Build and Run a Sample Using the Command Line
Before you begin, make sure your development environment is set up. If you have not already configured your environment, go to Configure Your System before proceeding.
You can use a terminal window or Visual Studio Code* for command-line development. Some tasks can be automated using extensions. To learn more, see Using Visual Studio Code with Intel® oneAPI Toolkits.
To compile and run a sample:
- Use the oneAPI CLI Samples Browser to locate a sample project.
- Build and run the project using Make* or CMake*.
Download Samples using the oneAPI CLI Samples Browser
Use the oneAPI CLI Samples Browser to explore the collection of online oneAPI samples. The oneAPI CLI Browser is a single-file, stand-alone tool that does not require any extra libraries. You can copy samples to your local disk as ready-to-build projects. The build instructions are included as part of the sample in a README file. Most oneAPI sample projects are built using Make or CMake.
Watch a video guide on creating a sample project with Intel® oneAPI using the command line.
To download and set up a sample:
- Open a terminal window.
- If you did not complete the steps in Option 2: One time set up for setvars.sh in the Configure Your System section, set system variables by sourcing setvars. You can choose to use either the Unified Directory Layout or the Component Directory Layout to ensure components version consistency. Learn more in the oneAPI Development Environment Setup.
The commands below assume you used the default install location. If you customized the installation folder, adjust the path to setvars | oneapi-vars accordingly.
Component Directory Layout:
For system-wide installations (requires root or sudo privileges):
. /opt/intel/oneapi/setvars.shFor local installations:
. ~/intel/oneapi/setvars.shUnified Directory Layout:
For system-wide installations (requires root or sudo privileges):
. /opt/intel/oneapi/<toolkit-version>/oneapi-vars.sh
For local installations:
. ~/intel/oneapi/<toolkit-version>/oneapi-vars.sh
- In the same terminal window, run the application (it should be in your PATH):
The oneAPI CLI menu appears:oneapi-cli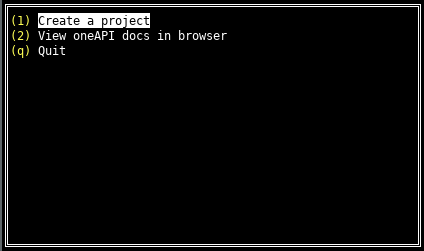
- Use the up and down arrow keys to select Create a project, then press Enter
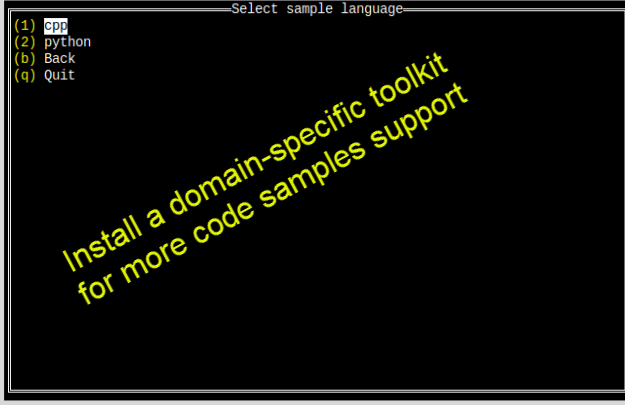
- The language selection will appear. For your first project, select cpp, then press Enter. The toolkit samples list appears.
- Select the Vector Add sample. Vector Add is a simple test application that help verify that the tools are setup correctly and can access your system's GPU:
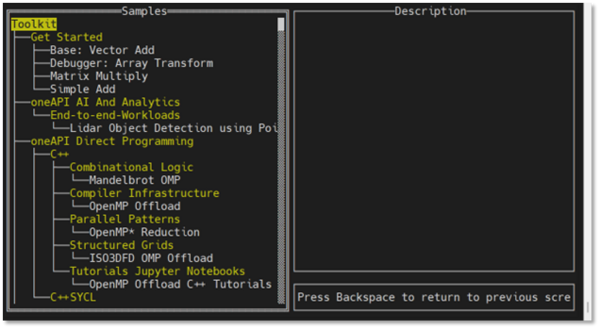
After you select a sample, press Enter.
