Developer Guide
Intel® oneAPI DPC++/C++ Compiler Handbook for FPGAs
ID
785441
Date
5/05/2025
Public
Intel oneAPI DPC++/C++ Compiler Handbook for FPGAs Overview
Introduction To FPGA Design Concepts
Intel oneAPI FPGA Development
Getting Started with the Intel oneAPI DPC++/C++ Compiler for Intel FPGA Development
Defining a Kernel for FPGAs
Debugging and Verifying Your Design
Analyzing Your Design
Optimizing Your Kernel
Optimizing Your Host Application
Integrating Your Kernel into DSP Builder for Intel FPGAs
Integrating Your RTL IP Core Into a System
RTL IP Core Kernel Interfaces
Loops
Pipes
Data Types and Arithmetic Operations
Parallelism
Memories and Memory Operations
Libraries
Additional FPGA Acceleration Flow Considerations
FPGA Optimization Flags, Attributes, Pragmas, and Extensions
Quick Reference
Additional Information
Document Revision History for the Intel oneAPI DPC++/C++ Compiler Handbook for Intel FPGAs
Notices and Disclaimers
Throughput
Resource Use
System-level Profiling Using the Intercept Layer for OpenCL™ Applications
Multithreaded Host Application
Utilizing Hardware Kernel Invocation Queue
Double Buffering Host Utilizing Kernel Invocation Queue
N-Way Buffering to Overlap Kernel Execution
Prepinning Memory
Simple Host-Device Streaming
Buffered Host-Device Streaming
Refactor the Loop-Carried Data Dependency
Relax Loop-Carried Dependency
Transfer Loop-Carried Dependency to Local Memory
Minimize the Memory Dependencies for Loop Pipelining
Unroll Loops
Fuse Loops to Reduce Overhead and Improve Performance
Optimize Loops With Loop Speculation
Remove Loop Bottlenecks
Improve fMAX/II with Shannonization
Optimize Inner Loop Throughput
Improve Loop Performance by Caching Data in On-Chip Memory
Global Memory Bandwidth Use Calculation
Manual Partition of Global Memory
Partitioning Buffers Across Different Memory Types (Heterogeneous Memory)
Partitioning Buffers Across Memory Channels of the Same Memory Type
Ignoring Dependencies Between Accessor Arguments
Contiguous Memory Accesses
Static Memory Coalescing
Specify Schedule fMAX Target for Kernels (-Xsclock=<clock target>)
Create a 2xclock Interface (-Xsuse-2xclock)
Disable Burst-Interleaving of Global Memory (-Xsno-interleaving)
Force Ring Interconnect for Global Memory (-Xsglobal-ring)
Force a Single Store Ring to Reduce Area (-Xsforce-single-store-ring)
Force Fewer Read Data Reorder Units to Reduce Area (-Xsnum-reorder)
Disable Hardware Kernel Invocation Queue (-Xsno-hardware-kernel-invocation-queue)
Modify the Handshaking Protocol Between Clusters (-Xshyper-optimized-handshaking)
Disable Automatic Fusion of Loops (-Xsdisable-auto-loop-fusion)
Fuse Adjacent Loops With Unequal Trip Counts (-Xsenable-unequal-tc-fusion)
Pipeline Loops in Non-task Kernels (-Xsauto-pipeline)
Control Semantics of Floating-Point Operations (-fp-model=<value>)
Modify the Rounding Mode of Floating-point Operations (-Xsrounding=<rounding_type>)
Global Control of Exit FIFO Latency of Stall-free Clusters (-Xssfc-exit-fifo-type=<value>)
Enable the Read-Only Cache for Read-Only Accessors (-Xsread-only-cache-size=<N>)
Control Hardware Implementation of the Supported Data Types and Math Operations (-Xsdsp-mode=<option>)
Generate Register Map Wrapper (-Xsregister-map-wrapper-type)
Allow Wide Memory Initialization (-Xsallow-wide-device-globals)
Specify Schedule fMAX Target for Kernels (scheduler_target_fmax_mhz)
Specify a Workgroup Size (max_work_group_size/reqd_work_group_size)
Specify Number of SIMD Work Items (num_simd_work_items)
Omit Hardware that Generates and Dispatches Kernel IDs (max_global_work_dim)
Omit Hardware that Supports Global Work Offsets (no_global_work_offset)
Reduce Kernel Area and Latency (use_stall_enable_clusters)
Configure Running and Debugging in a Visual Studio* Code Project
You can use the special version of GNU* GDB (gdb-oneapi) provided by the Intel® oneAPI Base Toolkit to debug your kernel through Visual Studio* Code (VS Code*) by following the instructions provided in Using Visual Studio Code with Intel® oneAPI Toolkits User Guide.
