Intel C++ Compiler 19.0 for Linux* Release Notes for Intel Parallel Studio XE 2019
This document provides a summary of new and changed product features and includes notes about features and problems not described in the product documentation.
Please see the licenses included in the distribution as well as the Disclaimer and Legal Information section of these release notes for details. Please see the following links for information on this release of the Intel® C++ Compiler 19.0 .
- Change History
- System Requirements
- How to Use
- Documentation
- Japanese Language Support
- Intel-provided debug solutions
- Samples
- Technical Support
- New and Changed Features in 19.0
- Parallel STL for parallel and vector execution of the C++ STL
- Support deprecated
- Support removed
- Known Limitations
- Disclaimer and Legal Information
Change History
Changes since update 6 (New in Intel® C++ Compiler 19.0.9)
This is release for Intel® Compilers 2019 Update 7, compilers version 19.0.9. Highlights for this release:
- 2019 Update 7 is provided for Linux only.
- 2019 Update 7 is only released in Composer Edition. No Profession or Cluster Edition packages are provided for this update.
- 2019 Update 7 is only a Compiler update. No other components have changed since PSXE 2019 Update 6.
- Only the Intel® C++ Compiler has changed. It has a fix for a minor issue related to the _mm_prefetch intrinsic. If you do not use the _mm_prefetch you will get no benefit from this update.
- 2019 Update 7 has no fixes for the Fortran Compiler.
- Both C++ and Fortran Compilers have updated license checking library files to address potential security issues.
The compiler version appears in the version string as version 19.0.9 in this PSXE 2019 Update 7. This is due to compiler updates released outside of Parallel Studio packages that used compiler versions 19.0.7 and 19.0.8. For details on compiler versions included in Parallel Studio releases please visit Intel compiler and Composer Update Version Numbers to Compiler Version Number Mapping.
Changes since Intel® C++ Compiler 19.0.5 (New in Intel® C++ Compiler 19.0.8)
This is release for Intel® Compilers 2019 Update 8, compilers version 19.0.8. Highlights for this release:
- Intel(R) Parallel Studio XE 2019 Update 6 Composer Edition contains Compiler Update 8.
- Compilers Update 6 and 7 are not available to the general public.
- Compilers Update 6 and 7 were special releases not available to all customers.
- New compiler option -m[no-]branches-within-32B-boundaries
- Corrections to reported problems
- Includes certain functional and security updates. We recommend updating for these functional and security updates.
Changes since Intel® C++ Compiler 19.0.4 (New in Intel® C++ Compiler 19.0.5)
- Includes certain functional and security updates. We recommend updating for these functional and security updates.
- Corrections to reported problems
- Floating License Server Upgrade Required
- For Linux: The Intel® C++ Compiler in this update includes a new -qnextgen compiler option that uses leverages Next Generation Technology. See the special Additional Requirements for ICC NextGen for more details.
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux* 8 support
Changes since Intel® C++ Compiler 19.0.3
(New in Intel® C++ Compiler 19.0.4 Eng/Jpn build 243)
IRC post date 05/23/2019
This is the final release of 2019 Update 4.
- Includes certain functional and security updates. We recommend updating for these functional and security updates.
- Corrections to reported problems
Changes since Intel® C++ Compiler 19.0.3
(New in Intel® C++ Compiler 19.0.4 build 227)
IRC post date 05/06/2019
This is the initial release of 2019 Update 4. This was released in Linux* and Windows* packages only (no macOS* release).
This compiler is only available in the Intel® Registration Center in packages for:
- Intel® Parallel Studio XE Composer Edition for Fortran and C++ Linux, 2019 Update 4 227
- Intel® Parallel Studio Composer Edition for Fortran and C++ Windows, 2019 Update 4 228
This version provides initial support for VS2019 Integrations and includes certain functional and security updates. We recommend updating for these functional and security updates. The default version "Update 4 Eng/Jpn" build should be used as it is the latest Update 4 compiler (see above). If you are macOS* user there was no "Update 4 initial" compiler release (see Update 4 Eng/Jpn above).
IRC LINKS: Download the "Update 4 227 or 228" compilers with the links below:
- For Linux*
- For Windows*
These packages contain both the Intel® C++ Compiler and the Intel® Fortran Compiler. During installation you can select one or both compilers using the CUSTOM installation options.
