Overview
Apple and Google are developing connectivity between smartphones and automotive infotainment systems. This connectivity uses the existing ecosystem of smartphones with the power of the car Human-Machine-Interface (HMI) system. Those who use their standalone smartphone without integrating into the car’s existing systems suffer from many difficult and thus dangerous operations. To address these problems, we introduce the “Smartphone as Next-Gen Automotive Infotainment" concept. This concept consists of several apps that are optimized for Intel® processor-based Android* devices, or incorporated with the Intel® Context Sensing SDK. In this article, we introduce several development examples such as 64-bit Android optimization, or adaptation of the Intel® Context Sensing SDK, and then explain how to integrate those into the automotive infotainment ecosystem.
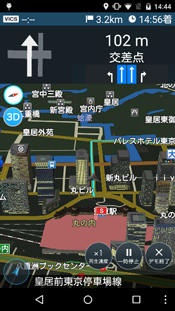
![ZENRIN Its-mo NAVI [DRIVE] ZENRIN Its-mo NAVI [DRIVE]](/content/dam/developer/articles/case-study/smartphone-as-next-gen-automotive-infotainment-concept/zenrin-its-mo-navi-drive-674880.png) Navigation Software – ZENRIN Datacom “ZENRIN Its-mo NAVI [DRIVE]”
Navigation Software – ZENRIN Datacom “ZENRIN Its-mo NAVI [DRIVE]”
Navigation software is a core component of the automotive infotainment system. We collaborated with ZENRIN Datacom, a long-established geolocation service company. They developed “ZENRIN Its-mo NAVI [DRIVE]” for Android.
With navigation software, showing the focal point means offering not only street layout and buildings, but also precise 3D terrain rendering. Thanks to full 3D architecture, users can enjoy driving with intuitive visual maps.
 Development Backgrounds
Development Backgrounds
ZENRIN Datacom is working hard to expand the automobile navigation market. Intel has worked closely with ZENRIN Datacom since Intel started working on Android optimization. For example, ZENRIN Datacom released first x86 native-supported navigation software for Android in 2012.
Focused on x86 64-bit Support
ZENRIN Datacom first became interested in 64-bit architecture because its application is graphically intensive, like mainstream gaming solutions, so wider data transfer could potentially improve performance. Due to its policy of “supporting various hardware and OS platforms aggressively,” ZENRIN Datacom focuses on code portability from the early stages of development. So supporting a 64-bit effort was a matter of simply incorporating basic methods such as working with a 64-bit register. Additionally, because of 64-bit support, the company’s application could reduce CPU load by about 20 percent1 compared to the 32-bit version. This improvement is aided by double-digit data bandwidth architecture.
1 Configuration: ASUS ZenFone* 2 ZE551ML: Intel® Atom™ processor Z3580, PowerVR G6430* graphics, 2 GB RAM, 1080x1920 resolution, CPU load measured by Intel® Graphics Performance Analyzers, Workload: Itsmo Navi [DRIVE] v2.7 32-bit/64-bit version, navigation demo mode.
 Voice Assistant Software – mia powered by netpeople* by iNAGO
Voice Assistant Software – mia powered by netpeople* by iNAGO
A vital part of a modern car infotainment system is a voice-activated system where the user can operate infotainment with voice without touching any buttons or the screen. In this category, iNAGO is one of the major “voice assistant” service providers and has a large number of adaptation achievements in car navigation systems. They also participated in developing this automotive infotainment concept.
 Development Backgrounds
Development Backgrounds
Voice interaction is one of the most suitable methods for drivers to use connected services since it does not disturb driving. iNAGO offers mia for Android to showcase its core conversational assistant technology. This app provides voice-based services such as restaurant search, local information search, weather forecasts, scheduling, mail, music, and more. iNAGO strategically collaborates with the car infotainment system to expand its usage model.
