Environment
The Intel® VROC GUI is a Windows* based application that provides users monitoring and management capabilities for the Intel® VROC storage subsystem. It offers a wide range of monitoring and management activities for the Intel® VROC based RAID subsystem. Consult the Intel® Virtual RAID on CPU (Intel® VROC) Graphical User Interface (GUI) Getting Started Guide to learn about:
- Installing the Intel® VROC GUI application
- Overview of the Intel® VROC GUI components
The RAID subsystem is defined as drives attached to the Intel® Volume Management Device (Intel® VMD) controller or the Platform Controller Hub (PCH) controller in RAID mode.
The Intel® VROC GUI application requires (at a minimum) Microsoft* .NET 4.7.2. Consult other installation requirements in What Are the Installation Requirements for the Intel® Virtual RAID on CPU (Intel® VROC) Graphical User Interface (GUI) Application?
Intel® VROC Installation
The Intel® VROC GUI application, drivers and supporting infrastructure are distributed through a single installation executable.
When the Intel® VROC installer is executed, it will perform the following tasks:
- If it detects that there is a newer version of the Intel® VROC (VMD NVMe* RAID)/Intel® VROC (Legacy NVMe* RAID) or Intel® VROC (SATA RAID) solutions already installed it will display a message requesting permission from the user to overwrite the newer version of the software.
- It will overwrite older versions of the installed software components.
- It will install the driver in accordance with Microsoft* PnP device detection method.
- It will create the following shortcuts within the start menu path: Start/Programs/Intel/Intel(R) Virtual RAID on CPU.
- It will provide the user a mechanism to list all available installation options.
- It will provide an option to specify a custom install path. If the specified install path is illegal, the Intel® VROC installer will cancel the installation.
- It will implement an option to store the steps of an installation to a log file. The default location is %temp%\Intel\Logs. The file name is IntelVROC.txt. If the installer sees that the file already exists, the log information is appended to the existing file.
- It will create a cached installer used for uninstalling. The location of this uninstaller is %programdata%\Package Cache\<some guid>. The exact path to the cached installer is stored in the product’s uninstall registry key. This registry key is HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\<some guid> (in the 32-bit hive), where the DisplayName value is the Intel® VROC’s display name. Also, the BundleCachePath value contains the full, exact path to the cached installer. If the BundleCachePath value does not exist, the wrong registry key is being looked at, because there should be two keys, if on a 32-bit system.
- It will implement an option to install the Intel® VROC GUI components only. When invoked with this option, the Intel® VROC installer software will install the User Interface (UI), Help UI System Service, and Notification Area Icon.
The product installer shall install the following components:
- Intel® VROC (VMD NVMe* RAID) drivers for Intel® VMD/Intel® VROC (Non-VMD NVMe* RAID)
- Intel® VROC (SATA RAID) driver for SATA
- Intel® VROC (SATA RAID) driver for sSATA
- Intel® VROC (SATA RAID) driver for tSATA
- Intel® VROC Help System Service
- Intel® VROC Notification Area Icon
Default Installation Path
The Intel® VROC installer software will install the Intel® VROC solution to a default folder unless specified otherwise.
The default path shall be C:\Program Files (x64)\Intel\Intel(R) Virtual RAID on CPU.
Intel® VROC (SATA RAID) Driver
The Intel® VROC installer will install separate driver binaries for the SATA, sSATA and tSATA controllers.
Intel® VROC (VMD NVMe* RAID) Driver
The Intel® VROC installer will install a single Intel® VROC (VMD NVMe* RAID) driver binary for all Intel® VMD devices enabled in the system.
Intel® VROC (Non-VMD NVMe* RAID) Driver
The Intel® VROC installer will install a single Intel® VROC (Non-VMD NVMe* RAID) driver binary for Intel NVMe* SSDs found in a supported platform (Non-VMD capable).
Understanding the Application
The Intel® VROC GUI application allows the user to optimize and maintain a healthy storage system by creating volumes, customizing performance settings, and managing storage system elements. The following information provides the user with a general overview of the storage system configuration and an individual review of all the areas contained in this application.
