Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-78F8709C-4EF5-4A87-80E6-7D5EE5E58952
Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-78F8709C-4EF5-4A87-80E6-7D5EE5E58952
Explore Parallelism Provided by the Topology of a Graph
This example explores the parallelism provided by the topology of a graph. To make the results as predictable as possible, use a graph that is explicitly parallel, as shown below:
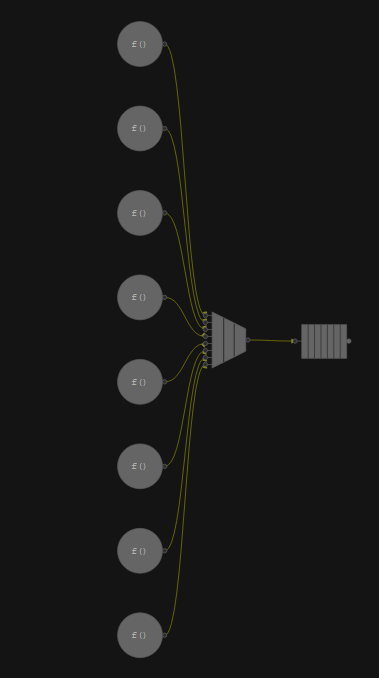
Because the source_node is serial, there is no parallelism provided from within the node. This ensures all parallelism observed is provided by the topology of the graph. Eight source_nodes are connected to a join_node and then to a queue_node. In this graph, only the source_nodes do useful work. Because the parallelism is solely from the topology of the graph, one item per source_node is enough to through the graph. Each source_node has a weight of 1s(1e6). The results of scalability analysis of the graph are shown below.
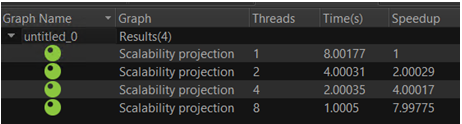
The speedup is directly proportional to the number of threads.