Developer Reference for Intel® oneAPI Math Kernel Library for Fortran
A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
v?Erf
Computes the error function value of vector elements.
Syntax
call vserf( n, a, y )
call vserfi(n, a, inca, y, incy)
call vmserf( n, a, y, mode )
call vmserfi(n, a, inca, y, incy, mode)
call vderf( n, a, y )
call vderfi(n, a, inca, y, incy)
call vmderf( n, a, y, mode )
call vmderfi(n, a, inca, y, incy, mode)
Include Files
- mkl_vml.f90
Input Parameters
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
n |
INTEGER, INTENT(IN) |
Specifies the number of elements to be calculated. |
a |
DOUBLE PRECISION for vderf, vmderf REAL, INTENT(IN) for vserf, vmserf DOUBLE PRECISION, INTENT(IN) for vderf, vmderf |
Array, specifies the input vector a. |
inca, incy |
INTEGER, INTENT(IN) |
Specifies increments for the elements of a and y. |
mode |
INTEGER(KIND=8), INTENT(IN) |
Overrides global VM mode setting for this function call. See vmlSetMode for possible values and their description. |
Output Parameters
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
y |
DOUBLE PRECISION for vderf, vmderf REAL, INTENT(OUT) for vserf, vmserf DOUBLE PRECISION, INTENT(OUT) for vderf, vmderf |
Array, specifies the output vector y. |
Description
The Erf function computes the error function values for elements of the input vector a and writes them to the output vector y.
The error function is defined as given by:
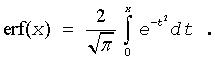
Useful relations:

where erfc is the complementary error function.
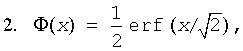
where
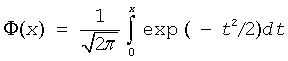
is the cumulative normal distribution function.
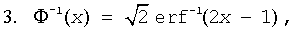
where Φ-1(x) and erf-1(x) are the inverses to Φ(x) and erf(x) respectively.
The following figure illustrates the relationships among Erf family functions (Erf, Erfc, CdfNorm).
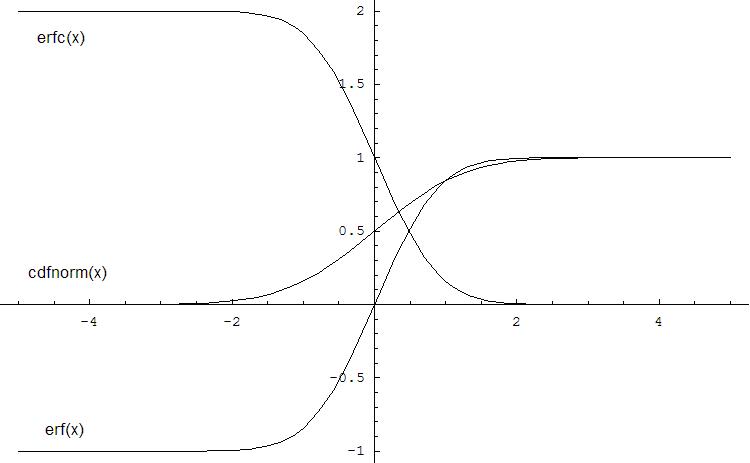
Useful relations for these functions:
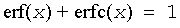
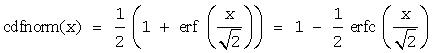
| Argument | Result | Exception |
|---|---|---|
| +∞ | +1 | |
| -∞ | -1 | |
| QNAN | QNAN | |
| SNAN | QNAN | INVALID |