Introduction
This article gives a quick overview of Intel® Video Pro Analyzer (Intel® VPA)'s wide range of advanced analysis capabilities, and how to get started with improving video quality and efficiency in video-related app development. (See also quick intro videos at bottom of article.)
Tap into Intel® VPA Advanced Video Analysis
Experts who work with video streaming know that video codecs are increasingly complex, and that customer quality expectations only get tougher. Video analysis tools are increasingly necessary—not only for codec innovators, but also for everyone who creates video bitstreams. With that in mind, Intel VPA helps video codec developers/architects, software experts, and validation engineers:
- Ensure that your outputs conform to codec specifications. Most decoders have extensive error resiliency/correction. It's all too easy for errors to be hidden by the decoder/player used for validation, which are not so nicely handled by another. Playback problems frequently sneak through even heavily validated products, waiting to be found by end customers. It’s not practical to test on all decoders, or even on the most popular subset. The best answer is to ensure that your bitstreams are completely compliant and without subtle dependencies on decoder robustness.
- Understand quality/performance tradeoffs. When tweaking parameters, adding new algorithms, or comparing codec implementations, you want to know not just whether quality was impacted (i.e., PSNR, SSIM, or subjective analysis), but why. Intel VPA lets you see what the encoder did at every stage in the process—down to the macroblock or even pixel level—to help you optimize for the solution you need.
- Debug. Quickly identify root-cause issues for faster fixes in your own software. And produce better bug reports that you can report to codec vendors (including Intel).
- Innovate for high-dynamic range (HDR) and access support for new spec additions like HEVC scalability extension (SHVC) and be able to see exactly what was encoded in bitstream headers. This includes the SEI messages currently used for multiple HDR formats.
Intel VPA is designed to help developers and QA/validation specialists bring a wide variety of products that produce video bitstreams to the next level. Its GUI is designed to be easy to navigate, fast, and to support working with high-resolution content. There is also a command line mode for batch operation.
Codecs and Containers Covered
Intel VPA covers several video elementary stream codecs in highest demand today and supports a wide variety of container formats.
|
Codec |
All major profiles |
Bit depth |
Color format |
Notes |
|
HEVC |
Yes |
8-14 bit |
4:2:0/4:2:2/4:4:4 |
SHVC, SCC, and MV-HEVC extension support |
|
VP9 |
Yes |
8-12 bit |
4:2:0/4:2:2/4:4:4 |
|
|
AVC |
Yes (up to high) |
8-10 bit |
4:2:0/4:2:2 |
|
|
MPEG2 |
Yes |
8 bit |
4:2:0/4:2:2 |
|
How to Use Intel VPA: Getting Started
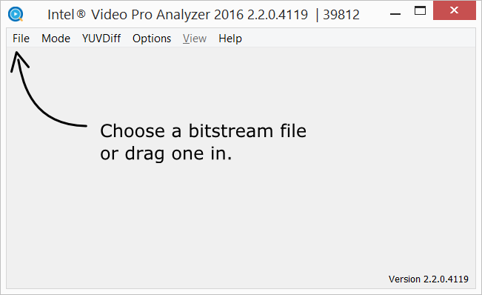
It’s easy to get started. Just follow the arrow to open the file you would like to investigate.
Understand the GUI layout
When you first open Intel VPA, there is a lot to see. Multiple views are available You can turn these on or off in the View menu based on preferences and needs.
• Stream View: Shows sequence of frames (choose the individual frame you want to investigate)
• Syntax Info: NAL units, headers, SEI messages, etc.