For your next steps, use this table and the notes that follow the table:
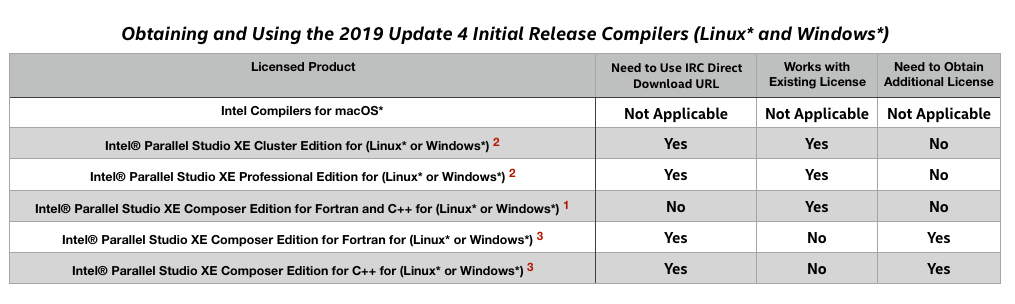
- If you are a licensed user of Intel Parallel® Studio XE Composer Edition for Fortran and C++ (Linux* or Windows*) you can find the "Update 4 227 or 228" compiler in your Downloads in Intel® Registration Center. It is not the default for Update 4. Use the Prior versions pull-down selector to find this "Update 4 227 or 228" release.
- If you are a licensed user of CLUSTER Edition or PROFESSIONAL Edition you will not see the download for this package in your IRC Products downloads list. Use the IRC LINKS above to directly download the package for your OS. Your existing license for CLUSTER Edition or PROFESSIONAL Edition will work with the "Update 4 initial" packages and compilers.
- Licensed users of the Composer Edition for Fortran or the Composer Edition for C++ use the IRC LINKS above to directly download the package for your OS. You will also need a new license which we will provide for the combined C++ and Fortran product Intel® Parallel Studio XE Composer Edition for Fortran and C++ (for your OS) - visit Technical Support and request your license. Make sure to indicate Linux* or Windows* or both. Again, this does not apply to macOS*.
Changes in this version:
- Includes certain functional and security updates. We recommend updating for these functional and security updates.
- Corrections to reported problems
Changes since Intel® C++ Compiler 19.0.2 (New in Intel® C++ Compiler 19.0.3)
- Corrections to reported problems
Changes since Intel® C++ Compiler 19.0.1 (New in Intel® C++ Compiler 19.0.2)
- Intel® C++ Compiler 19.0 Update 2 includes functional and security updates. Users should update to the latest version.
Changes since Intel® C++ Compiler 19.0 (New in Intel® C++ Compiler 19.0.1)
- Value safe simd options for #pragma omp simd
- New code names are to be supported in -[Q]x / -[Q]ax / -[m]tune / -[m]arch options.
- Custom memory allocator library
Changes since Intel® C++ Compiler 18.0 (New in Intel® C++ Compiler 19.0)
- Support for user defined induction for OpenMP* parallel pragmas
- Support for exclusive scan simd
- Bug fixes, including resolving a glibc issue on Ubuntu 18.04
- -openmp-simd set by default
- -rcd option deprecated
- support for cannonlake option
- Changes to mitigate speculative executive side channel and new -mindirect-branch option. Please see detailed article at Using Intel® Compilers to Mitigate Speculative Execution Side-Channel Issues available at /content/www/us/en/develop/articles/using-intel-compilers-to-mitigate-speculative-execution-side-channel-issues.html)
- New C++17 features supported
- nodynamic_align and vectorlength clauses for pragma vector
- Expanded partial support for OpenMP* TR6 Version 5.0 Preview 2
- New and changed compiler options
System Requirements
- 2GB of RAM (4GB recommended)
- 7.5GB free disk space for all features
- One of the following Linux distributions (this is the list of distributions tested by Intel; other distributions may or may not work and are not recommended - please refer to Technical Support if you have questions):
- Debian* 8.0, 9.0
- Fedora* 27,28
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux* 6, 7
- SUSE LINUX Enterprise Server* 12 (SP5), 15
- Ubuntu* 18.04 LTS, 17.10
- CentOS 7.1, 7.2
- Intel® Cluster Ready
- Linux Developer tools component installed, including gcc, g++ and related tools
- gcc versions 4.3 - 8.x supported
- binutils versions 2.20-2.29 supported
- Library libunwind.so is required in order to use the -traceback option. Some Linux distributions may require that it be obtained and installed separately.
