/function dot to:
Right-click a loop/function dot or a blank area in the Roofline chart to perform more functions, such as:
|
9 |
Show/hide the metrics pane:
|
10 |
Display the number and percentage of loops in each loop weight representation category. |
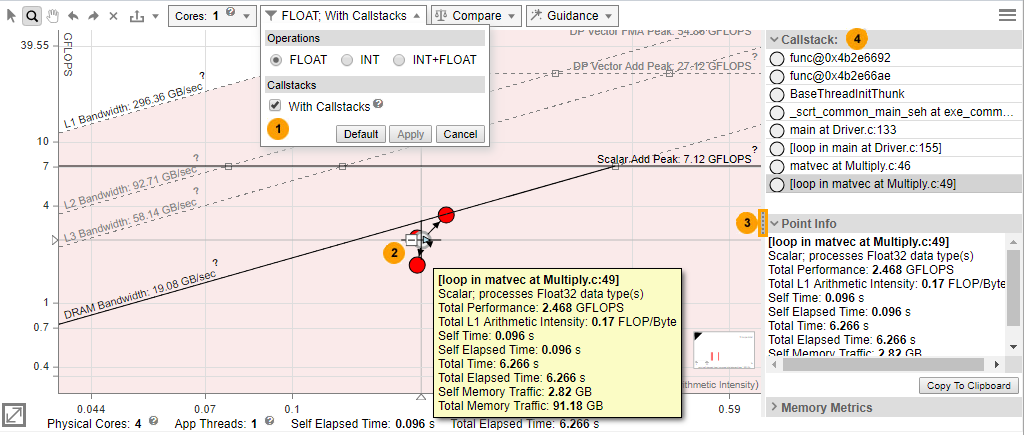
Roofline with Callstacks Chart (Medium Accuracy)
1 |
Enable the display of Roofline with Callstacks additions to the Roofline chart. |
2 |
Show/hide loop/function descendants:
You can also right-click a loop/function dot to open the context menu and expand/collapse the loop/function subtree. |
3 |
Show/hide the Callstack and other panes. |
4 |
You can also click an item in the Callstack pane to flash the corresponding loop/function dot in the Roofline chart. |
Memory-Level Roofline Chart (Medium Accuracy)

1 |
Visually emphasize the relationships among displayed memory levels and roofs for a selected loop/function dot by enabling the Show memory level relationships checkbox.
NOTE:
This checkbox is enabled by default.
|
2 |
Use the drop-down toolbar to:
|
3 |
Double-click a dot or select a dot and press SPACE or ENTER to examine how the relationships between displayed memory levels and roofs:
|
4 |
Show/hide the Memory Metrics and other panes. In the Memory Metrics pane:
|

 control to collapse descendant dots into the parent dot.
control to collapse descendant dots into the parent dot.  control to show descendant dots and their relationship via visual indicators to the parent dot.
control to show descendant dots and their relationship via visual indicators to the parent dot.