Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-31AC07CA-E2CC-410B-A66D-B92792216231
Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-31AC07CA-E2CC-410B-A66D-B92792216231
Media Engine Hardware
As described in Architecture section, Xe- Intel® Data Center GPU Flex Series and some other Intel GPUs contain media engine which provide fully-accelerated video decode, encode and processing capabilities. This is sometimes called Intel® Quick Sync Video. The media engine runs completely independent of compute engines (vector and matrix engines).
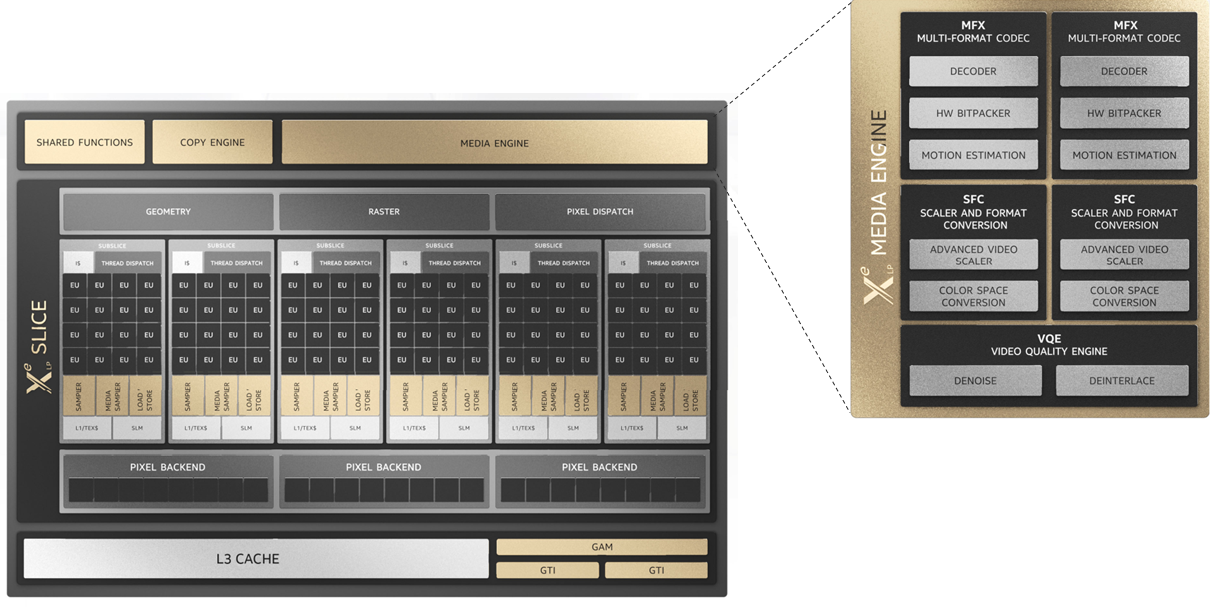
Several components can be used by applications:
MFX/Multi-format codec: hardware decode and encode. Some configurations include two forms of encode. 1) motion estimation + bit packing and 2) full fixed function/low power
SFC/scaler and format conversion: resize (primarily intended for downscaling), conversion between color formats such as NV12 and BGRA
Video Quality Engine: multiple frame processing operations, such as denoise and deinterlace.
This hardware has its own instruction queue and clock, so fully fixed function work can be very low power if configured to use low power pathways. This can also leave the slice capabilities on the GPU free for other work.
Supported codecs
New codec capabilities are added with each new GPU hardware generation.
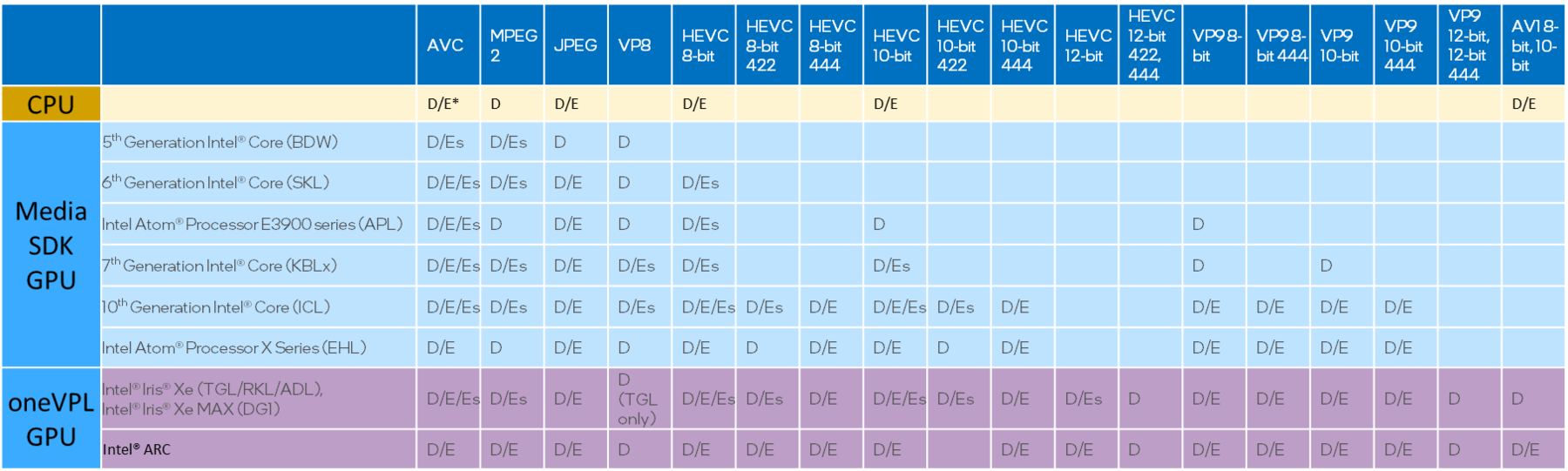
Note: in this table two kinds of encode are represented.
E=Hardware Encode via low power VDEnc
Es=Hardware Encode via (PAK) + Shader (media kernel +VME)
Intel® Arc A-series and Intel® Server GPU (previously known as Arctic Sound-M) add AV1 encode. This cutting edge successor to VP9 adds additional encode control for tile, segmentation, film grain filtering, and other new features. These increase encode quality at a given bitrate or allow a decrease in bitrate to provide increased quality.
