Intel® Desktop Processors:
- Desktop processors are primarily for desktop form factor, characterized by constant power need and mostly separate display, keyboard and mouse type of peripherals.
- Available as box and tray.
- For desktop boxed processors: Sold by retailers for users who want to build their own systems.
- For desktop tray processors: Available by original equipment manufacturers (OEMs).
- Available with locked and unlocked processors for overclocking.
- Unlocked processors include the “K” or “X” letters in their processor number. Examples: “K”, “KF”, “X”, and “XE”.
Intel® Mobile Processors:
- Mobile processors also called laptop processors.
- Mobile processors are primarily for laptop form factor, characterized by built-in battery, screen, keyboard and mouse type of peripherals.
- Available as tray only.
- Available by original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and sold as laptop computers and 2-in-1 PCs.
- Available with locked and unlocked processors for overclocking.
- Unlocked processors include the “K” or “X” letters in their processor number. Examples: “HK”, and “HX”.
Refer to understanding Intel® Core™ Processor suffixes in A Brief Guide to Our Latest Processor and Naming Updates.
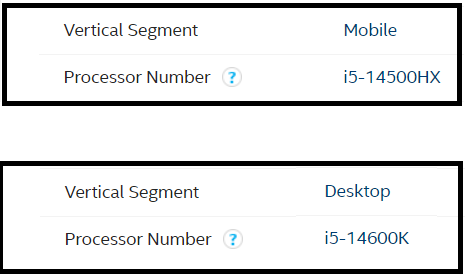
How to know if you have desktop or mobile processor
- Identify your Intel® Processor, or the processor you need to find the information for.
- Go to the Product Specifications page.
- Enter the processor number in the Search Intel.com field located upper-right corner.
- Click the processor's link from the search results page.
- Once you are on the processor specification page, click Essentials section.
- Look up the Vertical Segment.
Here is an example of two processors, one is mobile and one is desktop.