You can also use your native debugger if you disable code optimizations when you compile your code.
Before you can debug your application in VS Code*, you must configure running and debugging in your VS Code* project. You must complete the following instructions for each oneAPI project that you want to enable running and debugging in:
- Follow the steps in Set the Environment Variables and Launch Visual Studio* Code to launch VS Code* with the required oneAPI environment.
- Open the project file that you want to enable running and debugging for.
- If you have not yet compiled your project for debugging, compile your source code for emulation.
- Linux: Ensure that you include the -g and -O0 compiler command options. The -g option enables debugging and the -O0 option disables code optimizations.
icpx -fintelfpga -g -O0 <kernel code.cpp> -o fpga_emu
IMPORTANT:Disable code optimizations with the -O0 option only for emulation. Do not disable code optimizations for simulation or hardware compilation. - Windows: Ensure that you include the /DEBUG and /Od compiler command options. The /DEBUG option enables debugging and the /Od option disables code optimizations.
icx-cl -fintelfpga /DEBUG /Od /EHsc <kernel code.cpp> -o fpga_emu.exe
IMPORTANT:Disable code optimizations with the /Od option only for emulation. Do not disable code optimizations for simulation or hardware compilation.
If you are compiling a code sample, CMake generates the debug flags for you:
- Linux::
mkdir build cd build cmake <path_to_CMakeLists.txt> make fpga_emu
- Windows:
mkdir build cd build cmake <path_to_CMakeLists.txt> nmake fpga_emu
- Linux: Ensure that you include the -g and -O0 compiler command options. The -g option enables debugging and the -O0 option disables code optimizations.
- Click the Run and Debug icon in the Activity Bar (or press Ctrl+Shift+D).

- Click create a launch.json file.
- Select your debugger as follows:
- Linux: C++ (GDB/LLDB)
- Windows: C++ (Windows)
- Add the configuration to your launch.json file as follows:
- Place your cursor in between the [] of the "configurations":[] line and press Ctrl+Space to select from available launch templates:
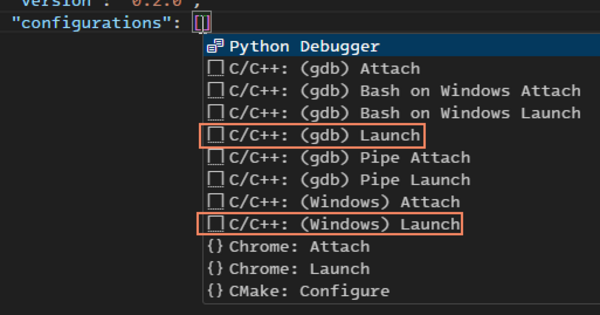
- Select a template as follows:
- Linux: Select C/C++: (gdb) Launch
- Windows: Select C/C++: (Windows) Launch
- Update the "program": "enter program name, for example ${workspaceFolder}/a.exe", pair to point at the executable file (generated when you compiled your kernel for emulation) that you want to debug.
- Place your cursor in between the [] of the "configurations":[] line and press Ctrl+Space to select from available launch templates:
- Save the launch.json file and close it.