A New Memory Class in the Latest Generation of Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors Rewrites the Performance Equation

With its official launch on April 2, the 2nd generation of Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors now includes support for Intel® Optane™ DC persistent memory. This introduces a flexible new tier to the traditional data center memory and storage hierarchy, architected specifically for data center usage. By deploying systems enabled by this new class of memory, customers can now optimize their workloads more effectively by moving and maintaining larger amounts of data closer to the processor, minimizing the higher latency that can occur when fetching data from system storage.
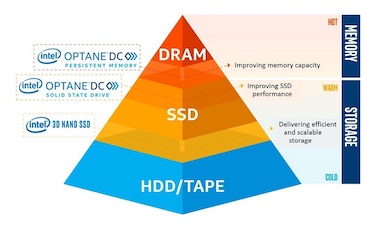
The importance of this innovation is that it fundamentally liberates the availability and flow of data, replacing methods that have been used for decades. Intel Optane DC persistent memory revolutionizes the performance calculation with big, affordable, persistent storage on the memory bus.
Independent software vendors (ISVs) are already using Intel Optane DC persistent memory to achieve lower latency, higher throughput, and greater application performance. Consider these three use cases and the operational benefits each business derives by deploying Intel’s innovative new approach to memory and storage.
Increased Capacity
AsiaInfo* Technologies Accelerates Business Applications
 AsiaInfo* Technologies, China’s largest business support systems (BSS) provider, serves an array of regional telecom carriers – and is busily gearing up for the inevitable arrival of 5G industrial internet in China, with vastly greater data rates to support a wealth of new applications. AsiaInfo expects the global digital BSS market to more than double over five years, rising to $5.8 billion by 20231. This massive expansion of data and new usage models will place unprecedented demands on its BSS infrastructure.
AsiaInfo* Technologies, China’s largest business support systems (BSS) provider, serves an array of regional telecom carriers – and is busily gearing up for the inevitable arrival of 5G industrial internet in China, with vastly greater data rates to support a wealth of new applications. AsiaInfo expects the global digital BSS market to more than double over five years, rising to $5.8 billion by 20231. This massive expansion of data and new usage models will place unprecedented demands on its BSS infrastructure.
To help drive that growth, AsiaInfo is rising to the challenge through BSS transformation that spans both software and hardware. With software optimizations targeted for optimal use of Intel Optane DC persistent memory, AsiaInfo is able to reduce query response latencies for a better customer experience.
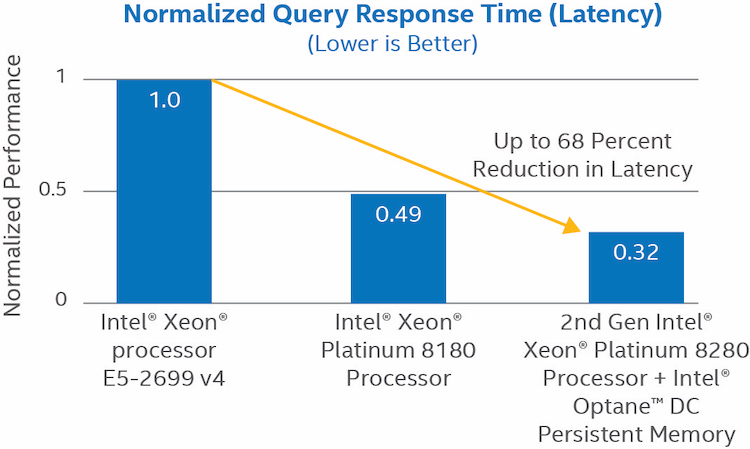
Figure 1. Intel® Optane™ DC persistent memory reduces query response time (i.e., latency) for AsiaInfo* BSS.2
AsiaInfo has leveraged this new persistent memory technology to deliver improved value to their customers by re-architecting their memory subsystem making it the primary data tier for both working data and long-term storage. It combines byte-addressability similar to dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) with storage-like persistence. That combination means it can be mapped directly into application address space, eliminating bottlenecks typically associated with reads and writes to conventional storage.
