A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
multinomial
Generates multinomially distributed random numbers.
Description
The multinomial class object is used in the generate function to provide multinomially distributed random numbers with ntrial independent trials and k possible mutually exclusive outcomes, with corresponding probabilities 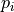 , where
, where 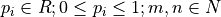 .
.
The probability distribution is given by:
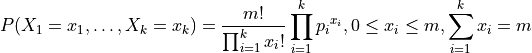
Product and Performance Information |
|---|
Performance varies by use, configuration, and other factors. Learn more at https://www.intel.com/PerformanceIndex. Notice revision #20201201 |
API
Syntax
namespace oneapi::mkl::rng {
template<typename IntType = std::int32_t,
typename Method = multinomial_method::by_default>
class multinomial {
public:
using method_type = Method;
using result_type = IntType;
explicit multinomial(double ntrial, std::vector<double> p); // deprecated since oneMKL 2023.0
explicit multinomial(double ntrial, sycl::span<double> p);
explicit multinomial(const param_type& pt);
std::int32_t ntrial() const;
std::vector<double> p() const;
param_type param() const;
void param(const param_type& pt);
};
}Devices supported: CPU and GPU
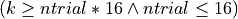 , where k is the probability vector length.
, where k is the probability vector length.
Include Files
oneapi/mkl/rng.hpp
Template Parameters
typename IntType = std::int32_t |
Type of the produced values. The specific values are as follows: std::int32_t std::uint32_t |
typename Method = oneapi::mkl::rng::multinomial_method:: by_default |
Generation method. The specific values are as follows: oneapi::mkl::rng::multinomial_method::poisson_icdf_based See brief descriptions of the methods in Distributions Template Parameter Method. |
Input Parameters
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
ntrial |
std::int32_t |
Number of independent trials m. |
p |
sycl::span<double> |
Probability vector of possible outcomes (length is k). |
- explicit multinomial(double ntrial, std::vector<double> p); is deprecated and will be removed in one of the next releases. Use explicit multinomial(double ntrial, sycl::span<double> p); instead.
When passing a sycl::span that is constructed over a user’s memory to the constructor, users must manage the memory under sycl::span by themselves. They must not destroy the memory while data are processed.