Additional Requirements to use the -qnextgen Option
- Linux Requirements:
- Ubuntu 18.04 or greater
- Redhat 8 - NOTE Redhat 7 NOT SUPPORTED
- Fedora 30, 31
- SLES 15
- Distributions based on the above should work but are not formally tested
- gcc versions: requires gcc versions 7.3 or greater (no older gcc versions supported)
- binutils 2.29.1 or greater
- glibc 2.26 or greater
Additional requirements to use the integration into the Eclipse* development environment
- Eclipse Platform version 4.7 with:
- Eclipse C/C++ Development Tools (CDT) 9.3.x
- Java* Runtime Environment (JRE) 8.0 (also called 1.8) or later
- Eclipse Platform version 4.8 with:
- Eclipse C/C++ Development Tools (CDT) 9.5.x
- Java* Runtime Environment (JRE) 7.0 (also called 1.8) or later
Notes
- The Intel compilers are tested with a number of different Linux distributions, with different versions of gcc. Some Linux distributions may contain header files different from those we have tested, which may cause problems. The version of glibc you use must be consistent with the version of gcc in use. For best results, use only the gcc versions as supplied with distributions listed above.
- Compiling very large source files (several thousands of lines) using advanced optimizations such as -O3, -ipo and -openmp, may require substantially larger amounts of RAM.
- Some optimization options have restrictions regarding the processor type on which the application is run. Please see the documentation of these options for more information.
How to use the Intel® C++ Compiler
Parallel Studio XE 2019: Getting Started with the Intel® C++ Compiler 19.0 for Linux* at /documentation_2019/en/compiler_c/ps2019/get_started_lc.htm. contains information on how to use the Intel® C++ Compiler from the command line and from Linux*.
The Intel® C++ Compiler for Linux* does not provide "modulefiles" for usage with the Environmental Modules software utility, but is well suited for such usage. See Using Environment Modules with Intel Development Tools for further information.
Documentation
Product documentation is linked from /documentation_2019/en/compiler_c/ps2019/get_started_lc.htm. Full documentation for all tool components is available at the Intel® Parallel Studio XE Support page.
Offline Core Documentation Removed from the Installed Image
Offline core documentation is removed from the Intel® Parallel Studio XE installed image. The core documentation for the components of Intel® Parallel Studio XE are available at the Intel® Software Documentation Library for viewing online. You can also download an offline version of the documentation from the Intel® Software Development Products Registration Center: Product List > Intel® Parallel Studio XE Documentation.
Japanese Language Support
Intel® compilers optionally provide support for Japanese language users when the combined English-Japanese product is installed. Error messages, visual development environment dialogs and some documentation are provided in Japanese in addition to English. By default, the language of error messages and dialogs matches that of your operating system language selection.
Japanese language support is provided with update 1 of the product.
Intel-provided debug solutions
- Intel®-provided debug solutions are based GNU* GDB. Please see Intel® Parallel Studio XE 2019 Composer Edition C++ - Debug Solutions Release Notes for further information.
Samples
Product samples are now available online at Intel® Software Product Samples and Tutorials
Technical Support
If you did not register your compiler during installation, please do so at the Intel® Software Development Products Registration Center at https://lemcenter.intel.com. Registration entitles you to free technical support, product updates and upgrades for the duration of the support term.
For information about how to find Technical Support, Product Updates, User Forums, FAQs, tips and tricks, and other support information, please visit: /content/www/us/en/developer/get-help/overview.html
Note: If your distributor provides technical support for this product, please contact them for support rather than Intel.
The Intel® Software License Manager has been updated to version 2.9 for this release. You must upgrade to this version before installing Intel Parallel Studio XE 2019 Update 4 with a floating license. Please refer for more details:
Intel® Software License Manager Download
Intel® Software License Manager Release Notes
New and Changed Features
The following features are new or significantly enhanced in this version. For more information on these features, please refer to the documentation.
New compiler option -m[no-]branches-within-32B-boundaries
This option is supported in versions 19.0 update 8 of the compiler and above. The details about this option can be found in the Intel® C++ Compiler 19.1 Developer Guide and Reference.
To find more information, see the link.
Value safe simd options for #pragma omp simd
Currently "#pragma omp simd" overrides FP value and exception safe settings. The following options change that legacy behavior and produce value and exception safe code even for SIMD loops.
- Qsimd-honor-fp-model[-]: Tells the compiler to obey the selected floating-point model when vectorizing SIMD loops
- Qsimd-serialize-fp-reduction[-]: Tells the compiler to serialize floating-point reduction when vectorizing SIMD loops.