Thanks to new 2nd generation Intel Xeon Scalable processor support for Intel Optane DC persistent memory, AsiaInfo is increasing its capacity to achieve faster response times on complex queries, all at a similar cost to DRAM-only solutions. This enables AsiaInfo to provision its BSS servers with larger amounts of total memory without increasing system expense. AsiaInfo now has the capacity to store more data closer to the processor, where it can be rapidly accessed for more responsive service.
Learn how AsiaInfo was able to achieve these results in this solution brief: Accelerating Telecom Business Software with Intel® Optane™ DC Persistent Memory.
Affordability
Redis* Labs Resolves the Cost vs. Capacity Trade-off
 In-memory databases (IMDBs) are popular for their ability to reduce latency by holding an entire dataset in active system memory. However, achieving that increased speed and responsiveness advantage can be cost-prohibitive, forcing many businesses to compromise between performance, scalability, and budgetary realities.
In-memory databases (IMDBs) are popular for their ability to reduce latency by holding an entire dataset in active system memory. However, achieving that increased speed and responsiveness advantage can be cost-prohibitive, forcing many businesses to compromise between performance, scalability, and budgetary realities.
In other words, responsiveness or affordability: take your pick. But now, the maker of one multi-model IMDB, Redis* Enterprise, is choosing both, by deploying new memory configurations based on Intel Optane DC persistent memory.
Redis* Labs has collaborated closely with Intel to optimize the Redis Enterprise database for Intel Optane DC persistent memory, achieving sub-millisecond latency at a cost lower than traditional DRAM. This new persistent memory technology allows Redis to enable larger memory capacities so that more hardware can be consolidated which in turn reduces the total cost of ownership, making it more affordable.
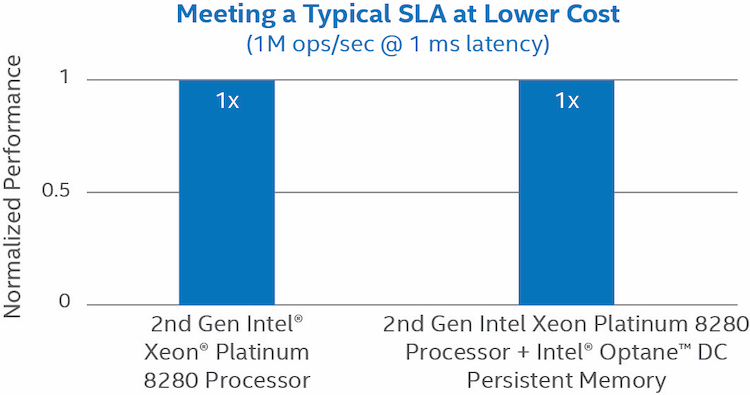
Figure 2. Maintaining a typical customer service level agreement (SLA) with reduced server cost.3
As Redis has demonstrated, data centers can now utilize 2nd generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors with Intel Optane DC technology to provision servers with unprecedented system memory capacities at lower cost than DRAM-only configurations. With Intel Optane DC persistent memory, developers can now place data in a flexible new tier that delivers dramatically improved performance versus traditional storage, at a vastly more affordable cost.
Read how Redis reduces total cost of ownership, making memory more affordable, in this solution brief: Break the Cost and Capacity Barrier with Intel® Optane™ DC Persistent Memory.