Storage System Configuration
The Intel® VROC storage system combines hardware capabilities with the Intel® VROC family of products to provide flexible data storage units on the user’s computer. Each data storage unit, or RAID configuration, consists of three elements that include:
- The physical disk: SATA or NVMe*
- The RAID array
- The RAID volume
When at least one RAID volume is present on the system, these elements are represented in the storage system.
Array
An array is a collection of two or more NVMe* or SATA disks in a RAID configuration and is the highest element in the hierarchy of a storage system. Once a volume is created, the disks in the array are used to create that volume within an array. An array can include one or two RAID volumes if the hardware allows it.
Volume
A volume is the storage area on two or more disks whose type dictates the configuration of the data stored. If the user created a volume for data protection, then the user’s storage system may include a RAID 1 volume spanning two NVMe* or SATA disks, which mirrors data on each disk.
Disks
A disk (Hard Drive Disk (HDD), Solid-State Drive (SSD)) physically stores data and allows read/write data access. If a disk is used to create a volume, it becomes an array disk because it has been grouped with other disks to form an array.
The storage system can also include ATAPI devices, which cannot be used to create a volume. They are a mass storage device with a parallel interface, such as CD-ROM, DVD/Blu-ray disc, or tape drive.
When selecting drives to be RAID volume members, a warning message will be displayed if there are any significant discrepancies between two or more selected drives. The warning message will be displayed if one of the following conditions is encountered:
- There is a combination of SSDs and HDDs used.
- There are at least two drives that have a size difference of more than 10%.
Navigation
The Intel® VROC GUI application is organized into navigation options located in a left bar. A description of each option is available in Intel® Virtual RAID on CPU (Intel® VROC) Graphical User Interface (GUI) Components.

Storage System Status
Anytime the Intel® VROC GUI application is launched, it opens to the status area. This is where the general state and health of the user’s storage system is reported, both in the storage system view and in details. Depending on the status, volume creation and management options may be available to enhance or repair the user’s storage system.
Understanding the Status Area
To get the full benefits of what the Intel® VROC GUI application has to offer, it is critical to maintain a healthy storage system. The application helps the user track and report any disk or volume related problems that could put the safekeeping of the user’s data at risk.
The storage system can be in the states described in the following table.
| Icon | Description |
|
| Reports that the system is functioning as expected, supported disks are present and connected to the computer. If an array is present, volume data is fully accessible. |
|
| The Create subsection is only available if the storage system meets the minimum requirements to create a volume. Depending on the available hardware, the user may be given the option to create a volume to protect data, optimize the disk performance, or create a custom volume. |
|
| The Manage subsection is only available if the storage system reports atypical conditions in a normal state. Typically, details or a recommended action are provided to help the user rectify any storage system conditions. |
|
| Reports that storage system data may be at risk due to a problem detected on one or more supported disks. |
|
| The Manage subsection displays any disk or volume states reported by the storage system that may require the user’s attention to keep data fully protected and accessible. Details or a recommended action are provided to help the user fix any storage system problems. For example, if the master disk in a recovery volume is reported as failed, we would recommend that the user rebuild the volume to another disk. Note: In this state, we recommend that the user backup any accessible data before taking action. |
|
| The Manage subsection displays any disk or volume states reported by the storage system that require the user’s immediate attention to keep data fully protected and accessible. Details or a recommended action are provided to help the user fix any storage system problems. For example, if the data on a RAID 1 volume appears inaccessible due to a failed array disk, we would recommend that the user rebuild the volume to another disk. Note: In this state, we recommend that the user backup any accessible data before taking action. |
Volume States
The table below shows the possible states a RAID volume may be in. Refer to Troubleshooting Tips for Intel® Virtual RAID on CPU (Intel® VROC) in Windows* Environments for more information to recover RAID volumes in degraded or failed state.
| Volume Type | Normal | Degraded | Failed |
| RAID 0 |
| Not Applicable |
|
| Single-Disk (Cache) |
|
|
|
| Single-Disk (Data) |
| Not Applicable |
|
| RAID 1 |
|
|
|
| RAID 5 |
|
|
|
| RAID 10 |
|
|
|
RAID-Ready Mode
A RAID-Ready system refers to a system that has been configured to support the Intel® VROC family of products. The system BIOS has the appropriate pre-boot drivers and has been configured for RAID mode. Intel® VROC will allow a pass-thru drive that contains data or a bootable operating system to become a RAID volume. This can be done while the system remains operational.