OpenMP SIMD specification and FP model flag can contradict in the requirement. Compiler’s default is to follow OpenMP specification and vectorize the loop. With this new flag, programmer can override so that the compiler follows the FP model flag instead and serialize the loop
Note1: When –qsimd-honor-fp-model is used and OpenMP SIMD reduction specification is the only thing causing serialization of entire loop addition of qsimd-serialize-fp-reduction will result in vectorization of the entire loop except reduction calculation which will be serialized.
Note2: This option does not affect auto-vectorization of loops.
New code names are to be supported in -[Q]x / -[Q]ax / -[m]tune / -[m]arch options.
code names supported :cascadelake, kabylake, coffeelake, amberlake, whiskeylake.
Custom memory allocator library
A new library "libqkmalloc" library is provided in the Intel C++ compiler 19.0 update 1. It provides a C level interface "qkmalloc()" for memory allocation. This allocation would replace standard routines.
- void* malloc(size_t size)
- void free(void* ptr)
- void* calloc(size_t nobj, size_t size)
- void* realloc(void* ptr, size_t size)
It also provides non C99 standard compliant memory allocation routine, which uses "weak" alignment void* _wmalloc(size_t size)
To use the library -
- Set the libqkmalloc.so path to the LD_PRELOAD =$INSTALL_DIR/compiler/linux/libqkmalloc.so
- Alternatively, define the linker option. Add -L and –l to indicate location and name of the library -L$QKMALLOC_LIB_PATH -lqkmalloc. Set up LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable at runtime to the library path (LD_LIBRARY_PATH="$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:$QKMALLOC_LIB_PATH").
Note:Non-Intel microprocessors runs the standard system malloc.
nodynamic_align and vectorlength clauses for pragma vector
- Explicit syntax for dynamic alignment
#pragma vector dynamic_align[(pointer)] #pragma vector nodynamic_alignWith no pointer specified, compiler behaves normally (automatically decides which pointer has to be aligned or doesn’t generate peel loop at all). With pointer specified, compiler generates peel loop for that pointer. With nodynamic_align clause, the compiler will not generate a peel loop.
- #pragma vector vectorlength(vl1,vl2, .. , vln)
#pragma vector vectorlength(vl1,vl2, .. , vln)Vectorizer chooses best vector length from the list according to cost model. If all vector length from the list are not profitable, the loop remains scalar. This pragma doesn’t force vectorization, thus it can be safely used for all loops.
Features from OpenMP* TR7 Version 5.0 Draft
Language features from the OpenMP* Technical Report 6 : Version 5.0 Preview 2 specifications are now supported.
- Explicit syntax for inclusive scan *
#pragma omp simd reduction[parallel](inscan, operator:list)
#pragma omp scan inclusive(item-list) - Explicit syntax for exclusive scan *
#pragma omp simd reduction[parallel](inscan, operator:list)
#pragma omp scan exclusive(item-list)
Prefix sum is computed correctly during vector execution - UDI for OpenMP* Parallel pragmas
#pragma omp declare induction ( induction-id : induction-type :step-type : inductor ) [collector( collector )]
For more information, see the compiler documentation or the link to the OpenMP* Specification above.
The Intel® C++ Compiler 19.0 supports the following features under the /Qstd=c++17 (Windows*) or -std=c++17 (Linux*/OS X*) options:
- Fold expressions(N4295)
- Inline variables(P0386R2)
- Construction rules for enum classes(P0138R2)
- Removing deprecated dynamic exception specifications(P0003R5)
- Make exception specifications part of the type system(P0012R1)
- constexpr lambda expressions(P0170R1)
- Lambda capture of *this(P0018R3)
- constexpr if-statements(P0292R2)
- Structured bindings(P0217R3)
- Separate variable and condition for if and switch(P0305R1)
- Please see C++17 Features Supported by Intel® C++ Compiler for an up-to-date listing of all supported features, including comparisons to previous major versions of the compiler.
The Intel® C++ Compiler 19.0 supports the following features under the /Qstd=c++14 (Windows*) or -std=c++14 (Linux*/OS X*) options:
- Please see C++14 Features Supported by Intel® C++ Compiler for an up-to-date listing of all supported features, including comparisons to previous major versions of the compiler.