Persistence
Aerospike* Achieves Greater Uptime Through Persistent Memory
 For nearly a decade, Aerospike* and Intel have worked together to provide real-time computing availability, with the performance and scale to support high-volume transactions and analytics on a single data platform. Leading companies rely on these capabilities to integrate smarter, faster decision-making into critical business processes. With the latest generation of Intel Xeon Scalable processors, Aerospike and Intel are dramatically enhancing these capabilities in Aerospike* Enterprise Edition 4.5, featuring deep optimizations for Intel Optane DC persistent memory. This new Aerospike offering is able to provide unprecedented scale for real-time computing, at affordable cost, and with even higher availability than traditional DRAM-only solutions.4
For nearly a decade, Aerospike* and Intel have worked together to provide real-time computing availability, with the performance and scale to support high-volume transactions and analytics on a single data platform. Leading companies rely on these capabilities to integrate smarter, faster decision-making into critical business processes. With the latest generation of Intel Xeon Scalable processors, Aerospike and Intel are dramatically enhancing these capabilities in Aerospike* Enterprise Edition 4.5, featuring deep optimizations for Intel Optane DC persistent memory. This new Aerospike offering is able to provide unprecedented scale for real-time computing, at affordable cost, and with even higher availability than traditional DRAM-only solutions.4
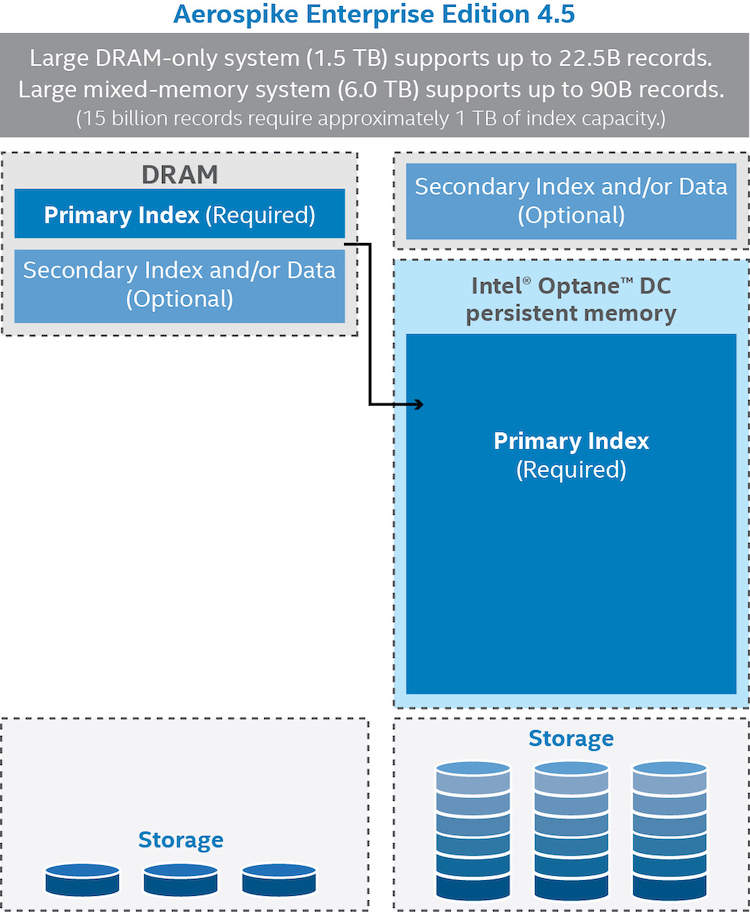
Figure 3. Aerospike* 4.5 with Intel® Optane™ DC persistent memory increases scalability by up to 4X versus DRAM-only solutions, while improving reliability and providing the same levels of performance.5
Besides enabling more memory and larger data volumes per server, Intel Optane DC persistent memory also supports high availability. That is, database indexes can be retained in persistent memory so that when systems are powered down for any reason, they can typically be restarted in a matter of seconds with the data intact in memory. For planned reboots, database startup times can be reduced by as much as 135 times.6
This enables non-disruptive maintenance for reduced downtime – software can be updated, security patches performed, and redundancy requirements easily met – all at a potentially lower cost.
Find out how Aerospike achieves greater uptime in this solution brief: Affordable Real-Time Computing at Petabyte Scale.
