A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
Memory Watch
Occurs when a task accesses a memory location marked by an ANNOTATE_OBSERVE_USES annotation. In this case, this problem provides informational feedback only and no action is required. This is useful for finding uses of specified memory locations while a task is executing.
One of the following has occurred:
ID |
Code Location |
Description |
|---|---|---|
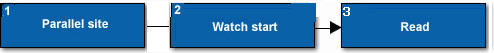
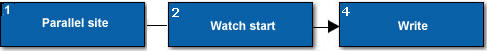
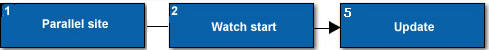
1 |
Parallel site |
If present, represents the location and associated call stack of the parallel site containing the Memory Watch problem. |
2 |
Watch start |
Represents the location and its associated call stack where an ANNOTATE_OBSERVE_USES() annotation marks a memory location. |
3 |
Read |
Represents the location and associated call stack where a task read the watched memory location. |
4 |
Write |
Represents the location and associated call stack where a task wrote the watched memory location. |
5 |
Update |
Represents the location and associated call stack where a task read and wrote the watched memory location. |
Example
void watch_memory()
{
ANNOTATE_OBSERVE_USES(&watch, sizeof(watch)); // Watch start
ANNOTATE_SITE_BEGIN(watch_site); // Parallel site
{
ANNOTATE_TASK_BEGIN(watch_task1);
{
ANNOTATE_LOCK_ACQUIRE(&watch);
watch++; /* watch memory */ // Read and/or Write
ANNOTATE_LOCK_RELEASE(&watch);
}
ANNOTATE_TASK_END();
ANNOTATE_TASK_BEGIN(watch_task2);
{
ANNOTATE_LOCK_ACQUIRE(&watch);
watch++; /* watch memory */ // Read and/or Write
ANNOTATE_LOCK_RELEASE(&watch);
}
ANNOTATE_TASK_END();
}
ANNOTATE_SITE_END();
ANNOTATE_CLEAR_USES(&watch);
}
This example reports all places that use the memory location referenced by watch during the call to watch_memory().
Possible Correction Strategies
To use ANNOTATE_OBSERVE_USES to help you correct an incidental sharing problem, do the following to mark places where you may be able replace uses of a shared memory location with uses of a non-shared memory location:
Add an ANNOTATE_OBSERVE_USES annotation to the task.
Find all uses of the shared memory location in the dynamic extent of the task.