"Automatic Overclock Failed" Message with Disabled Buttons Using Intel® XTU
Content Type: Troubleshooting | Article ID: 000093779 | Last Reviewed: 05/06/2025
An Overclock failed. Manual Tuning is currently Active message is displayed when attempting to use Automatic Overclock with Intel® XTU, and buttons are disabled/grayed out.
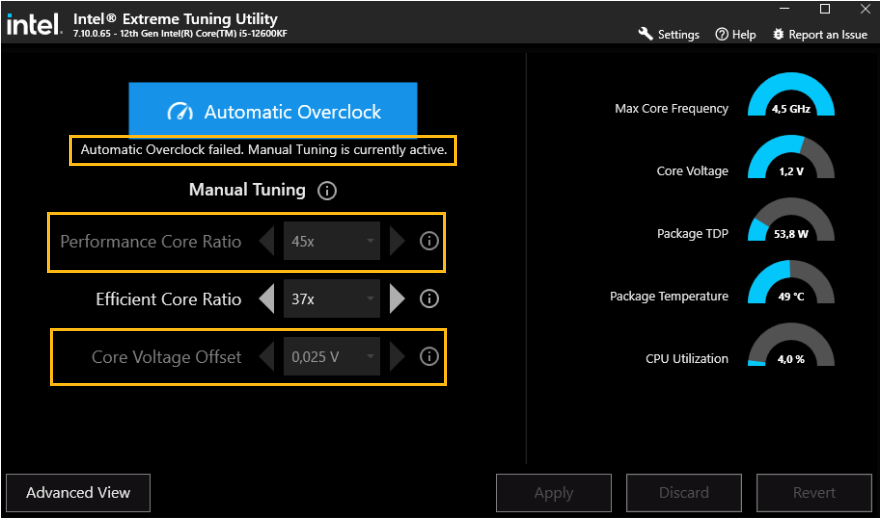
There can be a couple of reasons to why Intel® XTU Automatic Overclock Failed and some Overclocking (OC) buttons are disabled/grayed out:
| Note |
|
When Overclocking your processor consider the following: