The Intel® Server System D50DNP supports the following power supply options:
• AC 2700 W (80 Plus Titanium) for air-cooled configurations
• AC 3000 W (80 Plus Titanium) for liquid-cooled configurations
The server system can support up to four power supplies. Each power supply is hot-swappable and allows tool-less insertion and extraction from the rear of the chassis. Depending on the shipping configuration from Intel, systems may or may not have power supplies preinstalled.
Disclaimer: The Intel® Server D50DNP Family is designed to operate as described in this technical product specification when connected to a 200–240 V power source. Connecting to a lower voltage power line is not supported and may result in unreliable system operation. If a 200–240 V power source is not available, it is the responsibility of the system integrator to recalculate the total power consumption of the system.
| Note | All power supplies must be identical. Using different power supply options concurrently is not supported. This invalid configuration does not provide power supply redundancy and results in multiple errors being logged by the system. |
 |
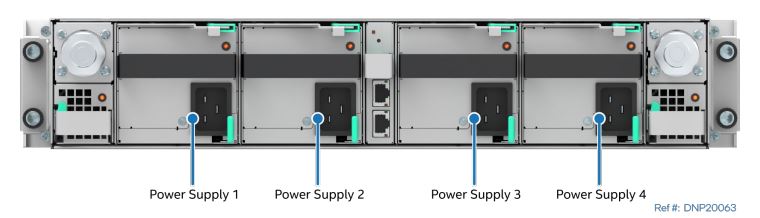
| Power Supply Module Identification – Air Cooled |
 |
| Power Supply Module Identification – Liquid Cooled |
 |
| 2700 W and 3000 W Power Supply Modules |
Power Supply Specification Overview
- AC 2700 W (80 Plus Titanium)
- AC 3000 W (80 Plus Titanium)
AC power supplies are auto-ranging, and the power factor is corrected.
| Note | Full power supply specification documents are available upon request. Power supply specification documents are classified as Intel Confidential and require a signed nondisclosure agreement (NDA) with Intel before being made available |
Power Supply Module Efficiency
Each power supply option is rated to meet specific power efficiency limits based on their 80 PLUS power efficiency rating. The following tables define the required minimum power efficiency levels based on their 80 PLUS efficiency
rating at specified power load conditions: 100%, 50%, 20%, and 10%.
The AC power supply efficiency is tested over an AC input voltage range of 115 VAC to 220 VAC.
| 2700 W AC Power Supply Option Efficiency (80 PLUS* Titanium) | |||||
 | Loading | 100% Of Maximum | 50% Of Maximum | 20% Of Maximum | 10% Of Maximum |
| Minimum Efficiency | 94% | 96% | 95% | 94% | |
| 3000 W AC Power Supply Option Efficiency (80 PLUS* Titanium) | |||||
 | Loading | 100% Of Maximum | 50% Of Maximum | 20% Of Maximum | 10% Of Maximum |
| Minimum Efficiency | 94% | 96% | 95% | 92% | |
AC Power Cord Specifications
The power connector on a 2700 W AC power supply follows the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 320 C20 standard.
The power connector on a 3000 W AC power supply follows the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 320 C22 standard.
Power Supply Configurations
The Intel® Server Chassis D50DNP can have up to four power supply modules installed. The Integrated BMC calculates the total power demand at the chassis level and distributes the power load among the installed power supply modules. A fully configured 4-module system supports the following power supply configurations:
- 4+0 combined power (non-redundant)
- 3+1 redundant power (module dependent)
- 2+2 redundant power (module dependent)
Redundant power and combined power configurations are automatically configured depending on the number of modules in the system. Should system thermal levels exceed programmed limits, platform management attempts to keep the system operational. For details, check Technical Product Specifications - Section 11.3 and Chapter 10.
If a power supply failure occurs, the redundant power configuration supports hot-swap extraction and replacement of the failed power supply. If a power supply failure occurs in a 4+0 configuration, the other three power supplies provide the power, and the system may throttle.
| Note | To power on the Intel® Server D50DNP minimum of 2 PSUs must be installed. |
Closed Loop System Throttling (CLST)
Closed-loop system throttling (CLST) prevents the system from crashing if a power supply module is overloaded or overheats. If the system power reaches a pre-programmed power limit, CLST throttles system memory and/or processors to reduce power consumption. System performance is degraded if throttling.
Smart Ride Through (SmaRT) Throttling
Smart Ride Through (SmaRT) throttling increases the reliability of a system operating in a heavy power load condition and contributes to remaining operational during an AC line dropout event. When AC voltage goes low, a fast AC loss detection circuit inside each installed power supply asserts a SMBALERT# signal to initiate a throttle condition in the system. System throttling reduces the bandwidth to both system memory and processors, which, in turn, reduces the power load during the AC line dropout event.
For more details, check Technical Product Specifications - Section 11 - System Power.