RAID-Ready Migration
- Pass-thru to a 2 to XX drive RAID 0 (Intel® VROC (VMD NVMe* RAID)/Intel® VROC (Non-VMD NVMe* RAID))
- Pass-thru to a 2 to 8 drive RAID 0 (Intel® VROC (SATA RAID))
- Pass-thru to a 2 drive RAID 1
- Pass-thru to a 3 to XX drive RAID 5 (Intel® VROC (VMD NVMe* RAID)/Intel® VROC (Non-VMD NVMe* RAID))
- Pass-thru to a 3 to 8 drive RAID 5 (Intel® VROC (SATA RAID))
- Pass-thru to a 4 drive RAID 10
Graphical User Interfaces
Intel® VROC will provide support for graphical user interfaces for management of RAID arrays and volumes on NVMe* SSDs directly connected via PCI express slots controlled/managed by the Intel® VMD enabled ports. This includes a graphical user interface in the operating system as well as a web-based graphical user interface for remote management: Intel® ASM.
Intel® VROC Pass-Thru Mode GUI Support
The Intel® VROC GUI application will provide support for Locate LED and Managed Hot-Plug to be selected by the user when Intel® VMD is enabled but the Intel® VROC RAID hardware upgrade key is absent from the platform. RAID functionality is disabled in this configuration.
Intel® VROC Enabled Mode GUI Support
The Intel® VROC GUI application will provide support for RAID managed, Locate LED and Managed Hot-Plug to be selected by the user when Intel® VMD is enabled, and an Intel® VROC RAID hardware upgrade key is present in the platform.
Intel® VROC GUI Version
The specific version of the Intel® VROC GUI application is obtained from the Help window by clicking on the About section. See more details in Intel® Virtual RAID on CPU (Intel® VROC) Graphical User Interface (GUI) Components.
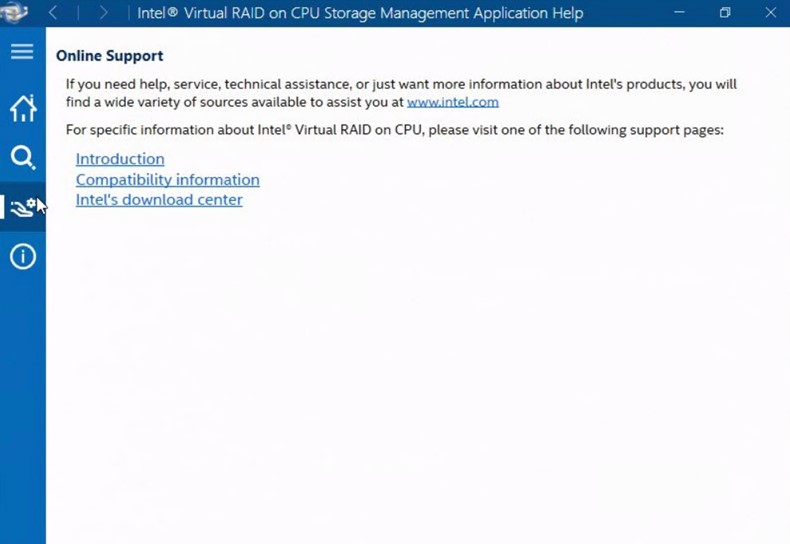
Intel® VROC GUI Online Support
In the Intel® VROC GUI Help menu, the sub-menu Online Support when selected will display a pop-up window with the support URLs as shown in the figure below. The user can use these resources to access the available online self-help support collateral.