Focused on Context-Oriented Development
This app originally had a Drive mode which used a simple UI with optimized information and graphics to minimize driver distraction, but it required manual operation to change the modes. For achieving full-automated operations, iNAGO developed an external API that can be manipulated from the Intel Context Sensing SDK (described later). This can be done by just simply providing Android standard “intent” action like the following:
package name: jp.co.inago.netpeoplea
Class name: jp.co.inago.netpeoplea.NPMainActivity
name: INPUT
value: DRIVE
Thanks to this function, the user can operate optimized UIs according to the situation – when you operate it while you are not driving the normal UI is displayed. When you drive, the UI changes to DRIVE mode automatically. Also, it is vital that the user can designate a destination searched by iNAGO’s mia to ZENRIN Datacom’s navigation software. To achieve this functionality, both companies cooperated to develop APIs compatible with each other. Now these two apps operate seamlessly, as if they are a single, integrated app.
 Context Aware Software – SmarterApps’ AutomateIt
Context Aware Software – SmarterApps’ AutomateIt
SmarterApps’ app in some ways is the core software for delivering next-gen automotive infotainment. Yes, most of the built-in or mobile-device-based infotainment systems have some level of concern about what should be done in car, but they ignore “car arriving” or “car leaving” usage. To fulfill this part, we prepared the Intel Context Sensing SDK and also asked SmarterApps to deliver a full automated user experience.
Development Background
SmarterApps’ product AutomateIt* is a mobile app for Android. Users can configure rules that make the device automatically respond to certain events. This saves time and more importantly doesn’t require the driver’s attention. Actions include switching the phone to silent at night or during calendar meetings, launching the navigation app when the user starts driving, and more. In addition, SmarterApps was already working with Intel to deliver an x86 native version app, so it was a good opportunity to strengthen the relationship.
Intel® Context Sensing SDK
Intel Context Sensing SDK is a library available for Android and Windows* that helps you easily incorporate context-aware capabilities and services. This SDK includes Context APIs, which can be used to create context-aware apps by taking advantage of many built-in context type providers. In addition, when you run Intel Context Sensing SDK-powered apps on Intel® processor-based devices that have a “Sensor Hub,” the SDK automatically utilizes its function to maximize battery life.
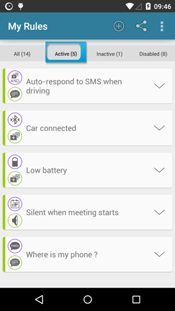 Intel Context Sensing SDK Adaptation and Car Mode Support
Intel Context Sensing SDK Adaptation and Car Mode Support
AutomateIt is built on sensing the user’s context and reacting to commands within that context, which makes the Intel Context Sensing SDK a perfect fit for the app’s core functionality. It provides a single API that wraps numerous system APIs, with the benefit of optimizing battery use on Intel processor-based devices. It also provides functions such as Activity Recognition that otherwise require using Google Play* Services library, which is not a part of Android and only exists on devices using the Google Play Store. Adapting the Intel Context Sensing SDK for the app could be done by simply adding Intel Context Sensing SDK libraries to the APK, then replacing relative APIs to those which the Intel Context Sensing SDK provided.
As part of a next-gen car infotainment system, AutomateIt added a feature that allows toggling the device to “Car Mode.” This feature lets you build rules that use the Intel Context Sensing SDK Activity Recognition feature as a trigger to identify that the user is driving and then pairs it with the new Action to activate “Car mode.”
 Context Aware Software – Neura*
Context Aware Software – Neura*
We should focus on not only the comprehensive user experience as it relates to the car, but also to the home or office locations. But how can we detect arriving or leaving from a home or office? We think Neura is one of best solutions for this usage. Neura is an AI-based awareness development platform, designed to profile, recognize, and predict the user of a mobile device. For example, after several learning periods, Neura can detect your arrival or departure automatically, and then do required actions automatically by itself or in connection with AutomateIt.