The Intel® C++ Compiler 19.0 supports the following features under the /Qstd=c++11 (Windows*) or -std=c++11 (Linux*/OS X*) options:
- Please see C++11 Features Supported by Intel® C++ Compiler for an up-to-date listing of all supported features, including comparisons to previous major versions of the compiler.
The Intel® C++ Compiler supports the C11 features under the /Qstd=c11 (Windows*) or -std=c11 (Linux*/OS X*) options:
- Please see C11 Support in Intel® C++ Compiler for an up-to-date listing of all supported features, including comparisons to previous major versions of the compiler.
New and Changed Compiler Options
For details on these and all compiler options, see the Compiler Options section of the Intel® C++ Compiler 19.0 User's Guide.
- -qopenmp-simd set by default
- New -xcannonlake option
- New -mtune=cannonlake option
- -rcd option enabled “fast” float-to-integer conversions, by using round-to-nearest instead of truncating rounding. This option has been deprecated.
For a list of deprecated compiler options, see the Compiler Options section of the Intel® C++ Compiler 19.0 User's Guide.
Parallel STL for parallel and vector execution of the C++ STL
Intel(R) C++ Compiler is installed with Parallel STL, an implementation of the C++ standard library algorithms with support for execution policies.
Features/API changes
- More algorithms support parallel and vector execution policies: find_first_of, is_heap, is_heap_until, replace, replace_if.
- More algorithms support vector execution policies: remove, remove_if.
- More algorithms support parallel execution policies: partial_sort.
To learn more, please refer to article https://software.intel.com/en-us/get-started-with-pstl
Support Deprecated
Intel® Cilk™ Plus deprecated in 18.0
Intel® Cilk™ Plus is a deprecated feature since Intel® C++ Compiler 18.0. For more information see Migrate Your Application to use OpenMP* or Intel® Threading Building Blocks (Intel® TBB) Instead of Intel® Cilk™ Plus
Support Removed
Offload support for Intel® Graphics Technology has been removed
Known Limitations
Parallel STL
unseq and par_unseq policies only have effect with compilers that support '#pragma omp simd' or '#pragma simd. Parallel and vector execution is only supported for a subset of algorithms if random access iterators are provided, while for the rest execution will remain serial. Depending on a compiler, zip_iterator may not work with unseq and par_unseq policies.
Pointer Checker requires a dynamic runtime library
When using the -check-pointers option, the runtime library libchkp.so must be linked in. When using options like -static or -static-intel with -check-pointers, be aware that this dynamic library will be linked in regardless of your settings. See the article at Pointer Checker in ICC for more information.
Disclaimer and Legal Information
| Optimization Notice |
|---|
| Intel's compilers may or may not optimize to the same degree for non-Intel microprocessors for optimizations that are not unique to Intel microprocessors. These optimizations include SSE2, SSE3, and SSSE3 instruction sets and other optimizations. Intel does not guarantee the availability, functionality, or effectiveness of any optimization on microprocessors not manufactured by Intel. Microprocessor-dependent optimizations in this product are intended for use with Intel microprocessors. Certain optimizations not specific to Intel microarchitecture are reserved for Intel microprocessors. Please refer to the applicable product User and Reference Guides for more information regarding the specific instruction sets covered by this notice. Notice revision #20110804 |
INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL(R) PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, BY ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT AS PROVIDED IN INTEL'S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHATSOEVER, AND INTEL DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, RELATING TO SALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT. UNLESS OTHERWISE AGREED IN WRITING BY INTEL, THE INTEL PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED NOR INTENDED FOR ANY APPLICATION IN WHICH THE FAILURE OF THE INTEL PRODUCT COULD CREATE A SITUATION WHERE PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH MAY OCCUR.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice. Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked "reserved" or "undefined." Intel reserves these for future definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to them. The information here is subject to change without notice. Do not finalize a design with this information.
The products described in this document may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the product to deviate from published specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order.
Copies of documents which have an order number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature, may be obtained by calling 1-800-548-4725, or go to: http://www.intel.com/design/literature.htm
Intel processor numbers are not a measure of performance. Processor numbers differentiate features within each processor family, not across different processor families. Go to:
http://www.intel.com/products/processor%5Fnumber/
The Intel® C++ Compiler is provided under Intel’s End User License Agreement (EULA).
Please consult the licenses included in the distribution for details.
Intel, Intel logo, Pentium, Core, Atom, Iris, Intel® Xeon®, Intel® Xeon Phi are trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and other countries.
* Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © 2018 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.