The Intel® Virtualization Technology abstracts hardware, enabling multiple workloads to share a common set of resources. Virtualization security protects virtualized IT infrastructure through a mix of software- and hardware-enabled controls and policies. Virtualization takes a single physical computer or server and partitions it into several virtual machines by separating computing environments from physical infrastructure. On shared virtualized hardware, multiple workloads can run in full isolation from each other in a performant manner.
Q: How do I find if the Intel Processor supports Intel® Virtualization Technology (VT-x)?
This information is available on the Product Specification page.
Follow the steps below:
- Identify your Intel® Processor, or the processor you need to find the information for.
- Visit the product specification page.
- Enter the Intel processor number in the Search Intel.com field located upper-right corner.
- Click the processor's link on the search results page.
- Once you are on the processor specification page, click Specifications section.
- Click Security & Reliability.
- Look up all the Intel® Virtualization fields.
Here is an example.

Q: How do I enable or disable Intel® Virtualization Technology (VT-x)?
Through the BIOS. With a VT-x supported Intel® Processor and a VT-x supported BIOS, VT-x can be enabled or disabled in BIOS. If the BIOS option is not available, refer to the motherboard vendor for support.
Q) How can I tell if Intel® Virtualization Technology (VT-x) is enabled or disabled in my system?
You can use the Intel® Processor Identification Utility to verify if your system is capable of Intel® Virtualization Technology.
Using the tool, Select the CPU Technologies tab. See if the Intel® Virtualization Technology options are checked or not.
Here is an example to show that the Intel® Virtualization is available.
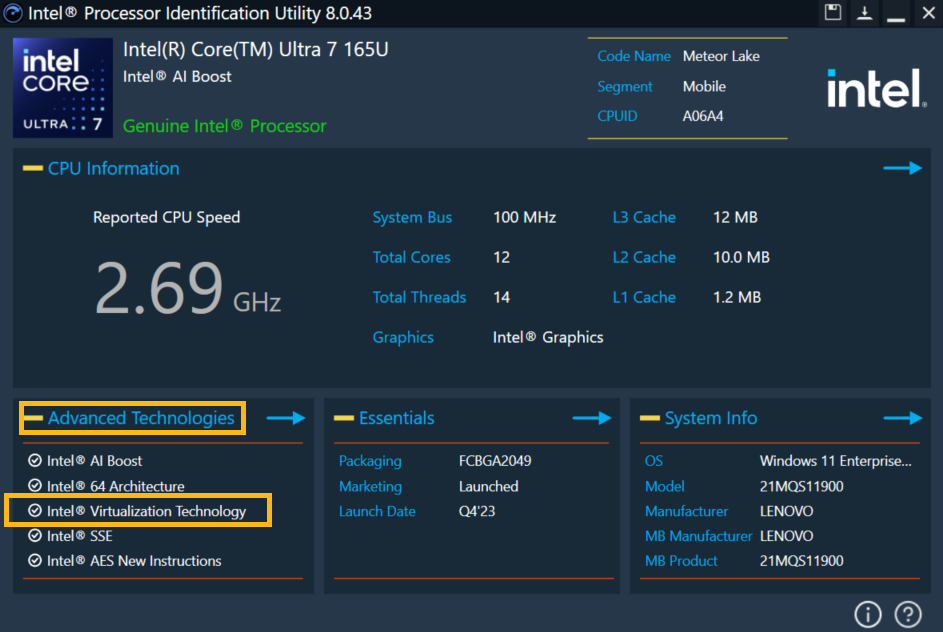
If Intel® Virtualization Technology is not checked in the tool, there might be a possibility your processor still supports Intel® Virtualization Technology, but it is already being used by some software that uses a hypervisor. In that case, you can also use the Task Manager to verify the situation.
Here is an example to show Intel® Virtualization is enabled using Task Manager.

Using the table below, you can see if your processor supports Intel® Virtualization, if it is disabled, and additional information.
| Intel® Processor Identification Utility | Task Manager | Observation |
| Intel® Virtualization Checked | Virtualization is Enabled | Intel® Virtualization is enabled and it is available to use. |
| Intel® Virtualization Checked | Virtualization is Disabled | Intel® Virtualization is disabled in BIOS. |
| Intel® Virtualization not Checked | Virtualization is Enabled | Intel® Virtualization is enabled but it is used by some other software on the machine. |
| Intel® Virtualization not Checked | Virtualization is Disabled | Intel® Virtualization is not supported by the processor. |
Q: If the Intel processor supports Intel® Virtualization technology (VT-x), should the chipset, OS, drivers support that too?
Intel® VT-x support requires that both the processor and BIOS support it. Although, if VT-d (Virtualization Trusted I/O is also needed, the BIOS, chipset, and processor must also support it).