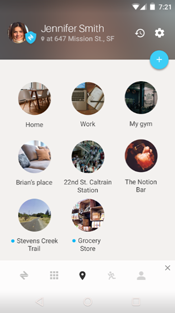 Development Background
Development Background
As a company whose mission is to create the most comprehensive digital picture of the user’s life, Neura welcomes any advancements in hardware technology that make data collection from sensors easier and more efficient. Neura believes that the future of handheld computing lies in hardware-enabled sensing solutions that are service-agnostic, such as Sensor Hub*. In addition, the Neura and Intel teams have the same philosophy of delivering next-gen user experience in cars, so working together was a natural fit.
x86 native support and Intel Context Sensing SDK Adaptation
Neura has developed x86 native architecture support, which includes just adding ”APP ABI :=x86” to the Application.mk. Neura has also optimized its sensor analysis algorithm for the test device provided by Intel, as it was the first time the system-on-chip sensor subsets were used. Because part of the test included an implementation of Intel Context Sensing SDK support, Neura has added it as well, adjusting the Machine Learning (ML) algorithms so that the utilization of the SDK became possible. The efforts to optimize Neura ML for the Intel Context Sensing SDK, which isn’t a regular part of Neura’s ML, were the biggest undertaking of the collaboration between Neura and Intel on this project.
Integrating the Four Apps into One System
Now we need to integrate the apps into one system—in this case, the Android device. We chose ASUS ZenFone 2 ZE551ML as a test device, and then installed the above apps as well as several related apps such as “car dashboard” app, which can correspond with “car mode” of Android (you can find several apps with this keyword in Google Play). In addition, we prepared specific rules for AutomateIt for arriving and leaving in a car. We used custom sensors and power plug conditions for triggers. Usually sensor monitoring sacrifices battery life because it prevent the CPU from deep sleeping, but thanks to the Intel Context Sensing SDK, this solution offloads sensor monitoring transaction to the Sensor Hub, then minimizes battery life impact. In the case of an arriving car, just attach the phone to the holder and plug to the power source; the phone immediately changes to car mode. Similarly, when you get out of the car, just unplug the power source and go, and the phone immediately goes back to normal mode. You can download the rules from AutomateIt’s rules market. Use “car infotainment” in the keyword search.
Conclusion
Working with these groups, we delivered a complete next-gen automotive infotainment system. We verified this system and confirmed its usability, and we will continue working with related vendors for further improvements. We can develop modern automotive infotainment system combining several techniques such as 64-bit Android optimization, or adaptation of the Intel Context Sensing SDK. Although this article focused on an Android target, all 4 companies always conscious about cross-platform or cross-architecture solutions, and of course Intel Context Sensing SDK also supports cross-platform solutions.
Related Vendors and Their Applications
ZENRIN DataCom provides various applications and services related to location. Its goal is to provide "reliable information centered around individual users with concern for the finer details" surpassing current information technology to provide a "service which provides the information necessary for users to take action. ”ZENRIN Its-mo NAVI [DRIVE]” is available at Google Play (Japan only).
iNAGO has led the way in Human-Computer Interaction for over a decade. Based in Tokyo and Toronto, it has worked with a variety of major companies to provide conversational personal assistants for any device, in fields ranging from mobile to finance. Their netpeople platform powers intelligent assistants that enable drivers to stay connected while keeping them safe. mia is available at Google Play (Japan only). An English version for North America is available upon request.
SmarterApps is an Israeli company developing mobile apps designed to make your smartphone smarter. The company’s main product is AutomateIt. AutomateIt is available at the Google Play.
Neura was founded in 2012 and is a leading provider of AI-based awareness development platforms. Constantly learning and adapting, Neura produces aggregated profiles of the user’s physical activity, real-time reactions to important moments in the user’s life and predictions regarding the user’s future actions. Neura is available at Google Play.
About the author
Sakemoto is Intel K.K. SSG (Software & Services Group), application engineer. He is responsible for software enabling and also he has been working with application vendors. Prior to his current job, he has been a software engineer for various mobile devices including embedded Linux* and Windows.