Persistent Memory: Where Memory and Storage Converge
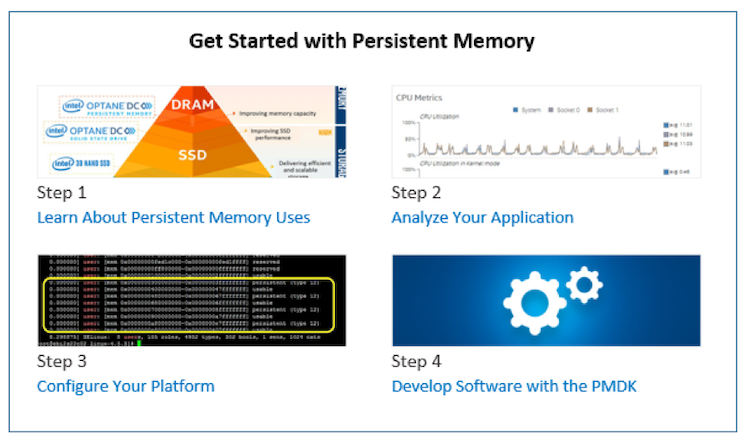
Develop innovative solutions that maximize memory capacity, data resiliency, and performance using Intel Optane DC persistent memory. Use these four steps to Get Started with Persistent Memory: address your memory challenges, analyze your application, configure Intel Optane DC memory modules, and develop software with the Persistent Memory Development Kit (PMDK).
Leverage a New Class of Memory Capacity, Affordability and Persistence
Learn about the game-changing advantages of building Intel Optane DC persistent memory into your data center solutions to reduce latency, increase uptime, and make DRAM-like performance more affordable.
Learn How Businesses are Using Intel® Optane™ DC Persistent Memory
- AsiaInfo* Solution Brief: Accelerating Telecom Business Software with Intel® Optane™ DC Persistent Memory
- Redis* Labs Solution Brief: Break the Cost and Capacity Barrier with Intel® Optane™ DC Persistent Memory
- Aerospike* Solution Brief: Affordable Real-Time Computing at Petabyte Scale
- Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors ISV Partners: Partners Deliver Enterprise-Scale Solutions
- Video: Gigaspaces* Drives Data-Intensive Use Cases
- Video: Virtuozzo* Scales Service Delivery
Transform Your Applications with Intel® Persistent Memory
Give your programs more room to run. Intel® persistent memory revolutionizes the performance equation with big, affordable, persistent storage on the memory bus. Use it to achieve lower latency, higher resilience, and more performance for your applications.
Visit Persistent Memory in the Intel® Developer Zone and join the memory revolution!
1 PR Newswire, “Global Digital Business Support System (BSS) market size to grow at a CAGR of 15.2%, https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/global-digital-business-support-system-bss-market-size-to-grow-at-a-cagr-of-15-2-300763635.html.
2 AsiaInfo Telco BSS* 3.1.1 + self-defined workload. OS: Red Hat Enterprise Linux* 7.5 kernel 3.10.0-957.1.3.el7.x86_64. Testing by Intel and AsiaInfo completed on Dec 28, 2018. Security Mitigations for Variants 1, 2, 3 and L1TF in place.
BASELINE: 2S Intel® Xeon® processor E5-2699 v4, 2.5 GHz, 18 cores, turbo and HT on, BIOS 251R01, 256 GB total memory, 32 slots / 32 GB / 1600 MT/s / DDR4 LRDIMM, 7 x 800 GB, Intel® SSD Data Center (Intel® SSD DC) S3700 + 4 2-TB Intel® SSD Data Center Family for NVMe*.
NEXT GEN: Intel® Xeon® Platinum 8180 processor, 2.5 GHz, 28 cores, turbo and HT on, BIOS x0007, 768 GB total memory, 32 slots / 32 GB / 1600 MT/s / DDR4 LRDIMM, 7 x 800 GB, Intel SSD DC S3700 + 4 2-TB Intel SSD Data Center Family for NVMe.