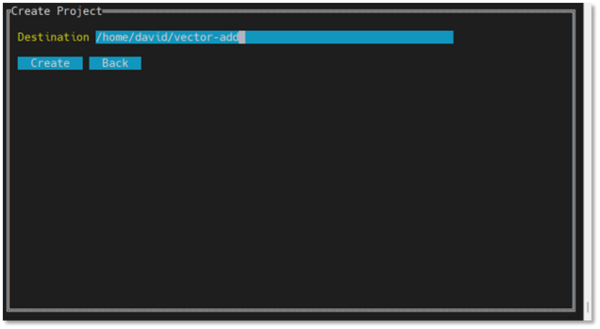
- Specify the location for the project. The default location includes the path from where the CLI Browser was run and the name of the project.
Press Tab to select Create, then press Enter:
Build and Run a Sample Using Make
- Open a command prompt.
- Navigate to the directory which you specified when creating (downloading) the project.
- Configure the project using either the buffer-based implementation or the Unified Shared Memory (USM) based implementation . Read more about these memory management techniques in the Vector Add Sample page.
Buffer-based implementation:
mkdir build cd build cmake ..Unified Shared Memory (USM) based implementation:
mkdir build cd build cmake .. -DUSM=1 - Build the program.
make cpu-gpu - Run the program for Unified Shared Memory (USM) or buffers.
./vector-add-buffers ./vector-add-usm
- Optional: Clean the program.
make clean
Build and Run a Sample using CMake
Vector add can only be run with Make. You can run a different sample using CMake, where <sample_name> is the name of the sample you want to run.
To find a sample that uses CMake, browse the oneAPI Samples GitHub repository and view the README file for each sample to see if the sample can be run with CMake.
- If necessary, re-run the command-line utility and select a CMake project that contains a CMakeLists.txt file.
cd <sample_name>
- Navigate to the build directory.
mkdir build cd build - Build the program. Run CMake in the build directory to create the makefile. Use the newly created makefile to build the executable.
cmake ../. make VERBOSE=1NOTE:Some samples require additional steps or arguments for building and/or running the sample. Review the sample's README.md file for specific details regarding how to build and run the sample. - Run the program.
make run - Clean the program.
make clean
See Troubleshooting section for help with common issues.
Compile and run a sample for FPGA
You can run the vector-add sample (or any FPGA SYCL code) in the following modes:
- Emulation: Verifies the code correctness. Compilation completes in few seconds. Use this mode if you are using the Intel® oneAPI Base Toolkit
- Report: Generates a static optimization report for design analysis. Compilation can take a few minutes to complete. When completed, you can find the reports in <project_name>.prj/reports/report.html. This can be used with the Intel® oneAPI Base Toolkit. For more information about the reports, refer to the FPGA Optimization Guide for Intel® oneAPI Toolkits.
- Hardware: Generates the actual bitstream on an FPGA device. Compilation can take few hours to complete. Use this mode to measure performance. To use this mode, download the Intel® Quartus® Prime Pro Edition software and BSPs separately. For more information, refer to the Install Software for Intel® FPGA Development Flow section in the Intel® oneAPI Toolkits Installation Guide for Linux* OS and Intel® FPGA Add-On for oneAPI Base Toolkit web page.
After downloading the vector-add design example using the oneAPI CLI Samples Browser, perform the following steps to compile and run the design:
- Change to the directory containing the vector-add design example using:
cd <vector-add directory on the same system> - Run the following make clean command before you start compiling:
make clean - Compile the design using one of the following options:
Compile for emulation using:
make fpga_emuCompile the report using:
make reportNOTE:You can view the report at vector-add_report.prj/reports/report.html. This does not generate an executable.Compile for hardware (takes longer to complete) using:
make fpga
NOTE:If you compiled the hardware on a development system, copy the executable file vector-add.fpga to the runtime system. - Run the design using one of the following options:
- Run the design for emulation using:
./vector-add-buffers.fpga_emu ./vector-add-usm.fpga_emu
NOTE:If you are using a separate development system, perform this step on that system. - Run the design on FPGA hardware using:
./vector-add-buffers.fpga ./vector-add-usm.fpga
NOTE:To understand the command used in the Makefile, refer to the Intel® oneAPI Programming Guide. - Run the design for emulation using:
See Explore SYCL* Through Samples to learn more.