• Selection Info/Unit Info: Details on the frame area selected
• Status: Details about how the stream was parsed
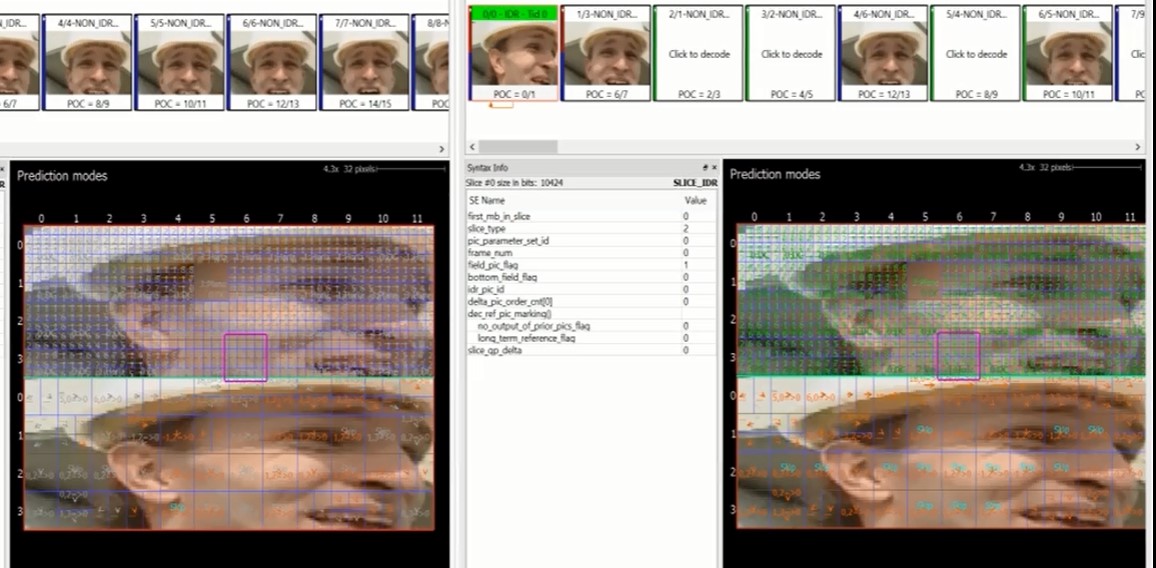
Intel VPA also offers a special feature called Dual View Mode (shown below) to easily view optimization comparison data.
Bitstream Error/Conformance Checks
As a first step, check for parsing errors in the status area. For clean inputs with no conformance problems, the triangle at the bottom of the Status view should be green. If it is not, click on the triangle to see more details
Clicking on individual warning/error lines shows exactly where the problem occurred in the Syntax Info view.
The problem NAL unit can be saved to a file for further analysis.
Modes
After checking for any issues with parsing the file, you can move to analyzing the contents. The first place to start is the Mode menu. To assist your analysis, Intel VPA groups many types of information by decode stage. The types of information visualized can be chosen under the Mode menu.
These include:
- Coding flow: Coding Tree Block/Macroblock order and index. If tiles or wavefronts are used, this can also show substream layout
- Predictions: Information related to prediction modes and partitioning
- Residuals: Residual signal and coefficients (+scan order), including decode steps of inverse quantization and inverse transformation
- Reconstruction: Reconstructed samples prior to deblocking
- Deblocking: Edges deblocked, filter modes, values changed by filters
- Sample Adaptive Offset (SAO): Offset parameters for each coding tree block
- YUV: Rinal decoded pixel values. If an original YUV file was opened from the YUVdiff menu then original YUV values and differences can be seen.
- Overlays: (next section) Several useful visualizations including heat, QP, prediction unit reference type, reference index, and (if an original YUV is loaded) local PSNR by coding tree block/macroblock
- Simple motion: Motion vectors (for P and B frames)
Note: The modes available vary by codec. The HEVC modes are described above. An example of a difference between the types of information available per codec format is: SAO is used only for HEVC; and VP9 has loop filter and coding efficiency modes.
Some modes have a detail view to display values that are too dense to show for the entire frame at once. When first switching to a new mode you will see the full frame summary, but where more details are available, you can right-click to view macroblock/pixel level information.
Check out also these few minute video overviews.
Intel VPA Error Resilience &
Intel VPA Quick Tour Stream Analysis Intel VPA Easy-to-Use GUI
Summary
This blog covers only the basics of what Intel VPA provides and how to start navigating the tool. Other key features, such as Video Quality Caliper and more, are covered in additional documentation updates.
For More Information
- Access the Intel VPA site
- For questions, please connect with Intel at:
Intel Media forum or Intel Premier Support
1Note that in the evaluation version, some features may be constrained. If you have special needs, our Sales Team will be delighted to help you.