Intel® oneAPI Math Kernel Library (oneMKL) - Data Parallel C++ Developer Reference
A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
oneapi::mkl::rng::negative_binomial
Generates random numbers with negative binomial distribution.
Description
The oneapi::mkl::rng::negative_binomial class object is used in the oneapi::mkl::rng::generate function to provide random numbers with negative binomial distribution and distribution parameters a and p, where p, a∈R; 0 < p < 1; a > 0.
If the first distribution parameter a∈N, this distribution is the same as Pascal distribution. If a∈N, the distribution can be interpreted as the expected time of a-th success in a sequence of Bernoulli trials, when the probability of success is p.
The probability distribution is given by:

The cumulative distribution function is as follows:
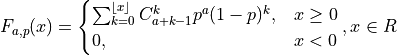
Product and Performance Information |
|---|
Performance varies by use, configuration and other factors. Learn more at https://www.intel.com/PerformanceIndex. Notice revision #20201201 |
API
Syntax
template<typename IntType = std::int32_t, typename Method = negative_binomial_method::by_default>
class negative_binomial {
public:
using method_type = Method;
using result_type = IntType;
negative_binomial(): negative_binomial(0.1, 0.5){}
explicit negative_binomial(double a, double p);
explicit negative_binomial(const param_type& pt);
double a() const;
double p() const;
param_type param() const;
void param(const param_type& pt);
};
Devices supported: CPU and GPU
Include Files
oneapi/mkl/rng.hpp
Template Parameters
typename IntType = std::int32_t |
Type of the produced values. The specific values are as follows: std::int32_t std::uint32_t |
typename Method = oneapi::mkl::rng::negative_binomial_method::by_default |
Generation method. The specific values are as follows: oneapi::mkl::rng::negative_binomial_method::nbar See brief descriptions of the methods in Distributions Template Parameter Method. |
Input Parameters
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
a |
double |
The first distribution parameter a. |
p |
double |
The second distribution parameter p. |