NEW: 2nd Gen Intel® Xeon® Platinum 8280 processor, 2.7 GHz, 28 cores, turbo and HT on, BIOS 1.018, 192 GB total memory, 12 slots / 16 GB / 1600 MT/s / DDR4 LRDIMM and 8 slots/ 128 GB / Intel® Optane™ DC persistent memory, 7 x 800 GB, Intel SSD DC S3700 + 4 2-TB Intel SSD Data Center Family for NVMe.
Performance results are based on testing as of Dec 28, 2018 and may not reflect all publicly available security updates. See configuration disclosure for details. No product can be absolutely secure.
3 Testing by Intel, 2/14/2019. Memtier benchmark. Redis Enterprise 5.4. Dataset created with 6 billion key/value pairs and 100 B keys (roughly 1 TB of data set). The test workload used 50/50 puts/ gets with a random distribution.
BASELINE: One node based on 2x 2nd Generation Intel® Xeon® Platinum 8280L processor (28 cores/56 threads per socket); ucode 0x4000013; Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology (Intel® HT Technology) and Intel® Turbo Boost Technology enabled; BIOS version: SE5C620.86B.0D.01.0286.011120190816; system DDR memory configuration: 1.5 TB (12x64 GB / 2666) per socket; total memory per node: 1.5 TB DDR; storage (boot): INTEL SSDSC2KB96, 1 TB; 2x Intel® Ethernet Converged Network Adapter for 40 GbE QSFP+; CentOS* Linux* 7 (Core); kernel: 4.19.8; run method: warm, data averaged over a five-minute interval; iterations and result choice: three runs (average). Raw results: 2.51 ops/sec @ 1 ms latency.
NEW: One node based on 2x 2nd Gen Intel Xeon Platinum 8280L processor (28 cores/56 threads per socket); ucode 0x4000013; Intel Hyper-Threading Technology and Intel Turbo Boost Technology enabled; BIOS version: SE5C620.86B.0D.01.0286.011120190816; BKC version: WW 4 2019 BKC; Intel® Optane™ DC Persistent Memory firmware version: 5336; system DDR memory configuration: 192 GB (6x16 GB / 2666) per socket; system Intel Optane DC Persistent Memory configuration: 1.5 TB (6x 128 GB / 2666) per socket; total memory per node: 192 GB DDR; 1.5 TB Intel Optane DC Persistent Memory; storage (boot): INTEL SSDSC2KB96, 1 TB; 2x Intel Ethernet Converged Network Adapter for 40 GbE QSFP+; CentOS Linux 7 (Core); kernel: 4.19.8; AEP mode: 2LM; run method: warm, data averaged over a five-minute interval; iterations and result choice: three runs (average). Raw results: 2.06 ops/sec @ 1 ms latency.
Performance results may not reflect all publicly available security updates. See configuration disclosure for details. No product can be absolutely secure.
Performance results are provided to you for informational purposes. Any differences in your system hardware, software or configuration may affect your actual performance.
4 Tests performed by Intel and Aerospike as of 27 February 2019 demonstrated that a server configured with DRAM + Intel® Optane™ DC persistent memory provided 95.74 percent of the performance of a system configured with an equivalent amount of DRAM-only memory. Baseline configuration: Intel® Xeon® Platinum processor 8280 (2.7 GHz, 28 cores), 1.5 TB total memory (24 x 64 GB @ 2666 MT/s DDR4 LRDIMM), 1 x Intel® SSD DC S3700 (800 GB) + 7 x Intel® SSD P4510 (2 TB) 2.5” PCIe, CentOS Linux* 7.4 kernel 4.19.8. New Configuration: Intel® Xeon® Platinum processor 8280 (2.7 GHz, 28 cores), 192 GB total memory, 12 slots x 16 GB @ 2666 MT/s DDR4 RDIMM plus 12 slots x 128 GB Intel® Optane™ DC persistent memory, 1 x Intel SSD DC S3700 (800 GB) plus 7 x Intel SSD P4510 (2 TB) 2.5” PCIe, CentOS Linux* 7.4 kernel 4.19.8.
