Intel® oneAPI Deep Neural Network Developer Guide and Reference
A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
Primitive Attributes: dropout
Introduction
In many DNN and GNN models, Dropout is used to improve training results. In some cases this layer can take a significant amount of time. To enhance training performance, optimize dropout by fusing it with the primitive.
Implementation
In oneDNN, dropout is a special operation akin to a binary post-op that gets applied to the output values of a primitive right before post-ops. It depends on a deterministic PRNG (current implementation uses a variation of Philox algorithm) and transforms the values as follows:
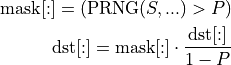
where:
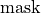 is the output buffer (always of the same dimensions and usually of the same layout as
is the output buffer (always of the same dimensions and usually of the same layout as 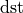 , but potentially differing from it in type that can only be u8) whose values may be either 0 if the corresponding value in
, but potentially differing from it in type that can only be u8) whose values may be either 0 if the corresponding value in 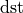 got zeroed (a.k.a. dropped out) or 1 otherwise
got zeroed (a.k.a. dropped out) or 1 otherwise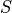 is the integer seed for the PRNG algorithm
is the integer seed for the PRNG algorithm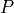 is the probability for any given value to get dropped out,
is the probability for any given value to get dropped out, 
API
C: dnnl_primitive_attr_get_dropout, dnnl_primitive_attr_set_dropout
C++: dnnl::primitive_attr::get_dropout, dnnl::primitive_attr::set_dropout
If the dropout operation gets specified in the primitive’s attributes, the user must provide three additional buffers to it on execution:
DNNL_ARG_ATTR_DROPOUT_MASK : through this ID the user has to pass the
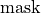 output buffer
output bufferDNNL_ARG_ATTR_DROPOUT_PROBABILITY : this is a single-value f32 input buffer that holds
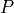
DNNL_ARG_ATTR_DROPOUT_SEED : this is a single-value s32 input buffer that holds