5 The 4X increase in memory per server is based on a typical, two-socket server configured with 24 x 64 GB DRAM DIMMs (= 1.5 TB of memory) versus the same server configured with 12 x 512 GB Intel® Optane™ DC persistent memory modules (= 6.0 TB of memory).
6 Tests performed by Intel and Aerospike as of 27 February 2019 demonstrated that an 8.7 TB database could be restarted in as little as 35 seconds on a server configured with DRAM + Intel® Optane™ DC persistent memory versus up to 4,745 seconds (1 hr 19 m 5 s) on a server configured with an equivalent amount of DRAM-only memory. Baseline configuration: Intel® Xeon® Platinum processor 8280 (2.7 GHz, 28 cores), 1.5 TB total memory (24 x 64 GB @ 2666 MT/s DDR4 LRDIMM), 1 x Intel® SSD DC S3700 (800 GB) + 7 x Intel® SSD P4510 (2TB) 2.5” PCIe, CentOS Linux* 7.4 kernel 4.19.8. New Configuration: Intel® Xeon® Platinum processor 8280 (2.7 GHz, 28 cores), 192 GB total memory, 12 slots x 16 GB @ 2666 MT/s DDR4 RDIMM plus 12 slots x 128 GB Intel® Optane™ DC persistent memory, 1 x Intel SSD DC S3700 (800 GB) plus 7 x Intel SSD P4510 (2 TB) 2.5” PCIe, CentOS Linux* 7.4 kernel 4.19.8.
All information provided here is subject to change without notice. Contact your Intel representative to obtain the latest Intel product specifications and roadmaps.
Intel® technologies’ features and benefits depend on system configuration and may require enabled hardware, software or service activation. Performance varies depending on system configuration. Check with your system manufacturer or retailer or learn more at intel.com.
Intel processors of the same SKU may vary in frequency or power as a result of natural variability in the production process.
For more complete information about performance and benchmark results, visit www.intel.com/benchmarks.
Intel does not control or audit third-party benchmark data or the web sites referenced in this document. You should visit the referenced web site and confirm whether referenced data are accurate.
Performance results are based on testing and may not reflect all publicly available security updates. See configuration disclosure for details. No product can be absolutely secure.
Software and workloads used in performance tests may have been optimized for performance only on Intel microprocessors. Performance tests, such as SYSmark and MobileMark, are measured using specific computer systems, components, software, operations and functions. Any change to any of those factors may cause the results to vary. You should consult other information and performance tests to assist you in fully evaluating your contemplated purchases, including the performance of that product when combined with other products. For more information go to http://www.intel.com/performance/datacenter.
Optimization Notice: Intel’s compilers may or may not optimize to the same degree for non-Intel microprocessors for optimizations that are not unique to Intel microprocessors. These optimizations include SSE2, SSE3, and SSSE3 instruction sets and other optimizations. Intel does not guarantee the availability, functionality, or effectiveness of any optimization on microprocessors not manufactured by Intel. Microprocessor-dependent optimizations in this product are intended for use with Intel microprocessors. Certain optimizations not specific to Intel microarchitecture are reserved for Intel microprocessors. Please refer to the applicable product User and Reference Guides for more information regarding the specific instruction sets covered by this notice. Notice Revision #20110804.
Cost reduction scenarios described are intended as examples of how a given Intel-based product, in the specified circumstances and configurations, may affect future costs and provide cost savings. Circumstances will vary. Intel does not guarantee any costs or cost reduction.
No license (express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise) to any intellectual property rights is granted by this document.
Intel disclaims all express and implied warranties, including without limitation, the implied warranties of merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose, and non-infringement, as well as any warranty arising from course of performance, course of dealing, or usage in trade.
This document contains information on products, services and/or processes in development. All information provided here is subject to change without notice. Contact your Intel representative to obtain the latest forecast, schedule, specifications and roadmaps.
The products and services described may contain defects or errors known as errata which may cause deviations from published specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
Intel, the Intel logo, Intel Optane, and Xeon are trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and other countries.
*Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners.